Ecosystems Part 1 Study Guide

Ecosystems Part 2 Name __________
Study Guide
The test will be matching, fill in the blank, and short answer.
Vocabulary
system ~ group of parts that work as a unit
stability ~ property of a
system in balance
ecosystem ~ system made up of living things and their environment
population ~ group of the
same species
living in the same place at the same time
community ~
group of organisms
living together and interacting
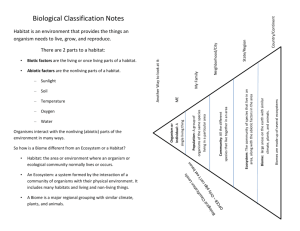
habitat ~ place that meets an organism’s needs
niche ~
role
of an organism in its habitat
producer ~ living thing that can
make its own food
consumer ~ living thing that
eats
other living things
decomposer ~ living thing that breaks down
dead
plants or animals for food
climate ~ average
weather
of a place over a long time
diversity ~
variety
of plants and animals
salinity~ amount of
salt
in something
Concepts & Questions
The open-ocean zone, near-shore zone, and intertidal zones are the three main life zones in the ocean. The narrow strip of land that is covered by ocean water during high tides is the intertidal zone.
The shallow area of ocean water that provides a habitat for many forms of life is the near-shore zone.
The deepest part of the ocean is the open-ocean zone.
A food web shows how different
food chains connect & overlap
.
An energy pyramid shows
how food energy is passed
from one organism to another along a food chain.
The 3 levels of a food chain are producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Ecosystems with lots of resource for meeting organisms’ needs often have many living things.
Explain why a tree is an open system instead of a closed system (think inputs and outputs)._________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
In our food chain tag, what would have happened to the stability of our ecosystem if there were too many hawks?__________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
What are the most basic parts of an ecosystem? ___
_______________________________________
Most natural systems have patterns that give them stability/inputs/outputs/diversity. (circle one)
An observation is something you can directly observe with your senses. An inference is a conclusion you come to based on your observations.
For example, in this picture,
I can observe that the boy is crying. I can then infer that he is sad or upset. I cannot
directly
observe how he is feeling, but I can infer his feelings based on the facial expressions that I observe.
You will be asked to look at a picture of animals in their habitat, and identify and make several observations and inferences.