RS_Water_S09 - NovakSciencePage
advertisement

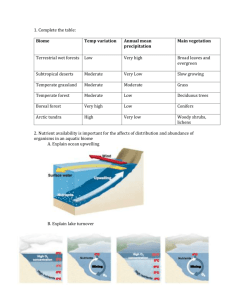
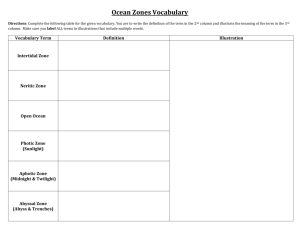
Review Sheet: WATER Vocabulary a. Aquifier b. Well c. Hot spring d. Geyser e. Degraded f. Point-source pollution Thank you for using Pencil g. Non-point source pollution h. Impermeable i. Sustainable j. PPM k. Wetlands l. Potable Water m. Biotic Factors n. o. p. q. r. s. t. u. Continental Shelf Photic zone Pelagic zone Intertidal zone Benthic zone Abyssal zone Upwelling Flocculation Freshwater – chpt 6 1. What is an aquifier and a well? (P. 174 & notes) 2. What is the difference between a hot spring and a geyser p. (172-173 and notes) 3. What are the three main ways humans use water? (notes) 4. What are 4 ways you can conserve water at home? (notes) 5. What are 4 ways water is contaminated (degraded/polluted) (p 175-176 & notes) 6. Define (a) impermeable, (b) sustainable, (c) ppm, (d) point source pollution, (e) non point source pollution (notes) 7. Why are wetlands important? (notes) 8. What are the 4 steps to water treatment before being potable (drinkable)? (lab) 9. How much water is used by the average American in a year? Give an example (notes) Oceans – chpt 14-16 10. What are the 4 ocean basins (p. 395 and notes) (The 5th is the Southern Ocean) 11. What tools do we use to measure the ocean floor (p. 396-397) 12. What are the 3 main features of the ocean floor? (P. 396) 13. (a) What is the continental shelf? (b) Why is it important? (P. 402) 14. What is the photic zone, pelagic zone, intertidal zone, benthic zone, and abyssal zone? (P. 430) 15. What two factors influence sea water density? (P. 423-424) 16. Where is the ocean surface temp. warmest? 17. What happens to temp as you inc depth? 18. What is an upwelling? (p.450 and notes) 19. What causes drag on waves? (457) 20. What is the MOST important organism in the sea and why? (p. 438 and notes) 21. Explain convection. (notes) Review Sheet: WATER Vocabulary a. Aquifier b. Well c. Hot spring d. Geyser e. Degraded f. Point-source pollution Thank you for using Pencil g. Non-point source pollution h. Impermeable i. Sustainable j. PPM k. Wetlands l. Potable Water m. Biotic Factors n. o. p. q. r. s. t. u. Continental Shelf Photic zone Pelagic zone Intertidal zone Benthic zone Abyssal zone Upwelling Flocculation Freshwater – chpt 6 1. What is an aquifier and a well? (P. 174 & notes) 2. What is the difference between a hot spring and a geyser p. (172-173 and notes) 3. What are the three main ways humans use water? (notes) 4. What are 4 ways you can conserve water at home? (notes) 5. What are 4 ways water is contaminated (degraded/polluted) (p 175-176 & notes) 6. Define (a) impermeable, (b) sustainable, (c) ppm, (d) point source pollution, (e) non point source pollution (notes) 7. Why are wetlands important? (notes) 8. What are the 4 steps to water treatment before being potable (drinkable)? (lab) 9. How much water is used by the average American in a year? Give an example (notes) Oceans – chpt 14-16 10. What are the 4 ocean basins (p. 395 and notes) (The 5th is the Southern Ocean) 11. What tools do we use to measure the ocean floor (p. 396-397) 12. What are the 3 main features of the ocean floor? (P. 396) 13. What is the continental shelf? (b) Why is it important? (P. 402) 14. What is the photic zone, pelagic zone, intertidal zone, benthic zone, and abyssal zone? (P. 430) 15. What two factors influence sea water density? (P. 423-424) 16. Where is the ocean surface temp. warmest? 17. What happens to temp as you inc depth? 18. What is an upwelling? (p.450 and notes) 19. What causes drag on waves? (457) 20. What is the MOST important organism in the sea and why? (p. 438 and notes) 21. Explain convection. (notes) Review Sheet: WATER Vocabulary a. Aquifier b. Well c. Hot spring d. Geyser e. Degraded f. Point-source pollution Thank you for using Pencil g. Non-point source pollution h. Impermeable i. Sustainable j. PPM k. Wetlands l. Potable Water m. Biotic Factors n. o. p. q. r. s. t. u. Continental Shelf Photic zone Pelagic zone Intertidal zone Benthic zone Abyssal zone Upwelling Flocculation Freshwater – chpt 6 1. What is an aquifier and a well? (P. 174 & notes) 2. What is the difference between a hot spring and a geyser p. (172-173 and notes) 3. What are the three main ways humans use water? (notes) 4. What are 4 ways you can conserve water at home? (notes) 5. What are 4 ways water is contaminated (degraded/polluted) (p 175-176 & notes) 6. Define (a) impermeable, (b) sustainable, (c) ppm, (d) point source pollution, (e) non point source pollution (notes) 7. Why are wetlands important? (notes) 8. What are the 4 steps to water treatment before being potable (drinkable)? (lab) 9. How much water is used by the average American in a year? Give an example (notes) Oceans – chpt 14-16 10. What are the 4 ocean basins (p. 395 and notes) (The 5th is the Southern Ocean) 11. What tools do we use to measure the ocean floor (p. 396-397) 12. What are the 3 main features of the ocean floor? (P. 396) 13. What is the continental shelf? (b) Why is it important? (P. 402) 14. What is the photic zone, pelagic zone, intertidal zone, benthic zone, and abyssal zone? (P. 430) 15. What two factors influence sea water density? (P. 423-424) 16. Where is the ocean surface temp. warmest? 17. What happens to temp as you inc depth? 18. What is an upwelling? (p.450 and notes) 19. What causes drag on waves? (457) 20. What is the MOST important organism in the sea and why? (p. 438 and notes) 21. Explain convection. (notes) Review Sheet: WATER Vocabulary a. Aquifier b. Well c. Hot spring d. Geyser e. Degraded f. Point-source pollution Thank you for using Pencil g. Non-point source pollution h. Impermeable i. Sustainable j. PPM k. Wetlands l. Potable Water m. Biotic Factors n. o. p. q. r. s. t. u. Continental Shelf Photic zone Pelagic zone Intertidal zone Benthic zone Abyssal zone Upwelling Flocculation Freshwater – chpt 6 1. What is an aquifier and a well? (P. 174 & notes) 2. What is the difference between a hot spring and a geyser p. (172-173 and notes) 3. What are the three main ways humans use water? (notes) 4. What are 4 ways you can conserve water at home? (notes) 5. What are 4 ways water is contaminated (degraded/polluted) (p 175-176 & notes) 6. Define (a) impermeable, (b) sustainable, (c) ppm, (d) point source pollution, (e) non point source pollution (notes) 7. Why are wetlands important? (notes) 8. What are the 4 steps to water treatment before being potable (drinkable)? (lab) 9. How much water is used by the average American in a year? Give an example (notes) 10. Oceans – chpt 14-16 11. What are the 4 ocean basins (p. 395 and notes) (The 5th is the Southern Ocean) 12. What tools do we use to measure the ocean floor (p. 396-397) 13. What are the 3 main features of the ocean floor? (P. 396) 14. (a) What is the continental shelf? (b) Why is it important? (P. 402) 15. What is the photic zone, pelagic zone, intertidal zone, benthic zone, and abyssal zone? (P. 430) 16. What two factors influence sea water density? (P. 423-424) 17. Where is the ocean surface temp. warmest? 18. What happens to temp as you inc depth? 19. What is an upwelling? (p.450 and notes) 20. What causes drag on waves? (457) 21. What is the MOST important organism in the sea and why? (p. 438 and notes) 22. Explain convection. (notes)