May 2015 CE Site code # 107200E-1215 Pediatrics Objectives by
advertisement

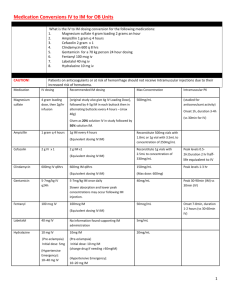
May 2015 CE Site code # 107200E-1215 Pediatrics Objectives by Reviewed/revised by Sharon Hopkins, RN, BSN, EMT-P To view on the Advocate Condell website visit: http://www.advocatehealth.com/condell/2015-ems-continuingeducation Date of CE presentation: May, 2015 Topic: Pediatrics Behavioral Objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, the EMS provider will be able to: 1. Recall and be able to apply the components of the Pediatric Assessment Triangle to determine if the child is sick or not sick. 2. Distinguish between the patient in respiratory distress versus respiratory failure. 3. Identify the components to tabulate for the GCS in the pediatric population. 4. Distinguish the stages of shock for the pediatric population. 5. Identify what could constitute an episode of ALTE (apparent life-threatening event). 6. Identify the pain management plan for the pediatric patient and successfully calculate dosing. 7. Actively participate in review of selected Region X SOP’s related to the topic presented. 8. Actively participate in review and correct identification of a variety of EKG rhythms. 9. Actively participate in case scenario and group discussion at your respective licensed level. 10. Actively participate in calculating and drawing up pediatric doses of medications. 11.Successfully complete the post quiz with a score of 80% or better. Bibliography: American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatric Education for Prehospital Professionals 3rd Edition. Jones and Bartlett. 2014 Bledsoe, B., Porter, R., Cherry, R. Paramedic Care Principles & Practices, 4th edition. Brady. 2013. Mistovich, J., Karren, K. Prehospital Emergency Care 9th Edition. Brady. 2010. Region X SOP’s; IDPH Approved April 10, 2014. Pediatric Assessment Triangle – PAT Appearance Work of Breathing Circulation IO Needles Math Calculation Formula #1: Mg ordered = mg on hand X ml ml on hand Line up mg across form mg and ml across from ml Cross multiply With fraction result, divide numberator (top number) by denominator (bottom number) Answer is ml needed Formula #2: D=DV H Desired ml = desired dose in mg x volume on hand dose on hand (mg) Lidocaine Discussion Lidocaine packaging 100 mg / 5 ml Patient weight 88 pounds; dose desired = 40 mg Patient weight 130 pounds; dose desired = 50 mg Patient weight 50 pounds; dose desired = 23 mg OPQRST Assessment O – onset P – provocation / palliation Q – quality in patinte’s words R – radiation S – severity on 0 – 10 scale or age appropriate scale T – time started Case Scenario #1 Fentanyl dose – for 132 pound 13 year-old Packaged: 100 mcg/2 ml Case Scenario #4 DCFS hot line 24/7 – 1-800-25- Abuse (1-800-252-2873 Group Practice #1 13 year-old – 90 pounds BVM rate to assist ventilations – Medication dosing: Narcan – Lidocaine DAI – Lidocaine for IO pain control (packaged as 100 mg/5ml) Group Practice #2 5 year-old; 45 pounds Medication dosing: Lidocaine for IO pain control (packaged as 100 mg/5ml) Group Practice #3 2 year-old; 23 pounds Medication dosing: Epinephrine 1:10,000 Atropine Etomidate Versed Group Practice #4 8 year-old; 60 pounds Medication dosing: Duoneb Group Practice #5 15 year-old; 128 pounds Medication dosing: Glucagon Dextrose Narcan File: CE, EMS; CE Packets; 2015: May Handout Peds