key to sample questions test 1
advertisement

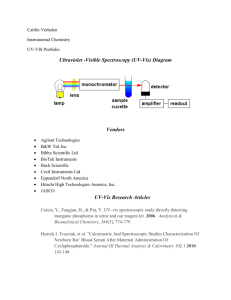
KEY CHEM 322 – study questions for test 1 Fill in the blank. a) If the absorbance of a 0.020 M sample is 0.150 in a 2.0 cm cell, what is the absorbance of a 0.010 M sample of the same type in a 1.0 cm cell? _______________ A 0.150 3.75 cm1 M1 bc 2.00 cm0.0200 M A = abc = (3.75 cm-1M-1)(1.00 cm)(0.010 M) = 0.0375 a b) By what factor is the signal-to-noise ratio improved if 1000 spectra are averaged _____. improvement in S/N = N 1000 31.6 c) At a particular wavelength, a solution that is 0.010 M in A has an absorbance of 0.26 and a solution that is 0.10 M in B has an absorbance of 0.16. What is the absorbance of a solution that is 0.010 M in A and 0.10 M in B? ______________ e) If a spectrophotometer reads 92% T with the blank and 53% T with the sample, what is the absorbance of the sample? ________ Iblank 0.92 I0 Isample 0.53 T Isample Iblank I0 A log0.576 0.240 0.53 0.576 0.92 f) Two emission lines occur at 772.0 and 772.8 nm. Determine how many lines a grating must have to resolve these emission lines in second order. ________ av e 772.4 966 2 1 0.8 R 966 N 483 n 2 resolving power required is R R = nN f. For a particular determination, the slope of the calibration curve was 0.153 L/mg. The standard deviation of the noise level for a blank sample was measured to be 0.022. What is the detection limit in concentration limits for this technique? DL c m ksbl 3(0.022) mg 0.431 -1 m L 0.153 Lmg g. Sketch a typical single beam UV spectrometer. Label the various parts and show the light path. Use the back of this page if you need more room 1 KEY CHEM 322 – study questions for test 1 h. Sketch the 19F NMR spectrum for 31P19F31H2. Assume that JPF = 6 Hz. and JHF =2 Hz. JPF JHF JHF JHF JHF i. What are the principal advantages and disadvantages of Fourier Transform Spectroscopy? advantages – speed of data collection, better resolution, better wavelength accuracy disadvantages – data must be transformed to be interpreted _______________________________________________________________________ j. What would allow you to distinguish the 1H NMR spectrum of CH3CH2OH from CH3CH2OCH3? Both have 3 main peaks but the chemical shifts will be the same. The ketone carbon would be significantly more downshifted than any other carbon CH3CH2OH has two triplets and an octet CH3CH2OCH3 has a quartet, a triplet and a singlet _______________________________________________________________________ k. What are the advantages of a double beam instrument as compared to a single beam instrument? double beam free from drift, can use less stable sources and detectors, solvent can be automatically subtracted single beam greater energy throughput, better S/N, few components, cheaper, require stable sources and detectors l. Briefly discuss Beer's Law. What is it and why does it sometimes fail? _________________________________________________________________________ m. How many spectra must be averaged to increase the signal to noise ratio by a factor of 5. improvemen t N 5 N N =25 ________________________________________________________________________ n. What is the maximum resolution in nm for a 2048 element multichannel detector if the wavelength range covered is 200 nm to 400 nm. The resolution will be the range divided by the number of elements resolution 400 200nm 0.0977 nm 2048 2 KEY CHEM 322 – study questions for test 1 ___________________________________________________________________________ o. If a 0.010 M sample has a transmittance of 90% what is the concentration of a solution of the same substance that has a %transmittance of 80%. Assume that Beer’s Law applies. A log0.9 0.0458 for the 0.010 M solution A log0.8 0.0969 for the solution that has %T = 80% A = abc A 0.0458 ab 4.58M1 c .01M for solution that has %T = 80% c A 0.0969 0.0212M ab 4.58M1 _________________________________________________________________________ p. (4) Convert 500 nm to the equivalent wavenumber (cm-1) ________ 1 1 109 nm m 1 2 20000 cm 500 nm m 10 cm __________________________________________________________________________ q. (5) What is the energy difference between two levels if the number of molecules in the upper state is one fourth as many as in the lower state. Assume the temperature is 500 K _______. E1 E0 kT n E ln 1 kT n0 n 1 E kT ln 1 1.38 1023 JK 1 500K ln 9.57 1021 J 4 n0 n1 e n0 ___________________________________________________________________________ Select the technique or techniques from the list below that would be appropriate for each of the following analyses. Indicate if any special sample preparation is needed. (transmission IR, reflectance IR, reflectance near-IR, Raman, UV-vis, fluorescence, NMR) a) determine if a water solution has a small benzene impurity UV-visible spectroscopy Raman spectroscopy may be useful but it may not be sensitive enough IR is sensitive but not useful for aqueous solutions b) determine the CO2 content of an air sample. IR spectroscopy c) distinguish between 1,2- and 1,3- dichlorobenzene NMR spectroscopy d) determine Fe3+ concentration in a water sample UV-visible spectroscopy _____________________________________________________________________________ Which one of the following statements is FALSE At the detection limit, the signal-to-noise ratio is about 3 The slope of a calibration curve is the sensitivity One of the reasons to use an internal standard is to eliminate matrix effects The accuracy of a Beer’s law plot decreases at both high and low absorbance. 3 KEY CHEM 322 – study questions for test 1 Which of the following is NOT an advantage of Raman spectroscopy as compared to IR spectroscopy. preparing a sample is usually easier in Raman the Raman detection limit is lower biological samples are easier to study in Raman Raman is better for detecting symmetric vibrations A typical source for an IR experiment is a globar a tungsten lamp an RF coil a D2 lamp The Raman shift for a CH vibration is 3000 cm-1 when the spectrum is excited with 500 nm radiation. The Raman shift for the same vibration excited with 250 nm radiation is 3000 cm 250 cm 1500 cm 6000 cm Which of the following techniques would be LEAST useful in determining if a compound is a ketone fluorescence IR Raman NMR The x axis of an IR spectrum usually has units of wavenumbers nm parts per million Which of the following techniques is LEAST used as a quantitative method fluorescence UV-Vis IR eV NMR the 19F NMR spectrum for 13C19F4 would look like which of the following Beers Law is more accurate in UV-Vis than in the IR because UV-Vis detectors are more sensitive than IR detectors the absorption bands in the UV-Vis are typically much stronger than in the IR the absorption bands in the UV-Vis are typically much broader than in the IR the energy of the photon is higher in the UV-Vis Which of the following will be TRUE for an NMR spectrum taken on a 200 MHz instrument as compared to a 100 MHz instrument the chemical shifts are twice as big the spin-spin coupling constants are twice as big the chemical shifts and the spin-spin coupling constants are the same on both both the chemical shifts and the spin-spin coupling constants are twice as big When a substance in a solid or solution exhibits fluorescence, the light emitted is of a shorter wavelength than that absorbed a longer wavelength than absorbed a higher energy than absorbed 4 KEY CHEM 322 – study questions for test 1 the same intensity as that absorbed The mid-IR covers the range 200 - 700 nm 400 - 4000 cm 4000 - 14000 cm 20 - 400 cm In Raman scattering lasers are used as sources and photomultipliers as detectors tungsten lamps are used as sources and photomultipliers as detectors lasers are used as sources and thermocouples as detectors lasers are used as sources and bolometers as detectors Which of the following is NOT a type of multichannel detector photodiode array charge coupled photographic film device photomultiplier In the figure shown above, which arrow corresponds to Raman emission? C A F H In the figure shown above, which arrow corresponds to UV or visible absorption? A B G H In the figure shown above, which arrow corresponds to IR absorption? B A F H In the figure shown above, which arrow corresponds to fluorescence? F A C H Which of the following techniques is LEAST used as a quantitative method 5 KEY CHEM 322 – study questions for test 1 fluorescence UV-Vis NMR near-IR Which of the following types of electronic transitions usually occurs at the lowest energy n Which substance could not be detected by infrared spectroscopy NaCl water benzene Which of the following is not a detector for visible light MCT detector vacuum phototube photomultiplier p. ethanol silicon photodiode Which of the following is NOT a nucleus commonly studied in NMR 16 19 13 O F C 1 H The signal observed in FT-NMR is called the spin-spin relaxation free induction decay spin-lattice relaxation Fourier transform Molar absorptivity varies with wavelength cell path length concentration detector Which of the following pair of spectroscopic techniques would be most useful for the determination of the structure of an unknown organic compound. NMR and IR NMR and UV-Vis IR and UV-Vis UV-Vis and fluorescence The term that refers to the raw signal observed in FT-NMR is free induction decay spin-spin splitting spin-lattice relaxation DEPT n FT-NMR the sample is irradiated with pulses of RF radiation because a short pulse can simultaneously excite all nuclei of a given type a pulse of high power radiation is more efficient than continuous radiation at the power levels used continuous radiation would cause saturation the use of pulses permits greater precision in the frequency that is applied Which group of instruments are most likely to be able to use the same type of detector. IR, Raman and UV-Vis Raman, fluorescence and UV-Vis IR, fluorescence and AA IR, fluorescence and UV-Vis Which one of the following pairs are common IR detectors? MCT and DTGS PMT and MCT DTGS and CCD 6 PMT and CCD KEY CHEM 322 – study questions for test 1 Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum is used in NMR spectroscopy? visible microwave UV radio wave Which one of the following parts of the IR spectrum tends to have the most information on characteristic group frequencies 200 - 800 nm 400 - 2000 cm 4000 - 14000 cm 20 - 400 cm Which of the following terms describes a radiationless processe for an electronic transition from a singlet to triplet state? intersystem fluorescence phosphorescence internal crossing conversion Which one of the following is a correct order in terms of increasing energy for photons radio wave < infrared < visible < UV radio wave < visible < UV < infrared radio wave < UV < infrared < visible infrared < visible < UV < radio wave Which one of the following most affect the resolution in FTIR spectroscopy? The type of detector The number of scans that is averaged The distance that the mirror moves The slitwidth The x axis of an IR spectrum usually has units of cm-1 nm parts per million eV Which one of the following vibrations would result in a strong peak in the IR spectrum but a weak peak in the Raman? The arrows indicate the movement of the atoms in the vibration. O O A calibration curve (A vs c) has the equation A = 0.174c + 0.021. Which expression should be used to determine the concentration of an unknown that has an absorbance of 0.400? 0.400 0.021 0.174 0.400 0.021 0.174 0.400 0.174 0.021 0.400 0.0174 How many peaks are in the 13C NMR spectrum of the following compound? Br Br . 2 3 4 7 5 KEY CHEM 322 – study questions for test 1 Which one of the following is FALSE about NMR spectroscopy? Increasing the strength of the magnet improves resolution Increasing the strength of the magnet improves sensitivity chemical shift is related to the spins of nearby nuclei the NMR peaks for solid samples tend to be very broad 8