Applied Mathematics and Informatics
advertisement

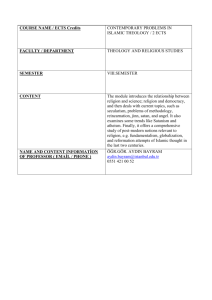
Major Higher Educational Programme Field of study: 010400 Applied Mathematics and Informatics. Specialty: High-Performance Computing and Parallel Programming Technologies. Degree: bachelor. Course mode: full-time. The period of study specified by the Federal State Educational Standards of Higher Education is 4 years. The study load of the bachelor’s programme specified by the Federal State Educational Standards of Higher Education is 240 ECTS points. The programme is meant to develop the students’ faculties in the fields of -to provide necessary basic theoretical knowledge in various areas of mathematics in scientific and technical fields, and in the economy; -to develop research skills in the field of mathematical physics, modeling, numerical methods and parallel computing; - to study computer science, programming languages and computer architectures including highperformance systems. The list of courses included in the curriculum of 010400.62 Applied Mathematics and Informatics. Specialty: High-Performance Computing and Parallel Programming Technologies. Fundamental humanitarian, social and economic courses. History Semester: 1 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to understand the internal logic and content of the historical process, to give an idea about the content of major scientific concepts, and the periodization of Russian history as a part of world history. The objectives of the course are to give students an idea of the historical methodology and chronology, to form students' historical consciousness, respect for the past and the people of their country, and for the history of other cultures, nations and states. Philosophy Semester: 2 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to help students develop a comprehensive idea of philosophy as an independent field of spiritual culture and theoretical studies. The objectives of the course are to introduce the features of the subject and methods of philosophy, specifics of philosophical knowledge, to consider the basic stages of the history of philosophy, to reveal the contents of basic philosophical problems and categories, to highlight the role of science in the development of civilization, relations between science and technology, and contemporary social and ethical issues associated with them. Foreign Language Semester: 1-4 ECTS points:8 Hours: 288 The course aims to form the students’ ability to intercultural communication, to develop foreign language skills to succeed in the field of their choice. The objectives of the course are to master lexical, grammatical, syntactic, phonological and orthographic components of a foreign language, and to develop a pragmatic component (discourse competence, functional competence). Economics Semester: 5 ECTS points: 2 Hours: 72 The course aims to form basic knowledge for understanding the basics of economics. The objectives of the course are to help the students understand the theoretical foundations of a market economy, patterns of economic agents’ behavior and activities of state economic policy; teach students to identify and analyse economic information, explain economic processes in the country, to know the history of the world economy and achievements of economic thought. Compulsory humanitarian, social and economic courses. Sociology Semester: 3 ECTS points: 2 Hours: 72 The course aims to understand the nature of social reality; to use empirical studies in assessing social organisation at any level; to develop sociological thinking; to understand a variety of means and methods in analysing the effectiveness of its activities. The objectives of the course are to form the understanding of basic problems of modern social cognition, theoretical foundations of the social science functioning, principles of correlation between methods and methodology of sociological knowledge; to transfer analysis skills of contemporary social problems in relation to a particular area of activity. Psychology and Education Semester: 7 ECTS points: 2 Hours: 72 The course aims to form the students’ willingness to think independently and to foresee the consequences of their own actions, to assess adequately their capabilities, to find the best way to translate the synthesis of psychological and educational opportunities in the professional sphere. The objectives of the course are to reveal the basic concepts, phenomena and major ideas within the content of the course, “learning”, “education”, “development”, “person”, “communication”, “cognitive processes”, “educational system”. History of Mathematics Semester: 2 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to build the general context of mathematical thinking as a cultural form of activity defined both by structural features of mathematical knowledge and the place of mathematics in sciences system. The objectives of the course are to teach to think logically, to carry the proof of the main results, to establish logical links between concepts, to apply knowledge to solve mathematical problems and problems related to the mathematical methods applications. Elective humanitarian, social and economic courses. Methods of Teaching Informatics and Mathematics Semester: 7 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to train future teachers of computer science and mathematics methods and technics of the subject they are going to teach. The objectives of the course are to develop theoretical foundations of teaching informatics and mathematics; to familiarise with new technology of training, to form and develop practical skills in the field. Modern Education Technology Semester: 7 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to familiarise students with a wide range of modern educational technology, ideas, schools, trends; methods of design, implementation, monitoring and diagnosis of the educational process, traditional and new forms of educational process organising. The objectives of the course are to generate the skills of design, implementation, evaluation and correction of the educational process with the use of traditional and new educational technologies, to study the theoretical foundations of modern educational technologies. Mathematical Methods in Economics Semester: 8 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to teach students to construct mathematical models of real economic objects; systematic analysis of the economy as a complex dynamic system. The objectives of the course are to development mathematical models of economic objects, systems and phenomena, to learn behavior of the economy participants, to study descriptive models of the economy, to analyse economic variables and statistics. Mathematical Methods in Sociology Semester: 8 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to acquire basic knowledge of sociological research methodology and methods, the ability to plan research and apply soundly methods for the quantitative analysis of sociological data. The objectives of the course are to build skills how to create a program of sociological research, to understand basic principles of measurement in sociology, skills to build different types of scales, to understand sampling and survey results analysis. Fundamental mathematical and natural scientific courses. Mathematical Analysis Semester: 1-2 ECTS points: 7 Hours: 252 The course aims to introduce the basic techniques of differential and integral calculus. The objectives of the course are to study theoretical foundations of mathematical analysis, to develop those parts of mathematical analysis whose apparatus is widely used in the major economic and managerial courses; to obtain skills to apply independently mathematical tools for educational problem solving of managerial and economic content. Algebra Semester: 1-2 ECTS points: 7 Hours: 252 The course aims to familiarise with the concepts of algebra, to develop clear logical thinking. The objectives of the course are to study theoretical foundations of algebra, to develop practically those parts of algebra whose apparatus is widely used in major economic and managerial courses; to obtain skills to apply independently mathematical tools for educational problem solving of managerial and economic content. Foundations of Informatics Semester: 1 ECTS points: 4 Hours: 144 The course aims to teach students how to build information models, to analyse the results, to use modern information technology. The objectives of the course are to provide students with basic theoretical and practical knowledge of information processing by computers, to form practical skills how to use modern information technologies software and hardware. Physics Semester: 6-7 ECTS points: 6 Hours: 216 The course aims to familiarise students with the basic methods of observation, measurement and experiment, to learn how to use theoretical knowledge for practical problem solving, both in mechanics and in interdisciplinary boundaries of mechanics with other branches of physics. The objectives of the course are to acquire knowledge about the basic principles and physical laws; to familiarise students with the basics of conducting physical experiments and analysis of measurements; to apply theoretical knowledge in practice. Comprehensive Analysis Semester: 4 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to learn the basics of classical theory of functions for one complex variable. The objectives of the course are to investigate functions differentiability of a complex variable, to calculate integrals, to apply complex analysis methods for computing integrals from real variable functions. Functional Analysis Semester: 5-6 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to acquire theoretical knowledge in the field of functional analysis and skills for its use; to familiarise students with the initial skills of mathematical modeling. The objectives of the course are to study the basic concepts and methods of linear and nonlinear functional analysis, to review their applications and to examine main spaces types’ morphology and types of functions spaces. Geometry Semester: 1-2 ECTS points: 6 Hours: 216 The course aims to form the mathematical culture of the students, to train students fundamentally in the field of geometry, to master modern geometry apparatus for later use in other fields of mathematical knowledge. The objectives of the course are to form complex knowledge about the basics of analytic geometry; to obtain skills and abilities for simple problem solving in geometry. Compulsory mathematical and natural scientific courses. Real Analysis Semester: 3-4 ECTS points: 11 Hours: 396 The course aims to teach students fundamentally in the field of real analysis, to master modern real analysis apparatus for using in other areas of mathematical knowledge. The objectives of the course are to familiarise with basic concepts, definitions and properties of real analysis objects, formulas and methods of allegations proof, possible spheres of their relations, and applications in other fields of mathematical knowledge. Equations of Mathematical Physics Semester: 5-6 ECTS points: 9 Hours: 324 The course aims to develop one of the modern methods of describing the physical world. The objectives of the course are to consider the basic types of mathematical physics equations, to consider string vibration and heat in the core, the Laplace equation and the Dirichlet problem analysis. Elective mathematical and natural scientific courses. Modern FORTRAN Semester: 1 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to familiarise students with the programming language FORTRAN and its application to numerical solution of some mathematical physics problems. The objectives of the course are to learn basics of the programming language FORTRAN, to create ideas about methods for the approximate problem solving of mathematical physics equations using FORTRAN. Programming in Java Semester: 1 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to familiarise with standard libraries of Java, Java extensions and their application. The objectives of the course are to study syntax extensions, introduced in Java; core libraries and Java technology; to learn how to write a Java program using basic libraries and technologies. Computer Modelling Semester: 2-3 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to familiarise with basic principles of modeling, and construction of static and dynamic models using modern software. The objectives of the course are to learn how to make models of complex systems and algorithms for simulating complex systems; to familiarise with simulation of complex systems, methods of random elements computer simulation, to conduct a statistical analysis of simulation results. Simulation Modelling Semester: 2-3 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to deepen theoretical knowledge about modeling as a general scientific method. The objectives of the course are to familiarise with simulation models types and queuing processes in different systems and to obtain planning skills of computer experiment. Fundamental field-oriented courses. Life Safety Semester: 3 ECTS points: 2 Hours: 72 The course aims to form the idea about the unity between effective professional activity and requirements for security and human safety, to obtain skills for appropriate and safe behavior in daily life and in extreme conditions. The objectives of the course are to give knowledge to make decisions for the protection of staff and civilians from the consequences of accidents, disasters, natural disasters; to master the methods of emergency situations forecasting and to examine natural disasters, major accidents and disasters affecting factors, to build skills of parameters control and negative impacts levels. Differential Equations Semester: 3-4 ECTS points: 6 Hours: 216 The course aims to understand basic concepts and principles of economic information, and to use econometric methods in order to deal with organisational and administrative tasks. The objectives of the course are to familiarise with the basics of differential equations; to form skills for mathematical research of economic problems; to get an idea how to apply differential equations in the economy. Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics Semester: 5-6 ECTS points: 6 Hours: 216 The course aims to introduce the basic concepts and methods of probability theory, to form skills how to build and examine probabilistic models of real economic processes. The objectives of the course are to study theoretical foundations of probability theory and mathematical statistics, to obtain skills how to apply independently mathematical tools for educational problem solving of managerial and economic content. Discrete Mathematics Semester: 2 ECTS points: 4 Hours: 144 The course aims to introduce the most important branches of discrete mathematics, and its application for practical problem solving. The objectives of the course are to form skills in combinatorial formulas, recurrence equations, generating functions, to study in detail graph theory algorithms, algorithms for constructing a variety of disjunctive normal forms, and to grasp the possibilities of their practical application. Computer Architecture Semester: 2 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to study the basic concepts of modern PC architecture, functions of major components of computer hardware, delivery mechanisms and information management. The objectives of the course are to learn the computer hardware, its technical specifications and features, as well as theoretical principles and provisions underlying architecture building. Languages and Programming Techniques Semester: 1 ECTS points: 4 Hours: 144 The course aims to study structured methods of constructing algorithms and translators. The objectives of the course are to teach students the formal theory of programming languages: syntax, semantics, methods of describing programming languages; to develop practical skills in the field of modern high-level languages, to learn general principles and rules of constructing high-level programming languages. Databases Semester: 5-6 ECTS points: 7 Hours: 252 The course aims to form theoretical knowledge in the field of management, storage and data processing, as well as practical skills in design and implementation of effective systems for data storage and processing. The objectives of the course are to master theoretical foundations of technologies for data storage and processing, to formulate the task for database developing, methods of conceptual design and to design database model in order to construct optimal and stable systems. Numerical Methods Semester: 4 ECTS points: 4 Hours: 144 The course aims to master classical numerical methods for solving applied problems in mathematics and physics. The objectives of the course are to get an idea of the approximate methods of calculation, methods for solving linear and non-linear equations systems, as well as the skills to solve applied computational problems using a PC. Operating Systems Semester: 3 ECTS points: 2 Hours: 72 The course aims to introduce the fundamental concepts and general principles of operating systems organisation; to examine processes and devices control, file systems, organisations, inter-process communication, to construct network services, to obtain skills how to work with programming interface operating systems. The objectives of the course are to obtain theoretical knowledge on appointment, composition and functioning of the operating system (OS); to develop skills in evaluating the performance of different operating systems, to obtain theoretical knowledge and practical skills of the user in the LAN and WAN. Computer Networks Semester: 7 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to obtain basic knowledge and practical skills in the development of key aspects of architecture and technology in modern computer networks. The objectives of the course are to study architecture, a scheme of the computer networks and their place in modern automated information systems; to learn how to use traditional and advanced technologies of local and global networks in practice. Computer Graphics Semester: 7 ECTS points: 4 Hours: 144 The course aims to build a graphical user culture by shaping of such competences as informational, design and engineering, communicational. The objectives of the course are to introduce the basic concepts of computer graphics, its purpose, to form the skills of using mathematical and algorithmic support for computer graphics; to develop practical skills to work with scanning, two-dimensional and three-dimensional vector graphics software. Game Theory and Operations Research Semester: 7 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to study theoretical foundations and specific mathematical models for applied production and economic decision-making problems under uncertainty conditions. The objectives of the course are to study theoretical basics how to use methods for solving problems of operations research, to learn linear programming methods, basic operations of problems research, methods for constructing mathematical models to solve applied problems. Compulsory field-oriented courses. Programming Fundamentals Semester: 2 ECTS points: 4 Hours: 144 The course aims to give students an idea about modern methods of information processing and phenomena studying by their numerical simulation on computers, to contribute to the development of their intellectual, creative abilities and critical thinking in the course of research, phenomena analysis, perception and interpretation of information. The objectives of the course are to learn the basics of modern information technologies; to master the techniques and methods of programming; to learn how to use software tools for processing and presentation of data obtained during a physical experiment. System and Application Software Semester: 3 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to give students theoretical and practical training in the field of system analysis, configuration, tuning and development of system software components in modern operating systems. The objectives of the course are to learn the internal organisation of operating system, models of its individual sub-systems, methods of organisation of processes interaction both within a single computer system and in distributed systems, the technologies of system software and application software development. Visual Programming Semester: 4 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to give the students an idea about modern methods of information processing and studying phenomena by their numerical computer; to contribute to the development of their intellectual, creative abilities and critical thinking in the course of research. The objectives of the course are to learn the basics of modern information technologies; to master techniques and methods of programming; to learn how to use software tools for processing and presentation of data obtained in the course of a physical experiment. Mathematical Modelling Semester: 5 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to teach students how to use mathematical modeling to study a variety of natural and social processes. The objectives of the course are to learn how to allocate the laws of nature, society and technology, and record them in the language of mathematics. Programming in Multiprocessor Systems Semester: 7-8 ECTS points: 7 Hours: 252 The course aims to learn the principles of organisation and various classes of microprocessor systems, to obtain skills of embedded programming. The objective of the course is to teach the basic principles of programming in multiprocessor systems. Design of Distributed and Parallel Programming Semester: 5 ECTS points: 6 Hours: 216 The course aims to learn modern methods, tools and techniques for distributed and parallel programming, techniques for creating high-quality software products. The objectives of the course are to study the basic concepts of programming languages, syntax, and semantics, formal methods of describing programming languages, methods and broadcast milestones, design of distributed and parallel programming. Architecture and Software of High-performance Clusters Semester: 3-4 ECTS points: 6 Hours: 216 The course aims to study modern high-performance computing systems, their software, and to obtain skills how to design programs for these computing systems in the modern technological environment. The objectives of the course are to learn the architecture of modern high-performance computing systems, to consider the problem of organising the calculations on high-performance computing systems, to study software engineering on high-performance computing systems. Optimization Methods Semester: 8 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to master basic techniques of mathematical modeling for optimization theory tasks, to develop skills of independent mathematical analysis. The objectives of the course are to familiarise with application models where nonlinear optimization issues arise, methods of reducing applications to nonlinear optimization tasks, and modern algorithms for solving problems of unconditional, conditional and global optimization. Elective field-oriented courses. Numerical Methods for Solving Problems in Continuum Mechanics Semester: 6 ECTS points: 4 Hours: 144 The course aims to study numerical methods for solving problems defined by continuum mechanics models. The objectives of the course are to present basic concepts that define the relationships and thermodynamic principles used in continuum mechanics, to study necessary mathematical tools problem solving in continuum mechanics. Artificial Intelligence Systems Semester: 6 ECTS points: 4 Hours: 144 The course aims to build a complete picture of the present state of the theory and practice of building intelligent systems for various applications. The objectives of the course are to get an idea of knowledge engineering and neuroinformatics fundamentals, application of artificial intelligence and the role of Artificial Intelligence and Neural Network in the development of computer science in general. Object-oriented Programming Semester: 7-8 ECTS points: 6 Hours: 216 The course aims to understand ideology and the key aspects of object-oriented programming (OOP), adequate for practical use in the professional field. The objectives of the course are to teach students how to design computer models of real and conceptual systems in accordance with the paradigm of component-oriented programming. Functional Programming Semester: 7-8 ECTS points: 6 Hours: 216 The course aims to study and practically apply means of functional programming for scientific and applied issues, to consider theoretical and applied aspects how to use software tools for solving problems of artificial intelligence. The objectives of the course are to understand theoretical foundations and practical tools of functional programming, to learn how to use theoretical basis and practical tools of functional programming in solving practical tasks. Graph Theory Algorithms Semester: 5 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to study mathematical description of the objects’ structure, to know the results of the structural properties of these objects, as well as algorithmic constructions achieved in this area to date. The objectives of the course are to obtain basic math concepts of the course, to be able to use basic graph theory optimization algorithms in order to solve theoretical and applied problems. Theory of Algorithms and Recursive Functions Semester: 5 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to form an idea of the algorithm, to introduce the current methods of formalizing the algorithm concept based on partial recursive functions concepts. The objectives of the course are to teach students how to distinguish between structural and non-structural facilities; to apply superposition operators, primitive recursion and minimisation of partial recursive functions construction; to introduce examples of unsolvable problems in mathematics and logic. C + + Language Semester: 5-6 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to familiarise with the design and implementation of algorithms for solving practical problems in C + +. The objectives of the course are to teach students the basics of programming based on the programming language C + +, the basics of structured programming on the basis of the programming language C + +; to instill skills of competent design, analysis and testing of solutions on PC. C # Language Semester: 5-6 ECTS points: 5 Hours: 180 The course aims to familiarise with the design and implementation of algorithms for solving practical problems in C#. The objectives of the course are to teach students the basics of programming based on the programming language C#. Algorithms for Numerical Analysis in C # Semester: 6 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to study a cross-platform library of numerical analysis in C #. The objective of the course is to teach students the fundamentals of programming based on C # programming language. Nonlinear Programming Semester: 6 ECTS points: 3 Hours: 108 The course aims to familiarise students with the theory of non-linear problem optimization, with algorithms for numerical analysis of specific classes of extremal problems, areas of mathematical optimization models possible application. The objectives of the course are to study the foundations of nonlinear programming theory, to introduce numerical methods of minimizing functions for different variables, and algorithms analysis for problems with constraints, to consider individual applications of nonlinear models.