Purposes
advertisement

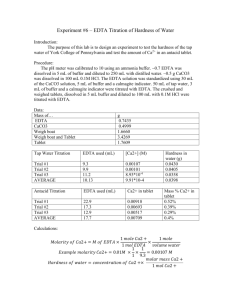
Experiment 21 Complexometric Titration Purposes 1. To learn the method of preparation and standardization of EDTA standard solution 2. To know the basic procession of complexometric titration 3. To grasp the applications of chrome black T or Xylenol orange indicator 4. To learn the applications of complexometry to determine the concentration of metal ions in unknown sample solutions Principle The complexing agent of EDTA or H4Y is the abbreviation of ethylendiaminetetraacetic acid. And the water soluble disodium salt of EDTA (Na2H2Y·2H2O), as a substitute, is widely employed in titrimetric analysis. Since the concentration of EDTA will be changed in the impure distilled water, the EDTA standard solution are usually prepared by indirect preparation and standardized with primary substance in the precisely experiment, thought the disodium EDTA can be refined to a primary standard. The prepared EDTA solution should be stored in polyethene bottles in order to avoid the EDTA react with the traces of metal ions yielded from the surface of glass vessels. To standardize the EDTA, there are some primary standard substance such as purified Zn, Cu, ZnO, Bi, CaCO3, MgCO3, ZnSO4·7H2O ect, and the Zn, ZnO and CaCO3 are usually the applications. In order to reduce the systemic errors, the conditions of determining a sample should be the same as the conditions of standardizing EDTA as possible. If, for example, the unknown ions ,such as Bi3+,Zn2+, Pb2+, Al3+, and so on, are determined, the EDTA solution should be adjusted to pH 5~6, and Xylenol orange used as indicator, then standardized with primary standard of Zn or ZnO. If the Ca2+, Mg2+ ions present in a sample to be determined, the CaCO3 should be utilized as the primary standard, the solution to be adjusted to about pH 10 with NH3- NH4Cl buffer solution, and using Eriochrome black T as indicator. There is, however, no sharp end point could be observed with calcium ions and Eriochrome black T (EBT). And the Mg-EBT in that of the pH region shows sharp wine-red in color compare with blue of the free indicator at the end point. So the MgCO3 can be used as an ideal primary standard substance. Traces of many metals, e.g., Fe3+, Al3+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, ect, will interfere the determination of Ca2+ and Mg2+ or water hardness using Erio. T indicator. Their interfere can be overcome by the addition of a little triethanolamine (masking the Fe3+, Al3+) and Na2S (masking the Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+). 1 The metallic ions, which in the complicated sample or react slowly with EDTA, e.g., Al3+, can be determined by back titration or displaced titration. 1.Determination of the hardness of water Historically, “hardness” was defined in terms of the capacity of a water sample to precipitate soap, an undesirable quality. Soap is precipitated by most cations with multiple charges. In natural waters, however, the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions generally far exceeds that of any other metal ion; thus, hardness has come to mean the total concentration of calcium and magnesium which expressed as c(Ca2+)/mmol·L-1. The determination of hardness is a useful analytical process for measuring the quality of water for household and industrial uses. The importance for the latter is due to the fact that hard water, upon heating, precipitate calcium carbonate, which then clogs boilers and pipes. Water hardness is ordinarily determined by an EDTA titration after the sample has been buffered to a pH of 10, and Eriochrome black T serves as the indicator. To determine the individual Ca2+ or Mg2+, the second sample is adjusted with the addition of NaOH to precipitate Mg(OH)2, then add the Cal-red indicator which only combines with the part of Ca2+ ions to form a red complex .After that, use EDTA standard solution to titrate the Ca2+ of the water sample solution. EDTA will usurp the Ca2+ inos from the complex derived from Ca2+ ions and the cal-red after it combine with all free Ca2+ ions in the solution because it can form a more stable colorless complex with ions than the cal-red. Finally, the color of the solution turn blue with all the free cal-red released from the red complex derived from Ca2+inos and the cla-red at the end point of the titration.Thus the Ca2+ can be determined by titrating with standard solution and the content of Mg2+ may be evaluated by subtracting the amount of Ca2+ from the total hardness of the water. In order to reduce the systemic errors, the MgCO3 be used as primary standard substance for the standardization of EDTA in this experiment. 1.1 Apparatus and Reagents Apparatus: Analytical balance, platform balance, acid buret(25 mL), conical flask(250 mL× 3), transfer pipet(20mL,25mL,100mL), volumetric flask(25 mL,250mL), beaker(150 mL,250mL), reagent bottle (1000 mL),graduated cylinder(5 mL,10 mL, 50 mL),glass rod,polyethene bottle - Reagent: Na2H2Y·2H2O(s,A.R.), 3 mol·L 1HCl, MgCO3(s, primary standand substance), 0.5%Eriochrome black T, pH 10 of NH3-NH4Cl buffer solution, 20%triethanolamine solution, 2%Na2S solution), Calconcarbonxylic acid indicator, NaOH solution(10%),universal pH indicator 1.2 Procedure 1. Preparation of 0.01mol·L-1 EDTA solution 2 Weigh about 1.5 g of Na2H2Y·2H2O with the platform balance,put it into a clean 500 mL beaker, dissolve the solid with distilled water, transfer the solution to a polythene bottle and dilute to about 400 mL. Mix the solution throughout and label the bottle. 2.Standardization of sodium EDTA standard solution Prepare a standard MgCO3 solution as follows. Scale precisely 0.20~0.22 g of primary standard MgCO3 which has been previously dried at 110℃ into a small clean beaker, add 5 drops - of water to moisten the solid and cover with a watch glass. Add 3 mL 3mol·L 1HCl solution dropwise from the mouth of the beaker. After the solid has dissolved, add 50 mL of distilled water (or deionized water) and boil gently for a few minutes to remove CO2. Cool the solution and rinse the surface of watch glass with the distilled water spray from a washing bottle. The distilled water rinsing the watch glass is collected together to the beaker. Transfer it quantitatively to a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilute to the mark, mix the solution throughout. Pipet 20.00 mL MgCO3 standard solution into a 250 mL conical flask, and add 10 mL NH3-NH4Cl buffer solution of pH 10 and 2~3 drops Eriochrome black T indicator. Titrate with EDTA standard solution to the point where the color changes from wine-red to pure blue and no tings of red should remain in the solution. Repeat the titration twice and calculate the concentration of EDTA solution. 20.00 1000 250 . 00 c(EDTA)= M (MgCO 3 ) V (EDTA) m(MgCO 3 ) 3.Determination of water hardness (1) To determine the total hardness - Pipet 50.00mL water sample into a 250mL conical flask, add 1~2 drops 3 mol·L 1HCl solution and boil gently for a few minutes to remove CO2. Cool the solution, then add 5 mL of triethanolamine, 10 mL NH3-NH4Cl buffer solution of pH 10, 10 drops Na2S solution, and 2~3 drops of Eriochrome black T solution. Titrate with EDTA solution until the color changes from wine-red to pure blue. Repeat the titration twice and according to the consumed volumn V1 of EDTA solution to calculate the total hardness of the water sample. Total hardness: c(Ca2+ )= c(EDTA ) V( - 1 EDTA ) ×1000(mmol·L 1) V (water sample ) 1.3 Recording and treating data 3 Table 1 Standardization of sodium EDTA solution Date: ℃ Temperature: Humidity: Experiment No. 1 2 3 m1 (Weighing bottle + Mass of MgCO3)/g m2 (Weighing bottle + Mass of MgCO3)/g m1-m2 (Mass of MgCO3)/g mdetermine (Mass of MgCO3)/g Indicator The change of color at the end point of titration V(MgCO3)/mL V Initial(EDTA)/mL V Final (EDTA)/mL Vconsume(EDTA)/mL c(EDTA)/mol·L-1 c Average (EDTA) /mol·L-1 Relative average deviation/% Table 2 Determination of hardness of water sample Experiment No. Indicator The change of color at the end point of titration V(water sample)/mL 3mol.L-1 Preparation of water sample HCl/drop Boil gently to remove CO2 Triethanolamine /mL NH3-NH4Cl buffer solution/mL Na2S /drop V Initial(EDTA)/mL V Final (EDTA)/mL Vconsume(EDTA)/mL c(Total hardness )/mol·L-1 c Average (Total hardness)/mol·L-1 Relative average deviation/% 4 1 2 3 100.00 100.00 100.00