Series and Parallel Circuits
advertisement

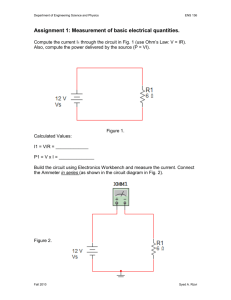
Series and Parallel Circuits Pre-Questions 1. What is an electric circuit? 2. What items are necessary to create an electric circuit? 3. How can you determine if a schematic shows a parallel or series circuit? Procedure 1. Go to http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=Circuit_Construction_Kit_DC_Only 2. Click “Run now.” Assignment #1 – One Light Bulb in SERIES CIRCUIT 1. Build this circuit: What do the blue dots represent? From which end of the batteries are they flowing? 2. Select the “Voltmeter” tool from the right side and connect it to your circuit as shown below. What does the voltmeter read? (Use proper units) Take one of the batteries away happens to the light bulb? What 3. Now, use the “Non-contact to points around the circuit. What do you notice? and connect the circuit. What happens to the voltmeter reading? Ammeter” measure the current at various Assignment #2 – Testing SERIES CIRCUITS 1. Draw a schematic for a series circuit with three batteries, one switch, and two lights. 2. Build this circuit in the simulator and complete the table Voltage across the batteries Voltage across light one Voltage across light two Current after batteries Current after light two Current after light one 3. Add a resistor after the second light. What happens to the brightness of the light? Complete the table. Voltage across the Voltage across light Voltage across light Voltage across batteries one two resistor Current after batteries Current after light one Current after light two Current after resistor 4. Remove one battery and connect the circuit. What happens to the brightness of the light? Complete the table. Voltage across the Voltage across light Voltage across light Voltage across batteries one two resistor Current after batteries Current after light one Current after light two Current after resistor 5. Take out three different wires from the circuit, one at a time and replacing it. What happens to the lights when wires are removed? Assignment # 3 – Testing PARALLEL CIRCUITS 1. Draw a schematic for a parallel circuit with one batteries, one switch, and two lights. 2. Build this circuit in the simulator and complete the table Voltage across the batteries Voltage across light one Voltage across light two Current after batteries Current after light two Current after light one 3. Add a resistor in a third parallel circuit. What happens to the brightness of the light? Complete the table. Voltage across the Voltage across light Voltage across light Voltage across batteries one two resistor Current after batteries Current after light one Current after light two Current after resistor 4. Add one battery and connect the circuit. What happens to the brightness of the light? Complete the table. Voltage across the Voltage across light Voltage across light Voltage across batteries one two resistor Current after batteries Current after light one Current after light two Current after resistor 5. Take out three different wires from the circuit, one at a time and replacing it. What happens to the lights when wires are removed? 6. Draw a schematic for a parallel circuit with two batteries and three lights each controlled by its own switch. 7. Build this circuit in the simulator and complete the table Voltage across the Voltage across light Voltage across light batteries one two Current after batteries Current after light one Current after light two Voltage across light three Current after light three Assignment #4 – Reflection Questions: 1. Using the tables from series circuits – how does adding a resistor impact the voltage throughout the circuit? Why (use Ohm’s Law to explain)? 2. Using the tables from series circuits – how does adding a resistor impact the current throughout the circuit? Why? 3. Using the tables from parallel circuits – how does adding a resistor impact the voltage throughout the circuit? Why? 4. Using the tables from series circuits – how does adding a resistor impact the current throughout the circuit? Why? 5. How does the type of circuit affect the brightness of two light bulbs? 6. When is a series circuit beneficial? Give an example of a series circuit that you are familiar with. 7. When is a parallel circuit beneficial? Give an example of a parallel circuit that you are familiar with.