Psychometric measurement
advertisement
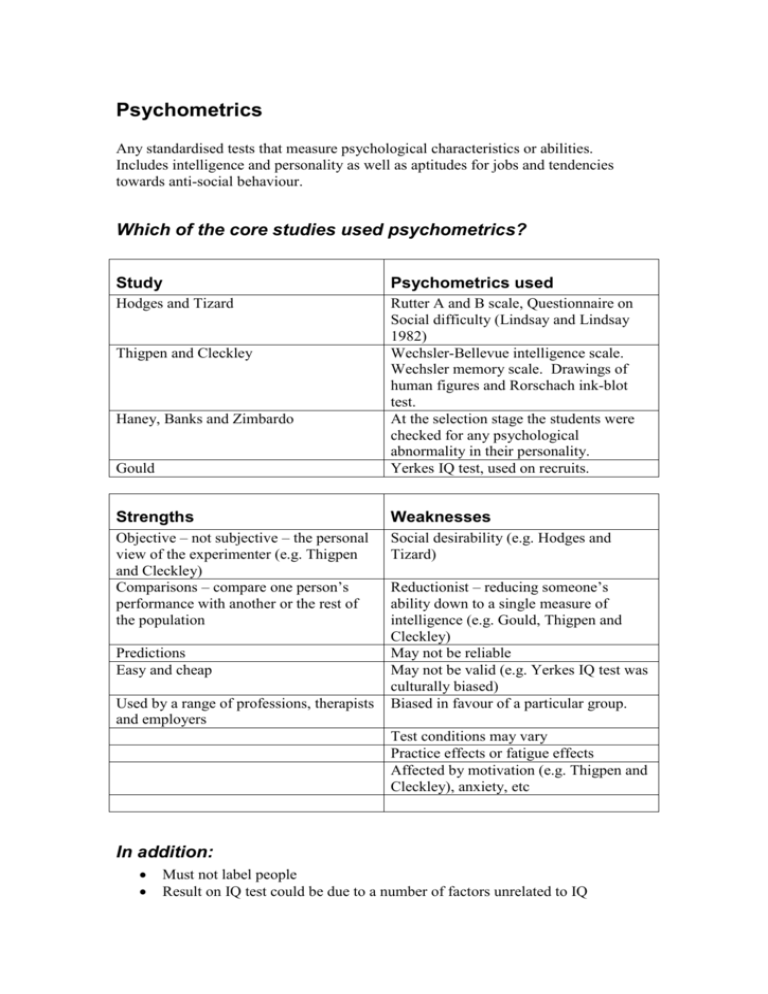
Psychometrics Any standardised tests that measure psychological characteristics or abilities. Includes intelligence and personality as well as aptitudes for jobs and tendencies towards anti-social behaviour. Which of the core studies used psychometrics? Study Psychometrics used Hodges and Tizard Gould Rutter A and B scale, Questionnaire on Social difficulty (Lindsay and Lindsay 1982) Wechsler-Bellevue intelligence scale. Wechsler memory scale. Drawings of human figures and Rorschach ink-blot test. At the selection stage the students were checked for any psychological abnormality in their personality. Yerkes IQ test, used on recruits. Strengths Weaknesses Objective – not subjective – the personal view of the experimenter (e.g. Thigpen and Cleckley) Comparisons – compare one person’s performance with another or the rest of the population Social desirability (e.g. Hodges and Tizard) Thigpen and Cleckley Haney, Banks and Zimbardo Predictions Easy and cheap Used by a range of professions, therapists and employers Reductionist – reducing someone’s ability down to a single measure of intelligence (e.g. Gould, Thigpen and Cleckley) May not be reliable May not be valid (e.g. Yerkes IQ test was culturally biased) Biased in favour of a particular group. Test conditions may vary Practice effects or fatigue effects Affected by motivation (e.g. Thigpen and Cleckley), anxiety, etc In addition: Must not label people Result on IQ test could be due to a number of factors unrelated to IQ Abilities could change People give different responses on tests than in real life (Hodges and Tizard). Measuring only one aspect of the person. Tests do not tell you whether the result is due to innate ability or has been learnt (Nature – Nurture debate) Psychometric measurement Core Studies 2 Section B revision Baron-Cohen, Leslie and Frith (autism) Hodges and Tizard (social relationships) Gould (IQ testing) Thigpen and Cleckley (multiple personality disorder) a) b) How was psychometric measurement used in each of the studies? What problems may psychologists have when they investigate behaviour using psychometric measurement? a) b) Baron-Cohen, Leslie and Frith (autism) – Using dolls answer to belief questions could possibly do, but real psychometric measurement involves the use of published tests; so the use of IQ tests to determine the verbal and non-verbal MA (Mental age) of the three groups of children (Autistic, Downs syndrome and Normal 4-5 year olds). Hodges and Tizard (social relationships) – Rutter scales A and B and Social Difficulties Scale – given to parents, teachers and adolescents. To find out about attachments to parents and peers. Gould (IQ testing) – Yerkes IQ test used on new recruits to American army in First World War. Consisted of Alpha test for people who could read and write (literate), Beta test (Illiterate) and an interview for those who failed these tests. Thigpen and Cleckley (multiple personality disorder) – IQ tests, EEG, personality tests Problems Point Social desirability Reductionist May not be valid Example H&T – Parents ‘understand if child upset’ –yes, adolescents – no. Baron-Cohen – IQ tests were reducing the children down to two scores – mental age – verbal / non-verbal Gould – lived in USA for long time with access to Comment If not result reflects what people would like to be seen as and not as they are. Intelligence manifests itself in many different ways – maths, musical, social, kinaesthetic. This questions whether BaronCohen matched correctly. This faulty testing could have far reaching Demand Characteristics Point Social desirability Reductionist May not be valid Practice/Fatigue effects education did better – cultural bias Eve white given the same test could memorise answers. consequences – immigration act Produces invalid results. Example H&T – ‘Parents would know when child is upset’ – Parents ‘yes’ -Adolescent ‘no’ Baron-Cohen – Overall mental ability of all ps was reduced to MA – verbal and non-verbal scores Gould – Culturally biased test Comment Want to appear to be good parents. Use lie detector questions. T&C – order effects – eve tested twice as white and black so difference could be due to practice or fatigue Intelligence manifests itself in many different ways – maths, musical, social, kinaesthetic Culture-free test is almost impossible. Culture-fair test possible, but cannot compare cultures. Effects reliability. (Fool experimenter). Test twice on different days – take average. Cultural bias (Point) – Gould – Yerkes test consisted of items that tested the recruits knowledge of American Life, (Example) Cultural bias in a test would disadvantage people from outside of the host culture (Comment) . Recording responses could be a problem, as you have to consider whether the person being tested is capable of responding in a particular way, even though they would know the answer (Point). Use of pencil to record answers on the Beta test. Illiterate people would not be used to holding a pencil. Possibly could not write down numbers (Example). The score of some people with particular difficulties in responding could be lower than their true level of intelligence. This could have been a potential problem in Baron-Cohen, but was successfully overcome by asking the children to give a simple verbal reply (Comment). Psychologists sometimes need to gather sensitive data from their interviewees. Not knowing the person interviewed very well could lead to the holding back of personal sensitive information (Point). In Hodges and Tizard, they built up a relationship with the families concerned over a period of up to 16 years, by visiting the homes with the questionnaire. This gave them a chance to put everybody at their ease. (Example). However, in doing this they might have caused too much to be said and could have opened up old wounds, causing the families to argue and get upset about their family relationships (Comment). Demand Characteristics is a problem, where the participant gives answers that they feel the experimenter wants, etc. In Thigpen and Cleckley, Eve White and Eve Black (the two personalities that reside in one woman) are both given an IQ test. There was nothing to stop Eve Black from deliberately getting some of the answers wrong so that she appeared to be different from Eve White (Example). It is important to know what the participant would like to convey in a questionnaire and to make sure that the impression they want to give matches the reality of the situation; perhaps the use of questions that detect inconsistencies would help to detect deliberate lies (Comment).







