2.2 Bv2 (Word, 167 KB)
advertisement

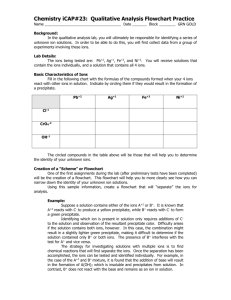
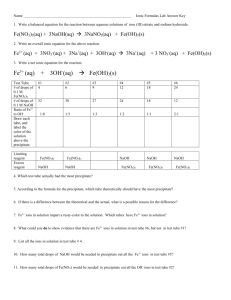
N Internal assessment resource Chemistry 2.2B v2 for Achievement Standard 91162 PAGE FOR TEACHER USE NZQA Approved Internal Assessment Resource Chemistry Level 2 This resource supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 91162 version 2 Carry out procedures to identify ions present in solution Resource title: What’s the Solution? 3 credits This resource: Clarifies the requirements of the standard Supports good assessment practice Should be subjected to the school’s usual assessment quality assurance process Should be modified to make the context relevant to students in their school environment and ensure that submitted evidence is authentic Date version published by Ministry of Education February 2015 Version 2 Quality assurance status These materials have been quality assured by NZQA. To support internal assessment from 2015 NZQA Approved number: A-A-02-2015-91162-02-5419 Authenticity of evidence Teachers must manage authenticity for any assessment from a public source, because students may have access to the assessment schedule or student exemplar material. Using this assessment resource without modification may mean that students’ work is not authentic. The teacher may need to change figures, measurements or data sources or set a different context or topic to be investigated or a different text to read or perform. This resource is copyright © Crown 2015 Page 1 of 9 Internal assessment resource Chemistry 2.2B v2 for Achievement Standard 91162 PAGE FOR TEACHER USE Internal Assessment Resource Achievement Standard Chemistry 91162: Carry out procedures to identify ions present in solution Resource reference: Chemistry 2.2B v2 Resource title: What’s the Solution? Credits: 3 Teacher guidelines The following guidelines are supplied to enable teachers to carry out valid and consistent assessment using this internal assessment resource. Teachers need to be very familiar with the outcome being assessed by Achievement Standard Chemistry 91162. The achievement criteria and the explanatory notes contain information, definitions, and requirements that are crucial when interpreting the standard and assessing students against it. Context/setting This activity requires students to use given qualitative procedures to identify ions in three unknown solutions. Conditions This assessment activity is designed to take place over 1–2 periods of in-class time. Adjust these conditions to suit your students and context. Resource requirements red litmus paper 1 mol L-1 HCl (aq) 0.1 mol L-1 AgNO3 (aq) 0.1 mol L-1 BaCl2 (aq) 1 mol L-1 NH3 (aq) 1 mol L-1 NaOH (aq) 0.1 mol L-1 KSCN (aq) 1 mol L-1 H2SO4 (aq) Unknown solutions: – A: KI – B: Fe(NO3)3 – C: FeSO4 – D: Zn(NO3)2 – E: Al2(SO4)3 safety goggles, test tubes, test tube racks, test tube brushes, droppers This resource is copyright © Crown 2015 Page 2 of 9 Internal assessment resource Chemistry 2.2B v2 for Achievement Standard 91162 PAGE FOR TEACHER USE Additional information You should not use the activity exactly as it is (same ions in same order) since it is available to all students and the assessment schedule includes examples of appropriate responses. For example, you could substitute the ions given in this activity with other appropriate ions (see EN 5). The teacher could substitute the procedure chart given in the student resources for an alternative flow chart/procedure that would enable students to identify the ions in solutions. You should carry out tests prior to the assessment to ensure that students will be able to identify the ions with the solutions provided. This resource is copyright © Crown 2015 Page 3 of 9 Internal assessment resource Chemistry 2.2B v2 for Achievement Standard 91162 PAGE FOR STUDENT USE Internal Assessment Resource Achievement Standard Chemistry 91162: Carry out procedures to identify ions present in solution Resource reference: Chemistry 2.2B v2 Resource title: What’s the Solution? Credits: 3 Achievement Achievement with Merit Carry out procedures to identify ions present in solution. Carry out procedures to justify the identification of ions present in solution. Achievement with Excellence Carry out procedures to comprehensively justify the identification of ions present in solution. Student instructions Introduction This assessment activity requires you to use given qualitative procedures to identify ions present in a number of solutions. You may carry out the qualitative procedures collaboratively. However you will need to individually write a report to support the identification of the ions in the solutions. You will work in groups of 2–3 to carry out the practical qualitative analysis procedures but your report must be written up individually. Teacher note: Modify the group size or make this an individual task to suit your context and students. Your teacher will guide you about how much time you will have for this activity. You will be assessed on how well you carry out these given procedures to identify the ions in the solutions. Task: Identifying Ions in Solutions Identify the ions In your groups, use the aqueous solutions and the procedures provided in Student Resources A and B to identify the ions present in each of the following unknown solutions. Unknown Solution Ion(s) to identify A anion B cation C D cation cation & anion E cation & anion Record the steps you used to identify the ions and any observations you made during the procedures. Use this primary data to identify the ion(s) in the solutions. This resource is copyright © Crown 2015 Page 4 of 9 Internal assessment resource Chemistry 2.2B v2 for Achievement Standard 91162 PAGE FOR STUDENT USE Report your findings Write a report to support the identification of the ion(s) in each of the solutions. For each ion identified: identify the ion by name or formula describe the steps you used to identify the ion describe the observations you made during each procedure identify by name or formula all precipitates formed write balanced equations for the formation of all precipitates write balanced equations for all complex ions formed link your observations to any equations you write for the formation of precipitates and/or complex ions. This resource is copyright © Crown 2015 Page 5 of 9 Internal assessment resource Chemistry 2.2B v2 for Achievement Standard 91162 PAGE FOR STUDENT USE Student Resource: Procedure Charts A. Testing for anions: Cl-, CO32-, I-, NO3-, OH-, SO42Ion Tests Observations Cl- Add red litmus does not change the colour Add AgNO3(aq) forms a white precipitate Add NH3(aq) precipitate dissolves Add red litmus turns red litmus blue Add HCl(aq) bubbles are produced Add red litmus does not change the colour Add AgNO3(aq) forms a yellow precipitate Add NH3(aq) precipitate remains Add red litmus does not change the colour Add AgNO3(aq) does not form a precipitate Add BaCl2(aq) does not form a precipitate Add red litmus turns red litmus blue Add HCl(aq) no bubbles are produced Add red litmus does not change the colour Add AgNO3(aq) does not form a precipitate Add BaCl2(aq) forms a white precipitate CO32- I- NO3- OH- SO42- This resource is copyright © Crown 2015 Page 6 of 9 Internal assessment resource Chemistry 2.2B v2 for Achievement Standard 91162 PAGE FOR STUDENT USE B. Testing for cations: Ag+, Al3+, Ba2+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Mg2+, Pb2+, Na+, Zn2+ Ion Tests Observations Ag+ Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) forms a brown precipitate Add 2 drops NH3(aq) to a new sample forms a brown precipitate Add excess NH3(aq) precipitate dissolves Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) forms a white precipitate Add excess NaOH(aq) precipitate dissolves Add 2 drops NH3(aq) to a new sample forms a white precipitate Add excess NH3(aq) precipitate remains Add H2SO4(aq) to a new sample forms a colourless solution Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) forms a white precipitate Add excess NaOH(aq) precipitate remains Add H2SO4(aq) to a new sample forms a white precipitate Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) forms a blue precipitate Add 2 drops NH3(aq) to a new sample forms a blue precipitate Add excess NH3(aq) forms a deep blue solution Fe2+ Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) forms a green precipitate Fe3+ Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) forms an orange precipitate Add 2 drops KSCN(aq) to a new sample forms a dark red solution Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) forms a white precipitate Add excess NaOH(aq) precipitate remains Add H2SO4(aq) to a new sample forms a colourless solution Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) forms a white precipitate Add excess NaOH(aq) precipitate dissolves Add 2 drops NH3(aq) to a new sample forms a white precipitate Add excess NH3(aq) precipitate remains Add H2SO4(aq) to a new sample forms a white precipitate Na+ Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) does not form a precipitate Zn2+ Add 2 drops NaOH(aq) forms a white precipitate Add excess NaOH(aq) precipitate dissolves in excess Add 2 drops NH3(aq) to a new sample forms a white precipitate Add excess NH3(aq) precipitate dissolves in excess Al3+ Ba2+ Cu2+ Mg2+ Pb2+ This resource is copyright © Crown 2015 Page 7 of 9 Internal assessment resource Chemistry 2.2B v2 for Achievement Standard 91162 PAGE FOR TEACHER USE Assessment schedule: Chemistry 91162 What’s the Solution? Evidence/Judgements for Achievement Evidence/Judgements for Achievement with Merit The student identifies the majority of ions (4), including the majority of ions which form precipitates (3/6), correctly. The student identifies the majority of ions (4), including the majority of ions which form precipitates (3/6), correctly. The student supports their identification of 4 ions with experimental observations. The student supports their identification of 4 ions with experimental observations. For each of the 4 ions, the student identifies by name or formula all precipitates formed and supports their responses with the evidence required. For each of the 4 ions, the student identifies by name or formula all precipitates formed, justifies their identification of the ions, writes balanced equations for all of the reactions where precipitates are formed, and links all precipitation equations to the observations made during the procedure. For example: The cation in Solution D is Zn2+ When 2 drops dilute of NaOH are added a white precipitate forms. The precipitate is zinc hydroxide / Zn(OH)2. When excess NaOH is added the precipitate dissolves. When 2 drops of NH3 is added a white precipitate forms. The precipitate is zinc hydroxide / Zn(OH)2. When excess NH3 is added the precipitate dissolves. The student supports their responses with the evidence required. The student identifies the majority of ions (6), including the majority of ions which form precipitates (3/6) and the majority of ions that form complex ions (2), correctly. The student supports their identification of 6 ions with experimental observations. For each of the 6 ions, the student identifies by name or formula all precipitates formed, comprehensively justifies their identification of the ions, writes balanced equations for all of the reactions where precipitates and complex ions are formed, and links all precipitation and complex ion equations to the observations made during the procedure. The student supports their responses with the evidence required. For example: The cation in Solution D is Zn2+ When 2 drops dilute of NaOH are added a white precipitate forms. The precipitate is zinc hydroxide / Zn(OH)2: Zn2+(aq) + 2 OH Evidence/Judgements for Achievement with Excellence (aq) Zn(OH)2(s) When excess NaOH is added the precipitate dissolves. When 2 drops of NH3 is added a white precipitate forms. The precipitate is zinc hydroxide / Zn(OH)2: For example: The cation in Solution D is Zn2+ When 2 drops dilute of NaOH are added a white precipitate forms. The precipitate is zinc hydroxide / Zn(OH)2: Zn2+(aq) + 2 OH(aq) Zn(OH)2(s) When excess NaOH is added the precipitate dissolves: Zn(OH)2(s) + 2 OH(aq) [Zn(OH)4]2(aq) Zn2+(aq) + 2 OH(aq) Zn(OH)2(s) When excess NH3 is added the precipitate dissolves. This resource is copyright © Crown 2015 or Zn2+(aq) + 4 OH(aq) [Zn(OH)4]2(aq) Page 8 of 9 Internal assessment resource Chemistry 2.2B v2 for Achievement Standard 91162 PAGE FOR TEACHER USE When 2 drops of NH3 is added a white precipitate forms. The precipitate is zinc hydroxide / Zn(OH)2: Zn2+(aq) + 2 OH(aq) Zn(OH)2(s) When excess NH3 is added the precipitate dissolves: Zn(OH)2(s) + 4 NH3(aq) [Zn(NH3)4]2+(aq) + 2 OH(aq) or Zn2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) [Zn(NH3)4]2+(aq) Final grades will be decided using professional judgement based on a holistic examination of the evidence provided against the criteria in the Achievement Standard. This resource is copyright © Crown 2015 Page 9 of 9