THE SPEED OF REACTIONS
advertisement

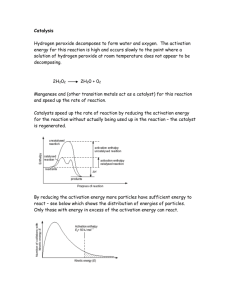
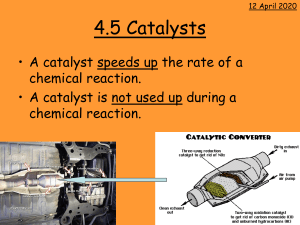
THE SPEED OF REACTIONS There have been several massive explosions in flour mills when flour dust has caught fire. These occur because the dust burns very quickly. An explosion is a very fast chemical reaction. Other reactions are much slower. For example, copper domes on the roofs of buildings will react with the air and turn green, but it can take many years for this to happen. The speed of a reaction is very important. In industry, chemical engineers need to know how long it will take for substances to react to make a product. Chemists have done a lot of work studying what makes a reaction fast or slow. All chemical reactions produce new substances. The speed of a reaction can be found by measuring how fast a new substance is produced. The reaction between acid and marble chips is a useful one to investigate. When marble chips are added to dilute acid in a flask, carbon dioxide is produced. As the reaction goes on, the flask becomes lighter because the carbon dioxide escapes. The speed of the reaction can be measured by putting the flask on the balance and measuring the loss of mass at regular intervals. Once the results have been obtained, they can be plotted on a graph. If you put time on the horizontal axis, the slope of the graph tells you how fast the reaction is at different times. Part A: this is the steepest part of the curve, which means that the reaction is fastest here. Lots of carbon dioxide is given off each second. Part B: the slope is less steep here; the reaction is slowing down. Part C: here the grapf has levelled off. This means that the reaction has stopped. No more carbon dioxide is being produced. Time/ seconds 0 10 20 30 40 50 Mass of carbon dioxide produced / grams 0.0 1.0 1.8 2.4 2.8 3.0 SPEEDING UP REACTIONS Imagine you are an athlete and you want to be able to run faster. You decide to change your diet, buy new running shoes and try out a weight-training programme. After doing all this, you find that there has been an improvement and you do run faster. However, because you changed all three 1 things at the same time, you do not know which of them actually helped you to run faster. The only way to find out is to change one thing at a time and measure any increase in your speed. The same problems can be found in chemistry. If you want to find out what makes a reaction go faster then you must change only one thing at a time. The things that can be changed in a chemical reaction are called variables. slow reactions large particles low concentrations low temperatures fast reactions small particles high concentrations high temperatures CATALYSTS There is a way to speed up a reaction without increasing the temperature or the concentration of the reactants. That is, by adding a substance called a catalyst. The picture shows the effects of adding manganese dioxide to hydrogen peroxide solution. Hydrogen peroxide solution is a liquid which decomposes very slowly to give oxygen and water, as shown in the equation: hydrogen peroxide → oxygen + water decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Normally this reaction is so slow that you cannot see any signs of it taking place. But when manganese dioxide is added, bubbles of oxygen are produced very quickly. We can say that manganese dioxide is a catalyst for the Chemist have discovered many different catalysts. However, all catalysts speed up some reactions are not used up during a reactiom. catalysts used in industry for making iron platinum vanadium oxide ammonia nitric acid sulphuric acid Catalysts are used in industry because they can speed up reactions. In a factory, costs are reduced by making products more quickly. Catalysts also let some reactions take place at lower temperatures. CATALYSTS AND THE ENVIRONMENT Catalytic converter is a device that fits onto the exhausts of cars and helps to break down harmful oxides of nitrogen into substances that do less damage to the environment. The catalyst contains metals such as platinum. 2