Climate and Vegetation SG
advertisement

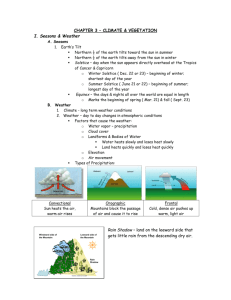
Chapter 3 - Climate and Vegetation Section 1 – Seasons and Weather A. The ___________ of the earth and its _________________ around the sun give us seasons 1. The Tropic of ______________ and the Tropic of ______________________ mark the points farthest north and south that the sun’s rays shine directly overhead at noon 2. The days on which this happens are the ___________________ Longest and shortest days of the year Beginning of summer and winter 3. Twice a year, on the ________________, day and night are equal all over the world Beginning of spring and fall B. Weather: condition of the atmosphere at a particular location and time 1. ________________: weather conditions at a particular location over a long period of time 2. Weather is the complex result of several conditions including: Amount of _________________ energy received Amount of _______________ ________________ in the air Cloud cover Landforms and bodies of __________________ ________________________ Air movement C. _________________________: falling water droplets in the form of rain, sleet, snow, or hail 1. There are three types of precipitation: ___________________________: sun heats moist air causing afternoon rain ___________________________: falls on the windward side of hills or mountains ___________________: cold fronts force warm, moist air up where it cools and produces precipitation 2. Rain Shadow: land on the leeward side of a mountain receives little precipitation due to process of orographic precipitation D. Extreme weather 1. ________________________: huge storms that form over warm tropical ocean waters Called _____________________ in the Pacific 2. _____________________: a powerful funnel-shaped column of spiraling air. 3. _____________________: a heavy snowstorm with wind of 35 miles per hour 4. _____________________: a long period of time with little or no rain. 5. _______________: when water spreads over land not normally covered with water. SG-3L 1 Section 2 - Climate A. Factors affecting climate: 1. Wind and ________________ currents help distribute the sun’s heat from one part of the world to another through convection 2. _____________________: the transfer of heat in the atmosphere by the upward motion of air 3. Ocean ___________________ are like rivers running through the oceans Affect temperature and precipitation on the continents B. Geographers divide the earth into three general zones of ___________________ 1. Low-Latitude Tropical Zone: Tropic of Caner to the Tropic of Cancer Hot all year Precipitation varies with _______________ patterns 2. High Latitude Polar Zones: circle the _______________ ____________and South Pole above 66° latitude Cold most of the year Highs may reach 50° F in ____________________ 3. Middle Latitude Temperate Zones: between the tropics and 66° Climates vary greatly between _________________ and _______________ 4. Elevation and topography also affect climate C. Causes of Climate Variation: 1. _______________ in the Earth’s orbit 2. Variations in solar radiation 3. Variations in the Earth’s tilt 4. Changes in atmospheric composition 5. Changes in location of ___________________________ 6. Volcanic eruptions have dramatic effects on _______________ Effects seldom last more than a few years 7. Sunspot activity drastically affects electronic equipment It may also affect Earth’s _______________, but more information is needed. D. Scientists believe deep-sea currents in the Pacific Ocean affect climate in a 2-5 year cycle 1. _____ ____________: easterly winds over the Pacific change direction Blow toward the Americas Brings heavy _____________ to the Americas Causes dry conditions in Australia and Asia SG-3L 2 2. La Nina: reverse or “normal” wind pattern Blow toward Australia and _____________ Heavy rain in Australia and Asia Dry conditions in the Americas E. Greenhouse effect: trapping of solar radiation by the earth’s _______________________ 1. Makes the planet warm enough to sustain life Section 3 – World Climate Regions A. The two most significant factors in defining a climate are 1. _______________________ 2. Precipitation 3. Other important elements include: Location on a _______________________ Topography _____________________ B. USE ORGANIZER FOR CLIMATE REGIONS Section 4 – Soils and Vegetation A. Soil: a thin layer of weathered _____________, _____________, air, and water 1. The world’s food supply depends on the top six inches of soil, called ________________ B. _____________, temperature, and moisture influence the type of vegetation that thrives naturally in a region 1. Vegetation patterns are identified on the basis of the ecosystems they support __________________: an interdependent system community of plants and animals _______________: the ecosystem of a region C. Biomes are further divided into: 1. __________________: categorized by the trees they support Deciduous: lose their leaves in the fall and grow new ones in spring Rain Forest: found in the tropics; stay green all year __________________: cone bearing 2. _______________________: mostly flat regions dotted with a few trees Called by different names; savanna, steppe, prairie, and pampas 3. __________________: little rain, can be “hot” or “cold”, sandy or rocky Cactus and sagebrush tolerate heat and need little water to thrive 4. _______________: cold much of the year Low, hardy vegetation SG-3L 3