Exam 3 Key - Chemistry
advertisement
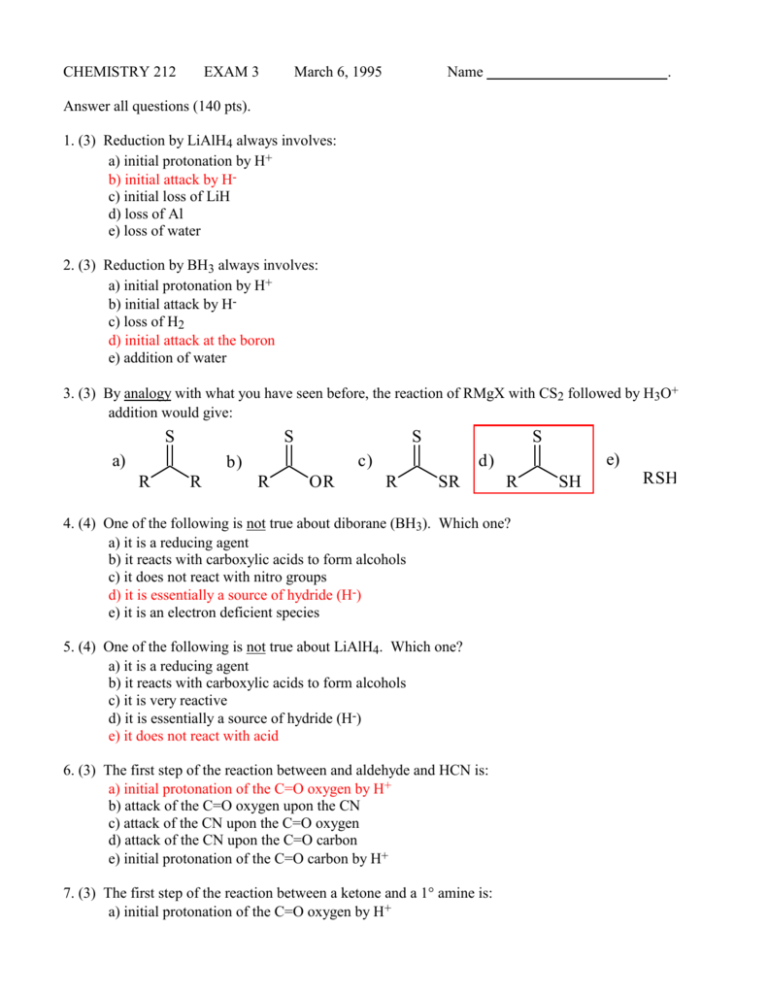
CHEMISTRY 212 EXAM 3 March 6, 1995 Name . Answer all questions (140 pts). 1. (3) Reduction by LiAlH4 always involves: a) initial protonation by H+ b) initial attack by Hc) initial loss of LiH d) loss of Al e) loss of water 2. (3) Reduction by BH3 always involves: a) initial protonation by H+ b) initial attack by Hc) loss of H2 d) initial attack at the boron e) addition of water 3. (3) By analogy with what you have seen before, the reaction of RMgX with CS2 followed by H3O+ addition would give: S S a) S c) b) R R S R OR e) d) R SR R 4. (4) One of the following is not true about diborane (BH3). Which one? a) it is a reducing agent b) it reacts with carboxylic acids to form alcohols c) it does not react with nitro groups d) it is essentially a source of hydride (H-) e) it is an electron deficient species 5. (4) One of the following is not true about LiAlH4. Which one? a) it is a reducing agent b) it reacts with carboxylic acids to form alcohols c) it is very reactive d) it is essentially a source of hydride (H-) e) it does not react with acid 6. (3) The first step of the reaction between and aldehyde and HCN is: a) initial protonation of the C=O oxygen by H+ b) attack of the C=O oxygen upon the CN c) attack of the CN upon the C=O oxygen d) attack of the CN upon the C=O carbon e) initial protonation of the C=O carbon by H+ 7. (3) The first step of the reaction between a ketone and a 1° amine is: a) initial protonation of the C=O oxygen by H+ SH RSH b) attack of the C=O oxygen upon the amine c) attack of the C=O carbon upon the amine d) attack by the amino N upon the C=O carbon e) initial protonation of the C=O carbon by H+ 8. (3) The carboxylic acid proton appears in its NMR spectrum at about: a) 7-8 b) 1-2 c) 3-4 d) 8-9 e) 11-12 9. (3) If the position for an aldehyde C=O str. in the IR spectrum is 1715cm-1 then a ketone C=O str. would be about: a) 1725 cm-1 b) 1785 cm-1 c) 1560 cm-1 d) 1705 cm-1 e) 1715 cm-1 10. (3) If the position for an aldehyde C=O str. in the IR spectrum is 1715 cm-1 then an -unsaturated aldehyde C=O str. would be about: a) 1725 cm-1 b) 1785 cm-1 c) 1560 cm-1 d) 1700 cm-1 e) 1715 cm-1 11. (3) The first step of the reaction between a ketone and a Grignard reagent is: a) initial protonation of the C=O oxygen by H+ b) attack of the C=O oxygen upon the Mg c) attack by R- upon the C=O oxygen d) attack by R- upon the C=O carbon e) protonation of the Grignard reagent 12. (4) One of the following is not true about aldehydes. Which one? a) they contain the formyl group b) they show a peak at ~9-10 in their 1H-NMR spectra c) they react more readily with nucleophiles than do ketones d) they react with Grignard reagents to form 3° alcohols e) they show a peak at ~200 ppm in their 13C-NMR spectra 13. (4) One of the following is not true about ketones. Which one? a) they react with NaBH4 to form 2° alcohols b) they show a strong peak at ~1700 cm-1 in their IR spectra c) they react less readily with nucleophiles than do aldehydes d) they react with primary amines to form compounds containing a C=N linkage e) they show a peak at ~12 in their 1H-NMR spectra 14. (3) One diagnostic feature in the NMR spectrum for carboxylic acids is that on addition of D2O the carboxylic acid proton signal: a) increases in strength b) becomes a doublet c) disappears d) moves upfield e) moves downfield 15. (3) When naming non-cyclic carboxylic acids, the number assigned to the carboxylic acid carbon is: a) always 1 b) decided by the numbering of the longest carbon chain c) always 2 d) as close to 1 as possible e) any number depending on the situation 16. (3) An epoxide is: a) HOOH b) a compound with 3-4 oxygens c) a cyclic ether d) a non-cyclic ether e) a compound with a C=O functionality 17. (3) True or False. The carbonyl carbon in an aldehyde is sp2 hybridized. 18. (3) True or False. The compound shown to the right is an example of an -unsaturated aldehyde H O 19. (3) True or False. The compound shown to the right would be named butanal. H O 20. (3) True or False. The functional group shown to the right is an acetal. H CH3 O O 21. (3) True or False. The molecule shown in the previous question would react readily with a Grignard reagent. 22. (3) True or False. An acetal reacts with aqueous acid to form an aldehyde. 23. (3) Which one of the following reagents is not an oxidizing agent? a) Jones b) PCC c) KMnO4 d) O3 24. (5) Draw the structure of 4-methyl-3-bromohexanal e) Zn / Hg, H+ CH3 O Br 25 (12) Show the first step (complete) and the consequence of the arrow-pushing mechanism for the reaction between each of the following: H O a) H I + CH3 CH3 b) O O O N O H H H2N O 26. (9) In each of the following pairs circle the species which would be the more reactive. a) HCN and propanal b) MeNH2 and acetone c) NaNH2 and acetone 27. (25) Show reasonable products from the following reactions. NPh2 O a) Ph2 NH CH2 CH3 b) CH3 O O C 1) Et2 CuLi + 2) H 3 O Et OH CHO c) HCN CN Br Br O d) NH2 N Cl Cl O e) O OH (excess) + Cl O H (cat.) Cl 28. (4) Name the following using any satisfactory method. COOH 4-ethyl-2-isopropylhexanoic acid 29. (12) Show the reagents required to effect the following transformations. (These can all be done in one step, or one pair of steps). You don't have to show how to prepare the reagents. a) O PPh3 b) O Zn / Hg HCl c) O O HO OH H+ O