Chem 3.4 Answers #11
advertisement

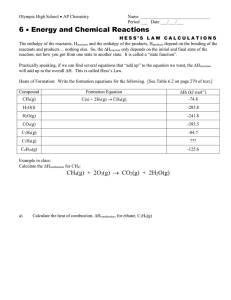
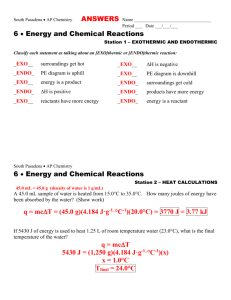
CHEMISTRY 3.4 WORKSHEET ELEVEN 1. (a) ANSWERS HEAT OF COMBUSTION & FORMATION 2. (a) (b) The energy change when one mole of the substance is formed from its elements with all reactants and products in their standard states. The energy change when one mole of the substance is completely burnt with all reactants and products in their standard states. The states at room temperature (25oC) and pressure (1 Atm) Zero 3. (a) ∆rHo = 52.3 - 226.7 = -174.4 kJ mol-1 (b) ∆rHo = (-1260) - 2(-277.7) - 2(-393.5) = -1260 + 555.4 + 787 = 82.4 kJ mol-1 (c) ∆rHo = (-1096) - (-110.5) (b) = -985.5 kJ mol-1 4. ∆rH = -2712 = 4(-393.5) + 5(-285.8) - ∆fHo(C4H9OH) -2712 = -1574 - 1429 - ∆fHo(C4H9OH) ∆fHo(C4H9OH) = -291 kJ mol-1 5. (a) C4H10 (g) + 6.5 O2(g) → 4CO2 (g) + 5H2O(l) (b) -2882 = 4(-393.5) + 5(-285.8) - ∆fHo(C4H10) ∆fHo(C4H10) = -1574 - 1429 + 2882 = -121 kJ mol-1 (c) Energy is required for bond breaking and energy is released when bonds are made. In combustion reactions, mainly C-O and H-O bonds are made while mainly C-C and C-H bonds are broken. The greater stability of C-O and H-O bonds compared to C-C and C-H means that there is always an overall release of energy in combustion. (a) C8H18 (g) + 12.5 O2(g) → 8CO2 (g) + 9H2O(l) (b) -5509 = 8(-393.5) + 9(-285.8) - ∆fHo(C8H18) ∆fHo(C4H10) = -3148 - 2572.2 + 5509 = -211.2 kJ mol-1 (a) (b) C2H5OH (l) + 3.5 O2(g) → 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O(l) ∆cHo = 2(-393.5) + 3(-285.8) - (-277.7) = -787 - 857.4 + 277.7 = -1366.7 kJ mol-1 6. 7.