Western Civilization syllabus
advertisement

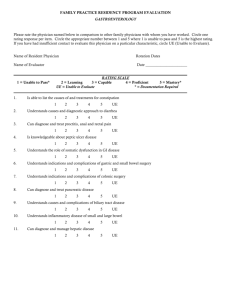
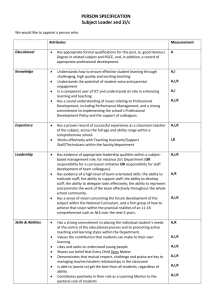
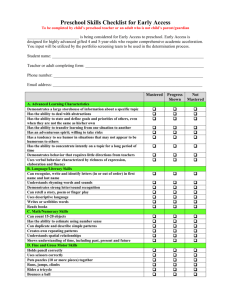
Goals and Objectives of the Western Civilization course Standard 1.0: The students will understand the terminology and concepts basic to the study of history. Students will: 1.1: differentiate between the years B.C. and A.D. 1.2: understand the role point of view and bias plays in the interpretation and reporting of historical events. 1.3: differentiate between primary and secondary sources. 1.4: understand terms basic to historiography (e.g. era, decade, century, etc) National History Standards http://nchs.ucla.edu/standards/worldera5.html Historical Thinking Standards http://nchs.ucla.edu/standards/thinking512_toc.html Contents of Historical Thinking Standards for Grades 5-12 Standard 1: Chronological Thinking A. Distinguish between past, present, and future time. B. Identify the temporal structure of a historical narrative or story. C. Establish temporal order in constructing historical narratives of their own. D. Measure and calculate calendar time. E. Interpret data presented in time lines and create time lines. F. Reconstruct patterns of historical succession and duration; explain historical continuity and change. G. Compare alternative models for periodization. Standard 2 : Historical Comprehension A. Identify the author or source of the historical document or narrative and assess its credibility. B. Reconstruct the literal meaning of a historical passage. C. Identify the central question(s) the historical narrative addresses. D. Differentiate between historical facts and historical interpretations. E. Read historical narratives imaginatively. F. Appreciate historical perspectives. G. Draw upon data in historical maps. H. Utilize visual, mathematical, and quatitative data. Standard 3 : Historical Analysis and Interpretation A. Compare and contrast differing sets of ideas. B. Consider multiple perspectives. C. Analyze cause-and-effect relationships and multiple causation, including the importance of the individual, the influence of RI GSE’s for Civics and Government and Historical Perspectives http://www.ride.ri.gov/Instruction/DOCS/CIVICS/RI_Civics_GSEs_HS-_912__Final_Version.pdf ideas. D. Draw comparisons across eras and regions in order to define enduring issues. E. Distinguish between unsupported expressions of opinion and informed hypotheses grounded in historical evidence. F. Compare competing historical narratives. G. Challenge arguments of historical inevitability. H. Hold interpretations of history as tentative. I. Evaluate major debates among historians. J. Hypothesize the influence of the past. Standard 4 : Historical Research Capabilities A. Formulate historical questions. B. Obtain historical data from a variety of sources. C. Interrogate historical data. D. Identify the gaps in the available records, marshal contextual knowledge and perspectives of the time and place. E. Employ quantitative analysis. F. Support interpretations with historical evidence. Standard 2.0: The students will Era 2 understand the classical traditions of Early Civilizations and the the Aegean and Mediterranean worlds. Emergence of Pastoral Peoples, They will . . . 4000-1000 BCE 2.1: describe the emergence of Greek city-states and the political, social, and legal characteristics of the polis. 2.2: explain the class divisions of Greek society and the social and political roles of major classes including slaves. 2.3: assess the importance of participatory government in Greek city-states for the development of Western political thought and STANDARD 3 The political, social, and cultural consequences of population movements and militarization in Eurasia in the second millennium BCE. Standard 3C The student understands how urban society expanded in the Aegean region in the era of Mycenaean dominance. Era 3 Classical Traditions, Major Religions, and Giant Empires, 1000 BCE-300 CE Contents of Historical Thinking Standards for Grades 5-12 Standard 1: Chronological Thinking Standard 2 : Historical Comprehension Standard 3 : Historical Analysis and Interpretation Standard 4 : Historical Research Capabilities Standard 5 : Historical Issues-Analysis and Decision-Making A. Identify issues and problems in the past. B. Marshal evidence of antecedent circumstances. C. Identify relevant historical antecedents. D. Evaluate alternative courses of action. E. Formulate a position or course of action on an issue. F. Evaluate the implementation of a decision. C&G 1 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of origins, forms, and purposes of government by… a. describing or explaining competing ideas about the purposes and functions of politics and government C&G 1: People create and change structures of power, authority, and governance in order to accomplish common goals. C&G 1 (9-12) –2 Students demonstrate an understanding of sources of authority and use of power, and how they are/can be changed, by… a. identifying how actions of a government affect relationships involving the individual, society and the government (e.g., Homeland Security) institutions. 2.4: compare/contrast the government, culture and values of Athens and Sparta. 2.5: compare/contrast the democracy in Athens with democracy as practiced in the United States. 2.6: explain the contributions of the major philosophers and historians. 2.7: describe the rise of Alexander the Great and compares and contrasts the Hellenistic and Hellenic periods. 2.8: describe the political economic, social intuitions of the Roman Republic. 2.9: analyze the transformation of Rome from republic to empire. 2.10: describe the major phases in the expansion of the empire and assess how imperial rule impacted Rome socially, politically, economically, and culturally. 2.11: evaluate the major legal, artistic, architectural, technological, and literary achievements of the Romans and the influence of Hellenistic culture traditions on Roman Europe. STANDARD 1 Innovation and change from 1000-600 BCD: horses, ships, iron, and monotheistic faith. Standard 1A The student understands state-building, trade, and migrations that led to increasingly complex interrelations among peoples of the Mediterranean basin and Southwest Asia. STANDARD 2 The emergence of Aegean civilization and how interrelations developed among peoples of the eastern Mediterranean and Southwest Asia, 600-200 BCE. Standard 2A The student understands the achievements and limitations of the democratic institutions that developed in Athens and other Aegean citystates. Standard 2B The student understands the major cultural achievements of Greek civilization. Standard 2C The student understands the development of the Persian (Achaemenid) empire and the consequences of its conflicts with the Greeks. Standard 2D The student understands Alexander of Macedon’s conquests and the interregional character of Hellenistic society and culture. STANDARD 3 How major religions and large-scale empires arose in the Mediterranean basin, China, and India, 500 BCE300 CE Standard 3A The student understands the causes and consequences of the unification of the Mediterranean basin under Roman rule. Standard 3B The student understands the emergence of Christianity in the context of the Roman Empire. STANDARD 5 Major global trends from 1000 BCE-300 CE. Standard 5A The student understands major global trends from 1000 BCE to 300 CE. Era 4 b. explaining how political authority is obtained and legitimized c. examining the historical origins of power and how that power has been exercised over time (e.g., divine right, popular sovereignty, social contract, “regime of truth”) C&G 4 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of political systems and political processes by… a. comparing and contrasting U.S. systems of government with others c. analyzing and interpreting sources (print and non-print discourse/media), by distinguishing fact from opinion, and evaluating possible bias/propaganda or conflicting information within or across sources (GSE R-10-8.4) C&G 5 (9-12)-2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the benefits and challenges of an interconnected world by… a. describing the interconnected nature of a contemporary or historical issue C&G 5 (9-12) -3 Students demonstrate an understanding of how the choices we make impact and are impacted by, an interconnected world by… a. predicting outcomes and possible consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action b. identifying and summarizing the intended and unintended consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action 2.12: explain the rise of Christianity in the Roman Empire and its fundamental teachings. 2.13: explain the persecution faced by Christians, Jews, and Druids in the Roman Empire. 2.14: analyze the similarities and differences between Judaism and Christianity. 2.15: explain how relationships between human and the physical environment lead to the formation of places and to a sense of personal and community identity. Expanding Zones of Exchange and Encounter, 300-1000 CE STANDARD 1 Imperial crises and their aftermath, 300-700 CE. Standard 1A The student understands the decline of the Roman empire. Standard 1B The student understands the expansion of Christianity STANDARD 2 Causes and consequences of the rise of Islamic civilization in the 7th-10th centuries. Standard 2A The student understands the emergence of Islam Standard 2C The student understands the consolidation of the Byzantine state in the context of expanding Islamic civilization. 2.16: analyze the causes for the decline of the Roman Empire and the emergence of the new areas of prominence. 2.17: compare/contrast the government, culture and religious beliefs of the Germanic tribes and the Romans Standard 3.0: The student will understand the redefining of societies in a period of intensified hemispheric interaction and. . . 3.1: explain the development of a new civilization in the Western Christendom in the 500 years following the breakup of the Roman Empire. 3.2: describe feudalism and how Era 4 Expanding Zones of Exchange and Encounter, 300-1000 CE STANDARD 4 The search for political, social, and cultural redefinition in Europe, 500-1000 CE. Standard 4A The student understands the foundations of a new civilization in Western Christendom in the 500 years following the breakup of the western Roman Empire. Standard 4B The student understands the coalescence of Contents of Historical Thinking Standards for Grades 5-12 Standard 1: Chronological Thinking Standard 2 : Historical Comprehension Standard 3 : Historical Analysis and Interpretation Standard 4 : Historical Research Capabilities Standard 5 : Historical Issues-Analysis and Decision-Making C&G 1 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of origins, forms, and purposes of government by… a. describing or explaining competing ideas about the purposes and functions of politics and government C&G 1: People create and change structures of power, authority, and governance in order to accomplish common goals. feudal relationships provide a foundation of political, social, and economic order in parts of Europe from the 11th century. 3.3: describe manorialism as a economic system in the 11th and 12th century Europe and analyze the legal, social, and economic position of serfs. political and social order in Europe. STANDARD 7 Major global trends from 300-1000 CE. Standard 7A The student understands major global trends from 300 to 1000 CE. Era 5 Intensified Hemispheric Interactions, 1000-1500 CE Standard 2 – The redefining of European 3.4: explain urban growth in the society and culture, 1000-1300 CE Mediterranean region and northern Europe and analyzes causes for the Standard 2A expansion of manufacturing trade The student understands feudalism and the growth of centralized monarchies and city-states and a money economy in Europe. 3.5: analyze the causes and consequences of the European Crusades in the Holy Land. 3.6: explain the changing political relationship between the Roman Catholic Church and secular states. 3.7: explain the role the Roman Catholic Church played as a religious, social, legal, and economic force in medieval society. 3.8: identify patterns of social change and cultural achievements in Europe’s emerging civilizations. in Europe. Standard 2B The student understands the expansion of Christian Europe after 1000. Standard 2C The student understands the patterns of social change and cultural achievement in Europe’s emerging civilizations. STANDARD 5 Patterns of crisis and recovery in Afro-Eurasia, 1300-1450 Standard 5A The student understands the consequences of Black Death and recurring plague pandemic in the 14th century. Standard 5B The student understands transformations in Europe following the economic and demographic crises of the 14th century. C&G 1 (9-12) –2 Students demonstrate an understanding of sources of authority and use of power, and how they are/can be changed, by… a. identifying how actions of a government affect relationships involving the individual, society and the government (e.g., Homeland Security) b. explaining how political authority is obtained and legitimized c. examining the historical origins of power and how that power has been exercised over time (e.g., divine right, popular sovereignty, social contract, “regime of truth”) C&G 4 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of political systems and political processes by… a. comparing and contrasting U.S. systems of government with others c. analyzing and interpreting sources (print and non-print discourse/media), by distinguishing fact from opinion, and evaluating possible bias/propaganda or conflicting information within or across sources (GSE R-10-8.4) C&G 5 (9-12)-2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the benefits and challenges of an interconnected world by… a. describing the interconnected nature of a contemporary or historical issue C&G 5 (9-12) -3 Students demonstrate an understanding of how the choices we make impact and are impacted by, an interconnected world by… a. predicting outcomes and possible consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action b. identifying and summarizing the intended and unintended consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action Standard 4.0: The student will demonstrate understanding of the Renaissance, Reformation, and Catholic Reformation by. . . 4.1: evaluating the unique conditions that existed in Italy which led to the development of the Italian Renaissance. 4.2: analyzing the social and intellectual significance of the technological innovation of printing with movable type. 4.3 : explaining connections between the Italian Renaissance and the development of humanist ideas in Europe north of the Alps. 4.4 : evaluating major achievements in literature, music, painting, sculpture, architecture in 16th-century Europe. 4.5: explaining discontent among Europeans with the late medieval Church, and analyzing the beliefs and ideas of the leading Protestant reformers. 4.6: explaining the aims and Era 6 The Emergence of the First Global Age, 1450-1770 STANDARD 2 How European society experienced political, economic, and cultural transformations in an age of global intercommunication, 1450-1750 Standard 2B The student understands the Renaissance, Reformation, and Catholic Reformation. Standard 2C The student understands the rising military and bureaucratic power of European states between the 16th and 18th centuries. Standard 2D The student understands how the Scientific Revolution contributed to transformations in European society. Contents of Historical Thinking Standards for Grades 5-12 Standard 1: Chronological Thinking Standard 2 : Historical Comprehension Standard 3 : Historical Analysis and Interpretation Standard 4 : Historical Research Capabilities Standard 5 : Historical Issues-Analysis and Decision-Making C&G 1 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of origins, forms, and purposes of government by… a. describing or explaining competing ideas about the purposes and functions of politics and government C&G 1: People create and change structures of power, authority, and governance in order to accomplish common goals. C&G 1 (9-12) –2 Students demonstrate an understanding of sources of authority and use of power, and how they are/can be changed, by… a. identifying how actions of a government affect relationships involving the individual, society and the government (e.g., Homeland Security) b. explaining how political authority is obtained and legitimized c. examining the historical origins of power and how that power has been exercised over time (e.g., divine right, popular sovereignty, social contract, “regime of truth”) C&G 4 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of political systems and political processes by… a. comparing and contrasting U.S. systems of government with others c. analyzing and interpreting sources (print and non-print discourse/media), by distinguishing fact from opinion, and evaluating possible bias/propaganda or conflicting information within or across sources (GSE R-10-8.4) policies of the Catholic Reformation, and assessing the impact of religious reforms and divisions on European cultural values, family life, and relations between men and women. 4.7: analyzing causes of religious wars in 16th and 17th century Europe, and their effects on the establishment of religious pluralism. C&G 5 (9-12)-2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the benefits and challenges of an interconnected world by… a. describing the interconnected nature of a contemporary or historical issue STANDARD 5.0: The student understands global expansion and encounter 1450-1750 and… 5.1: traces oceanic inter-linking of all major regions of the world from 1450-1600 led to global transformations. 5.2: explains how European society experienced political, Era 6 The Emergence of the First Global Age, 1450-1770 STANDARD 1 How the transoceanic interlinking of all major regions of the world from 1450-1600 led to global transformations. Standard 1A The student understands the origins and consequences of European overseas expansion in the 15th and 16th centuries. Standard 1B Contents of Historical Thinking Standards for Grades 5-12 Standard 1: Chronological Thinking Standard 2 : Historical Comprehension Standard 3 : Historical Analysis and Interpretation Standard 4 : Historical Research Capabilities Standard 5 : Historical Issues-Analysis and Decision-Making C&G 5 (9-12) -3 Students demonstrate an understanding of how the choices we make impact and are impacted by, an interconnected world by… a. predicting outcomes and possible consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action b. identifying and summarizing the intended and unintended consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action C&G 1 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of origins, forms, and purposes of government by… a. describing or explaining competing ideas about the purposes and functions of politics and government C&G 1: People create and change structures of power, authority, and governance in order to economic and cultural transformations in an age of global intercommunication. 5.3: identifies the economic, political and cultural interrelations among peoples of Africa, Europe, and the Americas. 5.4: analyzes the major shifts to capitalistic enterprises and commercialization. 5.5: evaluates the impact of human migration on physical and human systems. 5.6: explains how changing perception of places and regions reflect cultural change The student understands the encounters between Europeans and peoples of Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and the Americas in the late 15th and early 16th centuries. STANDARD 2 How European society experienced political, economic, and cultural transformations in an age of global intercommunication, 1450-1750. Standard 2A The student understands demographic, economic, and social trends in Europe STANDARD 4 Economic, political, and cultural interrelations among peoples of Africa, Europe, and the Americas, 1500-1750. Standard 4A The student understands how states and peoples of European descent became dominant in the Americas between the 16th and 18th centuries Standard 4B The student understands the origins and consequences of the trans-Atlantic African slave trade. STANDARD 6 The expansion of states and civilizations in the Americas, 1000-1500. Standard 6A The student understands the development of complex societies and states in North America and Mesoamerica. STANDARD 7 Major global trends from 1000-1500 CE. Standard 7A The student understands major global trends from 1000 to 1500 CE accomplish common goals. C&G 1 (9-12) –2 Students demonstrate an understanding of sources of authority and use of power, and how they are/can be changed, by… a. identifying how actions of a government affect relationships involving the individual, society and the government (e.g., Homeland Security) b. explaining how political authority is obtained and legitimized c. examining the historical origins of power and how that power has been exercised over time (e.g., divine right, popular sovereignty, social contract, “regime of truth”) C&G 4 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of political systems and political processes by… a. comparing and contrasting U.S. systems of government with others c. analyzing and interpreting sources (print and non-print discourse/media), by distinguishing fact from opinion, and evaluating possible bias/propaganda or conflicting information within or across sources (GSE R-10-8.4) C&G 5 (9-12)-2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the benefits and challenges of an interconnected world by… a. describing the interconnected nature of a contemporary or historical issue C&G 5 (9-12) -3 Students demonstrate an understanding of how the choices we make impact and are impacted by, an interconnected world by… a. predicting outcomes and possible consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action b. identifying and summarizing the intended and unintended consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action STANDARD 6.0: The student understands the causes and consequences of revolutions and patterns of nationalism and state building in the 18th and 19th centuries and … 6.1: defines the “isms”— including industrialization, capitalism, imperialism, colonization and nationalism within the context of their historical period. 6.2: evaluates different methods of allocating goods and services by comparing and contrasting different economic systems. 6.3: analyzes the causes and consequences of political revolutions. 6.4: explains the causes of consequences of agricultural and industrial revolutions. 6.5: explains the contributions of technological, scientific, and intellectual achievements to social and cultural change. Era 6 The Emergence of the First Global Age, 1450-1770 STANDARD 2 How European society experienced political, economic, and cultural transformations in an age of global intercommunication, 1450-1750. Standard 2E The student understands the significance of the Enlightenment in European and world history. Era 7 An Age of Revolutions, 1750-1914 STANDARD 1 The causes and consequences of political revolutions in the late 18th and early 19th centuries Standard 1A The student understands how the French Revolution contributed to transformations in Europe and the world. Contents of Historical Thinking Standards for Grades 5-12 Standard 1: Chronological Thinking Standard 2 : Historical Comprehension Standard 3 : Historical Analysis and Interpretation Standard 4 : Historical Research Capabilities Standard 5 : Historical Issues-Analysis and Decision-Making C&G 1 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of origins, forms, and purposes of government by… a. describing or explaining competing ideas about the purposes and functions of politics and government C&G 1: People create and change structures of power, authority, and governance in order to accomplish common goals. C&G 1 (9-12) –2 Students demonstrate an understanding of sources of authority and use of power, and how they are/can be changed, by… a. identifying how actions of a government affect relationships involving the individual, society and the government (e.g., Homeland Security) b. explaining how political authority is obtained and legitimized c. examining the historical origins of power and how that power has been exercised over time (e.g., divine right, popular sovereignty, social contract, “regime of truth”) C&G 4 (9-12) –1 Students demonstrate an understanding of 6.6: describes the causes of modern nationalism on European politics and society. 6.7: assesses the patterns of global change in the era of Western military and economic domination. 6.8: analyzes the causes and responses to European and American expansion. 6.9: explains the relationship between resources and the exploration, colonization, and settlement of different regions of the world and evaluate the subsequent policy decisions regarding the use of resources. 6.10: evaluates the impact of the entrepreneurial spirit of the development of industrialized nations political systems and political processes by… a. comparing and contrasting U.S. systems of government with others c. analyzing and interpreting sources (print and non-print discourse/media), by distinguishing fact from opinion, and evaluating possible bias/propaganda or conflicting information within or across sources (GSE R-10-8.4) C&G 5 (9-12)-2 Students demonstrate an understanding of the benefits and challenges of an interconnected world by… a. describing the interconnected nature of a contemporary or historical issue C&G 5 (9-12) -3 Students demonstrate an understanding of how the choices we make impact and are impacted by, an interconnected world by… a. predicting outcomes and possible consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action b. identifying and summarizing the intended and unintended consequences of a conflict, event, or course of action http://www.ride.ri.gov/Instruction/DOCS/CI VICS/RI_Civics_GSEs_K-12_Final_Version.doc