File
advertisement
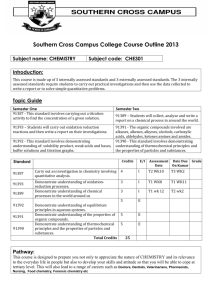
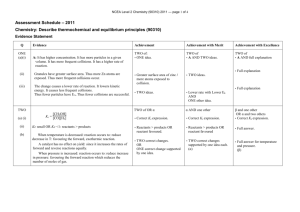
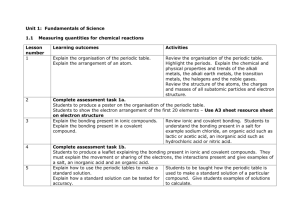
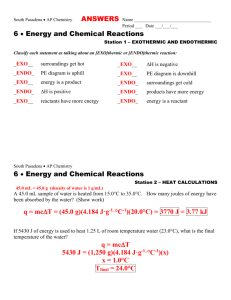
KBHS CHEMISTRY 2015 2015 Achievement Standard 91161 (v2) Carry out quantitative analysis Credits: 4 Practise Assessment NAME Achievement Carry out quantitative analysis Merit Carry out in-depth quantitative analysis Excellence Carry out comprehensive qualitative analysis KBHS CHEMISTRY 2015 SUBJECT REFERENCE: CHEMISTRY 2.1 Practise Assessment Achievement Standard 91161 (v2) Carry out quantitative analysis Credits: 4 Time allowed: 2 hours Student Instructions Sheet This is an individual practical and written activity which is carried out over the course of two periods. You will be assessed on each part and you are required to record your results and calculations. Make sure you: Show all working Give answers to the correct number of significant figures Use appropriate units Task 1 requires you to carry out an acid-base volumetric analysis. You will have one hour to complete this part of the assessment. Task 2 requires you to solve simple quantitative problems. You will have one hour to complete this part of the assessment. Each task must be completed independently. You will be instructed what task you are to begin with. KBHS CHEMISTRY 2015 Task 1: Volumetric Analysis Practical activity You are required to perform a titration to analyse the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid provided by your teacher. You will need: 25.0 mL pipette burette 3 conical flasks hydrochloric acid solution distilled water phenolphthalein indicator wash bottle standard sodium hydroxide solution (concentration = mol.L-1) Method: Titrate 25.0 mL samples of the hydrochloric acid solution with the standard sodium hydroxide solution using phenolphthalein as an indicator for the end point of the reaction Repeat the titration procedure until you have three (minimum) concordant results Record all of your burette readings in a systematic format that clearly indicates the volume of sodium hydroxide used in each titration Results: KBHS CHEMISTRY 2015 Calculations: Calculate the average titre volume of sodium hydroxide Use the known concentration of sodium hydroxide to calculate the amount of sodium hydroxide used in the titration. The balanced equation for the reaction occurring in the titration is: NaOH + HCl NaCl + H2O Calculate the concentration of hydrochloric acid solution used in the titration. Make sure to give your answer to three significant figures KBHS CHEMISTRY 2015 Task Two: Written Problems The molar masses below will help you carry out the following calculations. M(C) = 12.0 g.mol-1 M(O) = 16.0 g.mol-1 M(C2H6O) = 46 g.mol-1 M(H) = 1.00 g.mol-1 M(N) = 14.0 g.mol-1 -1 M(NH4NO3) = 80.0 g.mol M(C12H22O11) = 342 g.mol-1 M(PbI2) = 461 g.mol-1 M(Pb(NO3)2) = 331 g.mol-1 Question One A compound is 30.4% nitrogen and 69.6% oxygen, with a molar mass of 92.0 g.mol-1, calculate the empirical formula and molecular formula Empirical formula: Molecular formula: Question Two What is the mass of 0.606 mol of NH4NO3? Question Three Sucrose is a naturally occurring sugar. How many moles of sucrose are present in 22.0 mL of 0.180 mol.L-1 sucrose solution? KBHS CHEMISTRY 2015 Question Four Calculate the %C, %H and %O composition of sucrose (C12H22O11). %C composition: %H composition: %O composition: Question Five How many moles of ethanol, C2H6O, in 173 g of ethanol? KBHS CHEMISTRY 2015 Question Six 25 mL samples of KOH solution are titrated against 0.0344 mol.L-1 H2SO4 solution. The average titre of H2SO4 was 22.3 mL. Calculate the concentration of the KOH solution. 2 KOH + H2SO4 K2SO4 + 2 H2O Question Seven Lead nitrate, Pb(NO3)2, and potassium iodide, KI, react together to form a yellow precipitate of lead iodide, PbI2, as well as potassium nitrate, KNO3. Pb(NO3)2 + 2 KI PbI2 + 2 KNO3 Calculate the mass of Pb(NO3)2 needed to produce 6.92 g of PbI2.