LINGUISTICS 5300
advertisement

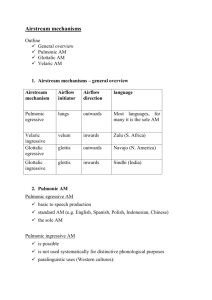
LINGUISTICS 5300 September 4, 2007 PHONETICS: PART 2 Review from last class; additional notes on consonant articulation o Airstream mechanisms o Consonant dimensions of classification (REVIEW) o Rhotics o Stridents/sibilants o Flap/tap/trill o Aspirated vs. unaspirated; released vs. unreleased Vowels: what makes them different from consonants? Dimensions of vowel articulation: o Height o Backness o ATR o lip rounding Diphthongs Regional differences in vowel articulations Phonation types: review PHONOLOGY Distributions: complementary vs. overlapping Phoneme vs. allophone; contrastive/distinctive vs. predictable Minimal pairs Conditioning environments Underlying vs. surface forms Writing rules HW: Odden- p. 61-64, problems 1-8 AIRSTREAM MECHANISMS: Airstream Pulmonic Glottalic Velaric INGRESSIVE No languages use these distinctively Implosives Clicks 1. Pulmonic (lung) airstream mechanism a. Egressive b. Ingressive 2. Glottalic airstream mechanism a. Egressive: ejectives b. Ingressive: implosives 3. Velaric airstream mechanism a. Egressive b. Ingressive: clicks EGRESSIVE Most speech sounds ejectives No languages exploit these Consonants: DIMENSIONS OF CLASSIFICATION I. STATE OF GLOTTIS (VOICED VS. VOICELESS) II. PLACE OF ARTICULATION a. Labial i. Bilabial ii. Labiodentals iii. Labiovelar b. Dental c. Alveolar d. Palatal i. Alveopalatal ii. Palatal e. Velar f. Pharyngeal g. Glottal III. MANNER OF ARTICULATION a. b. c. d. e. Stop Fricative Affricate Nasal Liquid i. Lateral ii. Rhotic f. Glide Additional: approximants (=glides+liquids); sibilants Practice: Give the symbol which matches the following articulatory description and an example from a word in English or some other language which contains this sound: a. b. c. d. voiceless alveopalatal fricative (voiced) velar nasal voiced interdental fricative (voiced) alveolar lateral liquid Give the articulatory description for the following symbols: e. f. g. h. h Practice articulatory descriptions for vowels: 1. [u] 2. [] 3. [i] 4. [] Give the symbol which matches the following description. mid central lax unstressed vowel low front unrounded lax vowel mid back rounded tense diphthong PHONATION TYPES: Phonation involves the vibration of the vocal folds. Phonation types refers to the ways in which vocal folds can be manipulated in order to produce speech categories. 1. Voiceless no vibration 2. Whisper no vibration 3. Breathy voice vocal fold vibration 4. Voice vocal fold vibration 5. Creak vocal fold vibration