Theory of reasoned action diagram
advertisement
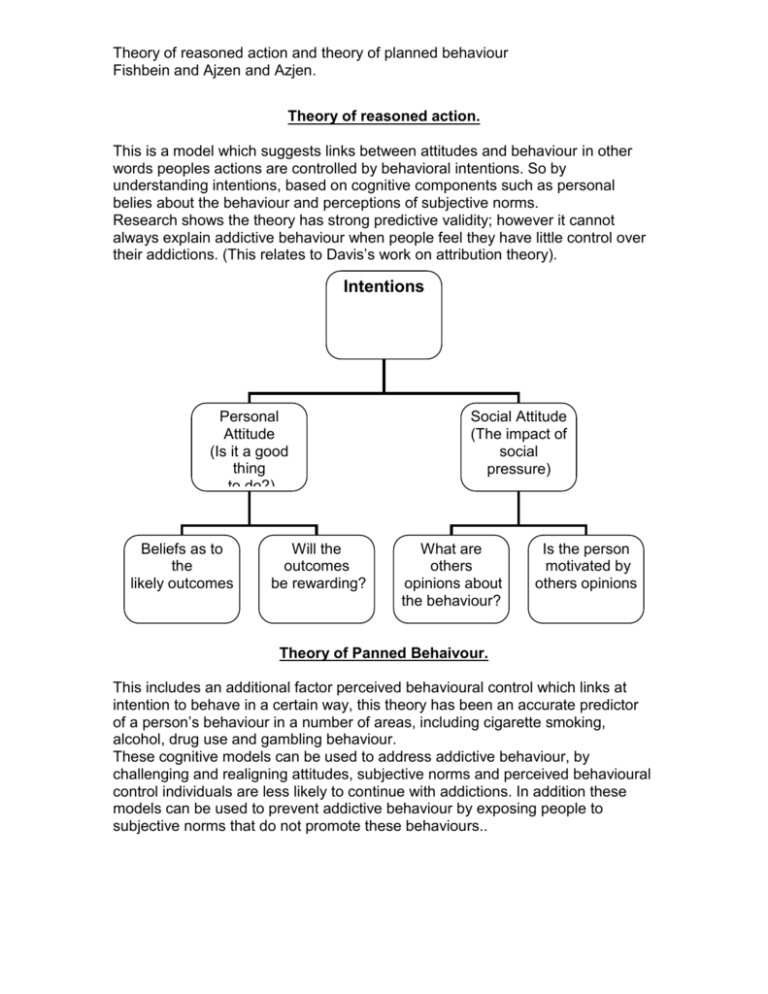
Theory of reasoned action and theory of planned behaviour Fishbein and Ajzen and Azjen. Theory of reasoned action. This is a model which suggests links between attitudes and behaviour in other words peoples actions are controlled by behavioral intentions. So by understanding intentions, based on cognitive components such as personal belies about the behaviour and perceptions of subjective norms. Research shows the theory has strong predictive validity; however it cannot always explain addictive behaviour when people feel they have little control over their addictions. (This relates to Davis’s work on attribution theory). Intentions Personal Attitude (Is it a good thing to do?) Beliefs as to the likely outcomes Will the outcomes be rewarding? Social Attitude (The impact of social pressure) What are others opinions about the behaviour? Is the person motivated by others opinions Theory of Panned Behaivour. This includes an additional factor perceived behavioural control which links at intention to behave in a certain way, this theory has been an accurate predictor of a person’s behaviour in a number of areas, including cigarette smoking, alcohol, drug use and gambling behaviour. These cognitive models can be used to address addictive behaviour, by challenging and realigning attitudes, subjective norms and perceived behavioural control individuals are less likely to continue with addictions. In addition these models can be used to prevent addictive behaviour by exposing people to subjective norms that do not promote these behaviours..