QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School
advertisement
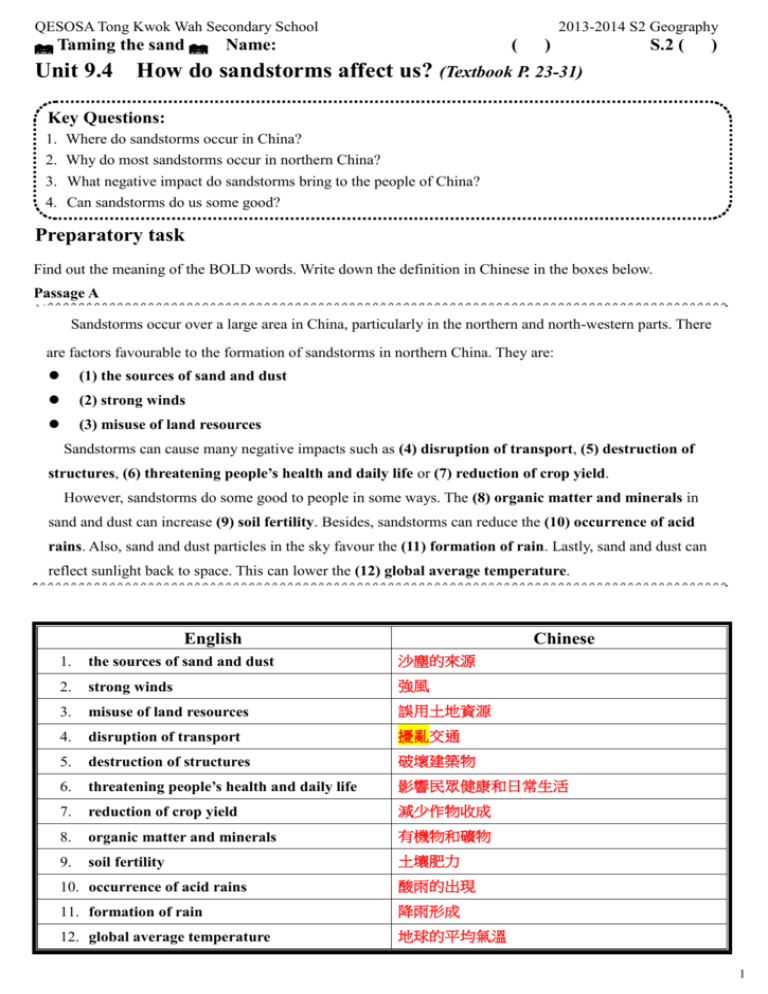
QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Taming the sand 2013-2014 S2 Geography Name: ( ) S.2 ( ) Unit 9.4 How do sandstorms affect us? (Textbook P. 23-31) Key Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Where do sandstorms occur in China? Why do most sandstorms occur in northern China? What negative impact do sandstorms bring to the people of China? Can sandstorms do us some good? Preparatory task Find out the meaning of the BOLD words. Write down the definition in Chinese in the boxes below. Passage A Sandstorms occur over a large area in China, particularly in the northern and north-western parts. There are factors favourable to the formation of sandstorms in northern China. They are: (1) the sources of sand and dust (2) strong winds (3) misuse of land resources Sandstorms can cause many negative impacts such as (4) disruption of transport, (5) destruction of structures, (6) threatening people’s health and daily life or (7) reduction of crop yield. However, sandstorms do some good to people in some ways. The (8) organic matter and minerals in sand and dust can increase (9) soil fertility. Besides, sandstorms can reduce the (10) occurrence of acid rains. Also, sand and dust particles in the sky favour the (11) formation of rain. Lastly, sand and dust can reflect sunlight back to space. This can lower the (12) global average temperature. English Chinese 1. the sources of sand and dust 沙塵的來源 2. strong winds 強風 3. misuse of land resources 誤用土地資源 4. disruption of transport 擾亂交通 5. destruction of structures 破壞建築物 6. threatening people’s health and daily life 影響民眾健康和日常生活 7. reduction of crop yield 減少作物收成 8. organic matter and minerals 有機物和礦物 9. soil fertility 土壤肥力 10. occurrence of acid rains 酸雨的出現 11. formation of rain 降雨形成 12. global average temperature 地球的平均氣溫 1 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Taming the sand 2013-2014 S2 Geography Name: ( ) S.2 ( ) 1. Where do sandstorms occur in China? (Textbook, p.24) The following map shows the distribution of sandstorms in China. Describe the distribution Sandstorms occur over a large area in China. They are particularly in the northern and north-western parts in China. Most severe sandstorms are found in north-western part in China. of sandstorms in China 2. Why do most sandstorms occur in northern China? (Textbook, p.25-26) Task 1: The following figures show the factors to the formation of sandstorms in northern China. Describe the factors. Factor (1) : The sources of sand and dust Deserts are the major source of sand and dust for sandstorms Major deserts are found in the northern and north-western parts of China such as - the Takla Makan Desert - the Gobi Desert Figure 2a Major paths of strong winds in spring and winter ad major sources of sand and dust in China. Some of the deserts lie on the path of strong winds. There are two main oaths of strong winds. 1. from the west and the north-west, moving eastern 2. from the north moving 2 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Taming the sand Name: 2013-2014 S2 Geography ( ) southward. S.2 ( ) Factor (2) : Strong winds Figure 2b China Monthly frequency of sandstorms in northern Figure 2c Winter monsoon in China Sandstorms occur most frequently in spring because China is affected by the monsoon climate / monsoon winds. In spring, (hot / cold) and (strong / weak) winds move from the continental interior to northern China. * Monsoon winds refer to winds that change with the seasons. - In summer monsoon, wind blows from sea to land (Eastern or South-eastern wind of Hong Kong). - In winter monsoon, wind blows from land to sea (Northern or North-eastern wind of Hong Kong). 3 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Taming the sand 2013-2014 S2 Geography Name: ( ) S.2 ( ) Factor (3) : Misuse of land resources Increase in population Misuse of land resources (e.g. overcutting, overgrazing , over-cultivation) Loss of vegetation cover Soil erosion Sources of sand and dust (increases / decreases) Sandstorms Task 2: List / Describe the factors to the formation of sandstorms in northern China. 1. The first factor is that there are the sources of sand and dust in northern China. 2. The second factor is that there are strong winds in northern China. 3. The third factor is that there is misuse of land resources in northern China. 3. What negative impact do sandstorms bring to the people of China? (Textbook, p.26-28) Task 1: The following figures show the negative impact brought by sandstorms. Identify and describe the negative impacts. Negative Impact (1) : Disruption of transport 4 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Taming the sand 2013-2014 S2 Geography Name: A car covered by sand and dust during a sandstorm ( ) S.2 ( ) Visibility is greatly reduced during sandstorm Large amounts of sand and dust blown into the sky reduces visibility. This threatens the safety of transport. Flights, road and rail services cancelled. Negative Impact (2) : Destruction of structures Sandstorm nearly buried a house in Nei Mongol Sandstorm hits Kuwait and Saudi Arabia Large amounts of sand and dust can bury and destroy structures such as roads and buildings. It can cause great economic loss. 5 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Taming the sand 2013-2014 S2 Geography Name: ( ) S.2 ( ) Negative Impact (3) : Threatening people’s health and daily life. People in Gansu wearing masks to protect Themselves from a sandstorm Tiananmen Square in Beijing during a sandstorm Sandstorms cause serious air pollution. They can cause discomfort to people’s eyes and breathing. Sand and dust may contain bacteria and fungi. They may cause diseases to people. It is dangerous to carry out outdoor activities during sandstorms. Schools, factories and offices have to be closed. The productivity of society will be affected. Negative Impact (4) : Reduction of crop yield Farmers are clearing sand and dust deposited Sunlight cannot reach the land surface as it is on vegetables reflected by sand and dust 6 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Taming the sand 2013-2014 S2 Geography Name: ( ) S.2 ( ) Source areas with sandstorms often suffer a loss of soil nutrients and organic matter. Strong winds may sometimes erode soil up to 1-10 cm in depth. The thinning of the topsoil makes the land less productive. It will hinder farming. Sand and dust may destroy young plants. When the sand and dust are deposited, it may bury field. It will affect farm production. Sand and dust in the atmosphere will reflect more sunlight. This will lower the amount of light absorbed by plants. It will affect plant growth. Task 2: List or describe the negative impacts brought by sandstorms. 1. The first negative impact is disruption of transport. 2. The second negative impact is destruction of structures. 3. The third impact is threatening people’s health and daily life. 4. The fourth impact is reduction of crop yield. 4. Can sandstorms do us some good? (Textbook, p.29) Task 1: The following photo some positive impacts brought by sandstorms. Identify and describe the positive impacts. The Loess Plateau (黃土高原) in northern China was formed by deep layers of sand and dust brought by sandstorms. Land is some areas is rich in minerals and organic matter, forming fertile topsoil. For hundreds of years, the land has supported dense farming activities. Extensive farmland in the Loess Plateau Sand and dust may contain organic matter and minerals such as iron. These materials help increase soil fertility in the receiving areas. It can improve farm production in 7 QESOSA Tong Kwok Wah Secondary School Taming the sand Name: 2013-2014 S2 Geography ( ) S.2 ( ) the receiving areas. When sand and dust are brought to the ( sea / river ), nutrients in water increase. This facilitates the growth of plant plankton. It can favour marine life. Sand and dust ca neutralize acids in gases. It can reduce the occurrence of acid rain. Sand and dust particles high up in the sky can act as condensation nuclei. It can favour the formation of rain. Sand and dust can reflect sunlight back to the space before it reached the earth’s surface. It can lower the global average temperature. Task 2: List or describe some positive impacts brought by sandstorms. 1. The first positive impact is improving farm production in the receiving areas. 2. The second positive impact is favouring marine life. 3. The third positive impact is reducing the occurrence of acid rain. 4. The fourth positive impact is favouring the formation of rain. 5. The fifth positive impact is lowering the global average temperature. 8