ice cloudy
advertisement
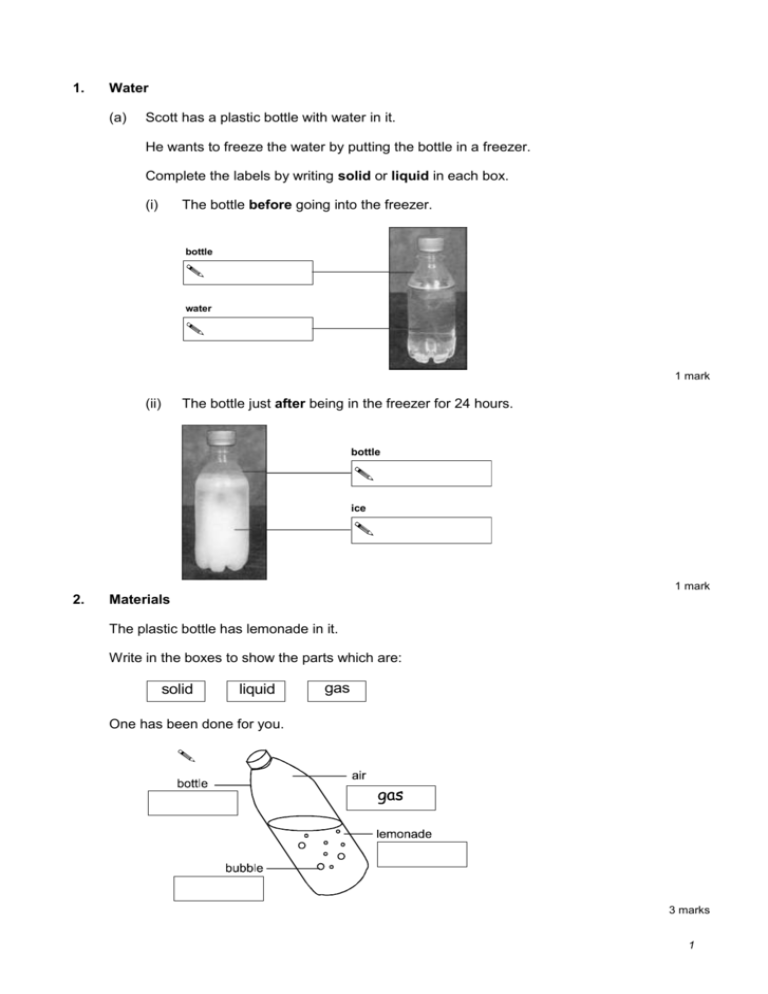
1. Water (a) Scott has a plastic bottle with water in it. He wants to freeze the water by putting the bottle in a freezer. Complete the labels by writing solid or liquid in each box. (i) The bottle before going into the freezer. bottle water 1 mark (ii) The bottle just after being in the freezer for 24 hours. bottle ice 1 mark 2. Materials The plastic bottle has lemonade in it. Write in the boxes to show the parts which are: solid liquid gas One has been done for you. 3 marks 1 3. Materials Some materials melt when they are warmed. Some materials burn when they are heated in a flame. Some materials do not change when they are warmed. Write the name of each material in the correct box. Include all the materials. Use each name only ONCE. Materials which melt when warmed. Materials which burn when heated in a flame. Materials which do not change when warmed. 7 marks 4. Materials Solids, liquids and gases have different properties. The chart below shows some of these properties. Complete the table by ticking to show the properties of solids, liquids and gases. The first row has been done for you. Some rows may need more than one tick. property solid liquid gas keeps its own shape flows easily through a pipe can make rigid or stiff structures can be squashed into a much smaller volume takes the shape of the container into which it is put 4 marks 2 5. Mixing materials Seema and Alan are mixing materials. They put different materials in four clear plastic bags. They tie the top of each bag. They watch what happens and record their observations. Mixture Observations Bag A: Brown sugar and water. Water turns brown and cannot see the sugar after a while. Bag B: Oil and water. Oil floats on top of the water. Bag C: Bicarbonate of soda and vinegar. Lots of fizzing. It looks frothy. Bag puffs up. Bag D: Bicarbonate of soda and oil. Bicarbonate goes in a lump at the bottom. (a) Write the names of the THREE liquids that the children used. (i) ............................................... (ii) ............................................... (iii) ............................................... 1 mark (b) Look at the table. In one bag dissolving was the only change. In which bag was dissolving the only change? ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark (c) The mixture in Bag C fizzed and the bag puffed up. Why did Bag C puff up? ...................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................ 1 mark 3 (d) Three of the mixtures can be separated to get the starting materials back again. One of the mixtures cannot be separated. Which bag has a mixture that cannot be separated? .......................................................... 1 mark 6. Solids and Liquids (a) Helen and Amy put an ice lolly in a dry glass jar. After 105 minutes they saw that the ice lolly had turned to liquid. What is the name of the process when a solid turns into a liquid? ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark (b) They saw drops of liquid forming on the outside of the jar. What is the name of this liquid? Tick ONE box. ice lolly steam water juice mist 1 mark (c) What is the name of the process which causes this liquid to form on the outside of the jar? ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark (d) Where did the liquid on the outside of the jar come from? ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark (e) A similar ice lolly was placed in a similar glass jar. They wrapped this second jar in a woollen scarf. 4 What would be the effect of the scarf on the ice lolly in the second jar? 1 mark 110 Tick ONE box. 100 The ice lolly in the second jar would: 90 80 turn to liquid more quickly 70 turn to liquid in the same time 60 turn to liquid more slowly 50 ºC 40 not turn to liquid at all 30 20 (f) Draw a line on the drawing of the thermometer to show the level of the liquid when the temperature is 45ºC. 10 0 liquid 1 mark 7. Toffee (a) Adrian and his dad are cooking toffee. The pictures below show how they make the toffee. 1. Put a metal tray into a freezer for an hour. 2. Stir sugar into some cold water. 3 Heat the mixture until it turns golden brown. 4 Pour the mixture into the cold tray from the freezer What happens to sugar when it is put into cold water and stirred? ..............................................................................................................…… 1 mark (b) What happens to some of the water when the mixture is heated? ..............................................................................................................…… 1 mark 5 (c) The mixture becomes very hot. Tick ONE box to show what Adrian should measure to find out how hot the mixture is. weight temperature volume time 1 mark (d) Adrian carefully stirs the hot mixture with a wooden spoon. The handle of the wooden spoon stays cool. Tick ONE box to explain why the handle of the wooden spoon stays cool. Wood cannot get hot. Wood is a poor conductor of heat. Wood is a hard material. Wood is a poor insulator of heat. 1 mark (e) Adrian takes the tray out of the freezer. He pours the runny mixture into the metal tray. He leaves the tray on a table for 10 minutes. The mixture becomes solid. Why does the runny mixture become solid? ..............................................................................................................…… 1 mark 8. Water Cycle (a) Some children are learning about the water cycle. The different forms of water are solid, liquid and gas. solid Put ONE tick in each row of the table below to show whether each one is solid, liquid or gas. One has been done for you. form of water liquid gas rain water vapour snow (3 marks) ice 6 (b) Sanjay says, ‘The water vapour rises from the land and sea into the air. It is part of the water cycle.’ The statements below describe a water cycle. Write the numbers to show the correct order, 1 to 5. Write ONE number in each box. The first one has been done for you. Water flows back to the sea in rivers. Clouds cool and water droplets form. Water vapour rises from the sea into the air. 1 Water vapour cools and turns back into water which forms clouds in the sky. Droplets of water fall back to the ground as rain. 1 mark 9. Breathing (a) Nick breathes onto a mirror. mirror It becomes misty. Choose one reason that helps to explain why the mirror becomes misty when he breathes on it. Tick ONE box. The mirror is hotter than his breath. The mirror is colder than his breath. The mirror is the same temperature as his breath. The mirror is dry. 1 mark (b) Name the process that makes the mist appear on the mirror. ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark 7 (c) After a few moments, the mist has gone. Nick has not wiped the mirror. What has happened to the mist to make the mirror look clear again? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark 10. Measuring temperature (a) Some children want to find out which material keeps a drink hottest. They fill three cups with hot water. metal cup polystyrene cup plastic cup They measure the temperature of the water. It is the same in each cup. What equipment do they use to measure the temperature of the water? ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark (b) They leave all the cups in the same place to cool. What else must the children keep the same for their test to be fair? Tick TWO boxes. The size of each cup. The material used to make the cups. The final temperature of the water. The volume of hot water in each cup. 1 mark (c) They measure the temperature again after 20 minutes. In their test, the polystyrene cup keeps the water hottest. Write metal, polystyrene and plastic in the correct order in the boxes below, to show how well each insulates heat. Good insulator of heat Poor insulator of heat 1 mark 8 (d) The children want to record their results on a graph. Which graph would best show the results at the end of their test? Tick ONE box. Starting temperature (°C) Temperature after 20 minutes (°C) metal polystyrene plastic metal polystyrene plastic Material Material Time cups were left to cool (minutes) Time taken to reach 25°C (minutes) metal polystyrene plastic metal polystyrene plastic Material Material 1 mark 11. Ice lollies (a) Some children are making ice lollies. The children cool the liquid. It changes into ice. Before cooling: After cooling: solid liquid Name the process that takes place when a liquid changes to a solid. ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark (b) Which TWO statements below show that an ice lolly is a solid? Tick TWO boxes. It has a fixed shape. It is cold. It is slippery. It is cloudy. It can’t be poured. 1 mark 9 (c) The children make ice lollies of different sizes. They time how long the lollies take to melt. Here are their results. Volume of lolly (cm3) Time taken to melt (minutes) 30 200 40 230 50 255 60 275 70 295 Describe the link between the volume of the lolly and the time it takes to melt. ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 2 marks 12. Citric Acid and Bicarbonate of Soda (a) Class 6B have these materials. Citric acid powder Bicarbonate of soda powder Water Tick ONE box in each row to show whether each material is a solid, a liquid or a gas. Material Solid Liquid Gas Citric acid powder Bicarbonate of soda powder Water 2 marks (b) The teacher mixes citric acid powder with water. The powder dissolves. Explain fully how the children could separate the mixture to get the citric acid powder back. ...................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................... 2 marks 10 13. Materials Drinking water can be made from salt solution. (a) To do this you would use heating to: ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark (b) Then you would use cooling to: ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... 1 mark 11