Ecology questions
advertisement
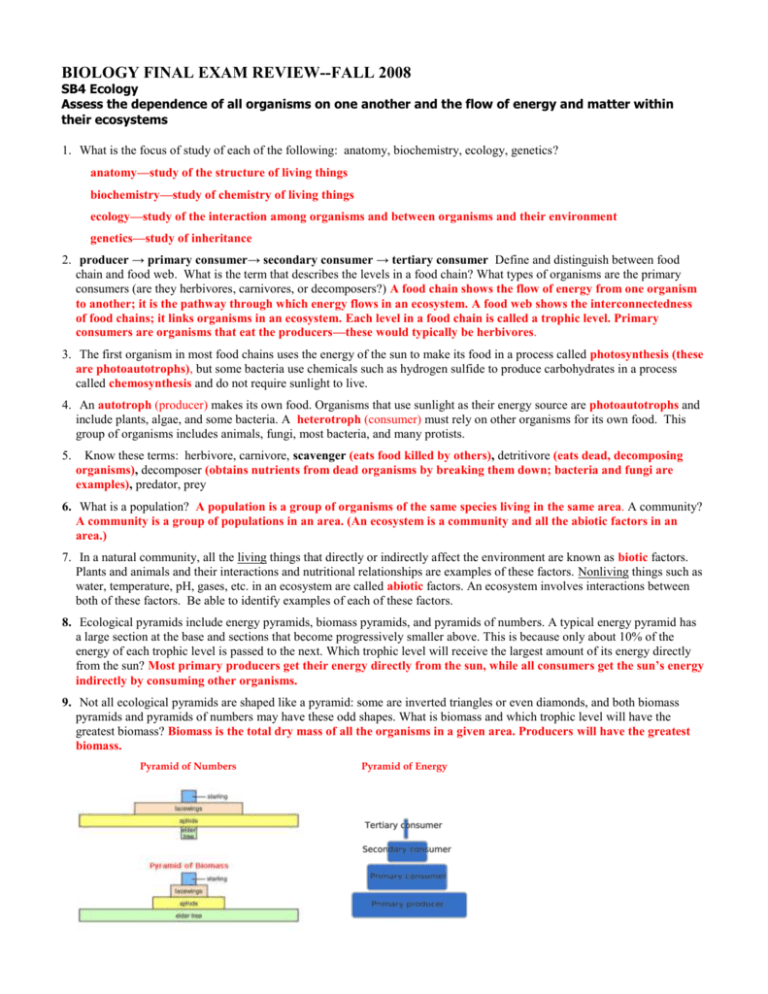
BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW--FALL 2008 SB4 Ecology Assess the dependence of all organisms on one another and the flow of energy and matter within their ecosystems 1. What is the focus of study of each of the following: anatomy, biochemistry, ecology, genetics? anatomy—study of the structure of living things biochemistry—study of chemistry of living things ecology—study of the interaction among organisms and between organisms and their environment genetics—study of inheritance 2. producer → primary consumer→ secondary consumer → tertiary consumer Define and distinguish between food chain and food web. What is the term that describes the levels in a food chain? What types of organisms are the primary consumers (are they herbivores, carnivores, or decomposers?) A food chain shows the flow of energy from one organism to another; it is the pathway through which energy flows in an ecosystem. A food web shows the interconnectedness of food chains; it links organisms in an ecosystem. Each level in a food chain is called a trophic level. Primary consumers are organisms that eat the producers—these would typically be herbivores. 3. The first organism in most food chains uses the energy of the sun to make its food in a process called photosynthesis (these are photoautotrophs), but some bacteria use chemicals such as hydrogen sulfide to produce carbohydrates in a process called chemosynthesis and do not require sunlight to live. 4. An autotroph (producer) makes its own food. Organisms that use sunlight as their energy source are photoautotrophs and include plants, algae, and some bacteria. A heterotroph (consumer) must rely on other organisms for its own food. This group of organisms includes animals, fungi, most bacteria, and many protists. 5. Know these terms: herbivore, carnivore, scavenger (eats food killed by others), detritivore (eats dead, decomposing organisms), decomposer (obtains nutrients from dead organisms by breaking them down; bacteria and fungi are examples), predator, prey 6. What is a population? A population is a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area. A community? A community is a group of populations in an area. (An ecosystem is a community and all the abiotic factors in an area.) 7. In a natural community, all the living things that directly or indirectly affect the environment are known as biotic factors. Plants and animals and their interactions and nutritional relationships are examples of these factors. Nonliving things such as water, temperature, pH, gases, etc. in an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. An ecosystem involves interactions between both of these factors. Be able to identify examples of each of these factors. 8. Ecological pyramids include energy pyramids, biomass pyramids, and pyramids of numbers. A typical energy pyramid has a large section at the base and sections that become progressively smaller above. This is because only about 10% of the energy of each trophic level is passed to the next. Which trophic level will receive the largest amount of its energy directly from the sun? Most primary producers get their energy directly from the sun, while all consumers get the sun’s energy indirectly by consuming other organisms. 9. Not all ecological pyramids are shaped like a pyramid: some are inverted triangles or even diamonds, and both biomass pyramids and pyramids of numbers may have these odd shapes. What is biomass and which trophic level will have the greatest biomass? Biomass is the total dry mass of all the organisms in a given area. Producers will have the greatest biomass. Pyramid of Numbers Pyramid of Energy 10. The term biodiversity refers to the sum total of the variety of organisms in the biosphere. 11. fox Identify the primary consumers in the diagram by drawing a circle around them. snake Identify the secondary consumers by drawing a rectangle around them. frog insects Oak tree Identify the tertiary consumers by drawing a triangle around them. The snake and the fox are both secondary and tertiary consumers. mice grass rabbit lettuce In the diagram to the left, which organism is classified as both a primary and a secondary consumer? The mouse is a primary consumer because it eats grass, but it is also a secondary consumer because it eats insects that ate producers. Which three organisms are competing for the same food source? The insects, mice, and rabbits all compete for the grass. 10. The relationship between two species that need the same resources for survival is called competition. One species will be better at obtaining the resources, resulting in a decline in the number of individuals in the other population. 11. Distinguish between these relationships: symbiosis—a long-term relationship between two species, commensalism—one species benefits from the relationship while the other species is neither helped, nor harmed, mutualism—both species benefit from the relationship, parasitism—one species benefits and the other species is harmed. 12. Define niche—the unique position occupied by a species in an ecosystem; its role or job in the ecosystem; what it eats, where it eats, where it nests, when it reproduces, when it feeds, etc. 13. Ecological succession describes the predictable change in species in an area over time. Which type of succession begins on bare rock? Primary succession begins on bare rock, such as that produced by a lava flow or exposed by a retreating glacier. Which type of succession begins where soil already exists? Secondary succession occurs where soil already exists. It may occur after a natural disaster such as a forest fire or flood or after a farmer abandons a plowed field. 14. What are pioneer organisms? Pioneer organisms, or pioneer species, are the first organisms to inhabit an area. What is a climax community? A climax community is a community that has undergone ecological succession and is generally stable, with little change 15. In which biome would mostly deciduous trees such as oak, hickory, and maple trees be found? Deciduous trees are typical of the Temperate Deciduous Forest, sometimes simply called the Temperate Forest. Coniferous trees may also be found in the temperate forests. Some deciduous trees are also found in the Taiga, but the taiga is predominantly characterized by evergreen trees such as pines and firs. 16. Which biome is characterized by very low temperatures, little precipitation, and permafrost? Brrrrr. The tundra. 17. What characteristic animals would be found in the biome that has cold to moderate winters, warm summers, fertile soils, and is home to a variety of vegetation, such as coniferous trees, broadleaf deciduous trees, flowering shrubs, and ferns? This describes the temperate deciduous forest, and typical animals include bears, wolves, whitetailed deer, foxes, raccoons and squirrels. 18. Which biome do we live in? Georgia is located in the temperate deciduous forest. 19. Which biome has the greatest biological diversity? The tropical rainforests have the greatest biological diversity. 20. Lakes and ponds are the most common standing-water ecosystems; while rivers and streams make up flowingwater ecosystems. 21. What kind of water is found in an estuary? Estuaries are found where a river flows into the ocean. The water in an estuary is not fresh because it contains some salt, but it is not as salty as ocean water. The salt concentration may vary with the tides. 26. Population size generally increases as long as resources are plentiful and the birth rate exceeds the death rate. As resources in a population become less available, population growth slows and levels out as indicated in the graph. What is the term that describes the maximum number of individuals that an ecosystem can sustain? carrying capacity carrying capacity The number of organisms that enter (immigration) or leave (emigration) a population also affects the size of a population. 27. What two factors allow a population to increase in size? immigration and birth rate Decrease? emigration and death rate 28. Label the graphs as representing exponential or logistic growth logistic exponential 29. Name three renewable resources. Wind energy and solar energy are renewable resources, as are many agricultural products. Name an important resource that is nonrenewable. Oil and coal are nonrenewable resources. 30. Study the carbon cycle. In what form is carbon found in the atmosphere? (hint: plants use this gas for photosynthesis) Carbon is found as carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. What processes release carbon into the atmosphere? [hints: (1) all organisms need to be able to use the energy from their food (2) human actions are responsible for much of the carbon that is added to the atmosphere] Carbon dioxide is naturally released into the atmosphere by cellular respiration and volcanic activity. Excess amounts of carbon dioxide are also released by the burning of fossil fuels 31. What is the term for the natural phenomenon that maintains Earth’s temperature range when certain gases reflect heat back to the Earth’s surface? The greenhouse effect is the natural phenomenon that helps maintain Earth’s temperature. 32. What is the term for the increase in Earth's average temperature caused by the buildup of carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere? Global warming occurs when excess greenhouse gases accumulate in the atmosphere and reflect additional heat back to the earth. What can we do to slow the buildup of CO2 in the atmosphere? Since burning fossil fuels adds a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, the development and use of alternative energy sources would slow the buildup of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 33. Power plants that burn coal with a high sulfur content have a negative impact on the environment, including damage to forests and aquatic ecosystems. What environmental problem is caused by these coal-burning power plants? The sulfur in the coal reacts with water vapor in the atmosphere, producing acid rain. Acid rain negatively affects forest and freshwater ecosystems. 34. Which animal has modified ecosystems more than any other animal and has had the greatest negative impact on world ecosystems? Humans must take the blame for the greatest negative impact on world ecosystems. 35. One of the greatest threats today to biological diversity is the destruction of the places that organisms live. What is the term that describes the place where an organism lives? The place where an organism lives is its habitat. 36. Define endangered species. An endangered species is a species that is on the brink of extinction—the population of these species has shrunk to levels that make it difficult to sustain the species. 37. What chemical that is released into the atmosphere by human actions is the major cause of ozone depletion? Chlorfluorocarbons, or CFCs, are the major cause of ozone depletion. 38. The water cycle includes several steps including the uptake of water through the roots of plants and the release of water vapor to the atmosphere by plants. What is the name of the process by which plants release water vapor to the atmosphere? Plants release water vapor to the atmosphere by the process of transpiration, which is evaporation through the leaves of the plants. Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation, Runoff, etc. are all a part of the water cycle, but plants are an essential part of the water cycle through uptake of water by the roots and transpiration. SB1c Macromolecules-FINAL EXAM REVIEW Identify the function of the four major macromolecules 1. What element is found in ALL organic compounds? CARBON 2. What are the 4 major macromolecules found in living things? CARBOHYDRATES, PROTEINS, NUCLEIC ACIDS 3. Which type of organic compound is produced during photosynthesis and is the main source of energy for living things? CARBOHYDRATES What are the monomers (subunits) of these compounds called? SACCHARIDES 4. Cellulose, sugar, starch, glycogen and chitin are examples of which type of macromolecule? CARBOHYDRATES 5. What type of organism contains cellulose in its cell walls? PLANTS (Fungi contain chitin in their cell walls) 6. Like other macromolecules, proteins are composed of monomers. What are the monomers of proteins called? AMINO ACIDS 7. Proteins perform a variety of functions in a cell. The function of a special group of proteins is to speed up the chemical reactions of metabolism. What are proteins that do this called? ENZYMES ARE THE PROTEINS THAT SPEED UP CHEMICAL REACTIONS. Other proteins may control the rate of chemical reactions, regulate cell processes, build tissues such as bone and muscle, transport materials, or fight disease. 8. There are two types of nucleic acids. What are the 2 types of nucleic acids, and what is the function of each type? DNA— STORES HEREDITARY INFORMATION, CONTAINS CODED INSTRUCTIONS FOR MAKING PROTEINS RNA—IS USED TO ACTUALLY MAKE THE PROTEINS; 3 TYPES OF RNA—mRNA, tRNA, rRNA 9. What are the monomers of nucleic acids? DNA IS A DOUBLE-STRANDED, HELICAL MOLECULE COMPOSED OF NUCLEOTIDES. RNA IS A SINGLE-STRANDED MOLECULE WHICH CAN HAVE SEVERAL FORMS, BUT WHICH IS ALSO COMPOSED OF NUCLEOTIDES 10. Oils, fats, and steroids do not dissolve in water. To which group of macromolecules do they belong? OILS, FATS, AND STEROIDS ARE ALL TYPES OF LIPIDS. LIPIDS FUNCTION IN ENERGY STORAGE, AS PARTS OF MEMBRANES, AND AS WATERPROOF COVERINGS. THEY DO NOT DISSOLVE IN WATER. MOST CONTAIN FATTY ACIDS, WHICH HAVE A POLAR, HYDROPHILIC HEAD AND NON-POLAR, HYDROPHOBIC TAILS. 11. Review the structure of the plasma membrane. What type of organic molecule found in plasma membranes forms the bilayer? THE BILAYER IS FORMED FROM PHOSPHOLIPIDS. What type of organic molecule found in plasma membranes acts as channels and pumps to move substances across the membrane? PROTEINS ACT AS CHANNELS AND PUMPS TO MOVE SUBSTANCES ACROSS THE MEMBRANE. 12. Carbohydrates and lipids both serve as a source of energy in living things. Which of these macromolecules releases more energy when metabolized? LIPIDS STORE MORE ENERGY THAN THE OTHER TYPES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES. SB1d Water Explain the Impact of Water on Life Processes 1. What is diffusion? Diffusion is the random movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. Is energy required in this process? No cellular energy is required for this process. 2. What is osmosis? Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Is energy required in this process? Since this is a form of diffusion, NO cellular energy is required for this process. 3. The large ovals in the diagram below represent cells in a solution. The hexagons represent dissolved solutes. The solutes cannot cross the cell membrane. solution A solution B solution C Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Identify each solution as hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic. Indicate the direction in which water will move across the membrane in each diagram and tell whether the cell will swell, shrink, or stay the same. 4. When an animal cell is placed in fresh water, it will burst. What does osmotic pressure (the pressure of the water against the membrane) have to do with this? The fresh water is hypotonic with respect to the egg, so osmotic pressure causes water to move into the cell. The cell will eventually burst as the cell membrane is stretched and weakened. 5. Does the process illustrated below require energy? How do you know? No energy is required because the process is facilitated diffusion. The solute molecules are moving from an area of high concentration through the protein channel to an area of lower concentration. What does the circled structure represent? The circled structure represents a channel protein. What is the name of the process? The process is facilitated diffusion. For what reasons would the solute need to go through the circle structure instead of through the phospholipid bilayer? Solutes that are too large to pass between the lipids in the cell membrane may pass through the channel protein. Molecules that are not soluble in lipids would also be unable to pass through the membrane and would need to pass through the channel protein. solutes 6. Define homeostasis. Homeostasis is the maintenance of stable internal conditions in living things. Some single-celled organisms have a structure called the contractile vacuole, which pumps excess water out of the organism, thus maintaining homoeostasis by keeping a constant water balance within the cell. 7. Some materials are too large to enter or leave a cell through the cell membrane by diffusion or facilitated diffusion. Large food particles may enter the cell by one of these processes, and waste products may leave by the other method. The diagrams below illustrate the processes by which these materials enter or leave the cell. Label each diagram with the term that describes the process illustrated. Do these processes require energy? Yes, these processes require energy. They are forms of active transport. endocytosis exocytosis 8. Refer to the illustration below: Are the H + ions being transported from a region of high to low concentration or from a region of low to high concentration? Does the process illustrated below require energy? Is it active or passive transport? As indicated by the arrow, the hydrogen ions are moving from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Movement against the concentration gradient requires the use of cellular energy and is therefore a method of ACTIVE transport. SB1b Enzymes-Final Review Explain how enzymes function as catalysts 1. Enzymes work with specific substrates. What model attempts to explain this mechanism of enzyme specificity? The lock and key model explains how enzymes work with specific substrates. In this model, the reaction cannot occur unless the substrates fit into a specific region of the enzyme called the active site. Once the substrate fits into the active site, the enzyme changes shape and catalyzes the formation of the product. 2. Enzymes influence chemical reactions in living systems by decreasing the activation energy needed for chemical reactions to occur. How does this affect the rate at which reactions occur? When the amount of energy needed to start the reaction is decreased by the enzyme, the reaction can occur more quickly; the enzyme speeds up the chemical reaction. 3. The graph provided for you below is labeled. Be able to interpret an unlabeled graph that shows the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction when an enzyme is present and when no enzyme is present. In the graph below, circle the double-arrowed line that represents the amount of energy required when an enzyme is used. Compare this energy to that needed when no enzyme is present. Will this chemical reaction occur more quickly when the enzyme is present or when it is not present? The amount of energy needed when an enzyme is present is much lower than the amount needed when no enzyme is present. The reaction can occur more quickly since less energy must be obtained. 4. Recognize an enzyme, substrate and products in a picture as shown below. Note that substrates bind to the active sites of enzymes where they are converted into products. Circle the active site of the enzyme in the first picture below. Choose any color and color the substrate. 6. What are 3 factors that affect the functioning of enzymes? Enzyme function can be affected by pH (the enzyme may be less effective or cease to function at high or low pH values), substrate concentration (if there is little substrate, the reaction will occur slowly), and temperature (the enzyme may be less effective or cease to function at high or low temperatures). Product concentration may also affect the functioning of some enzymes. (be able to interpret graphs such as those shown above to identify the optimum conditions at which an enzyme might function) Optimum function occurs at the highest point on the Y-axis, representing the rate of enzyme activity. SB3a Photosynthesis – Final Review Explain the cycling of energy through the process of photosynthesis and respiration 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. What is the difference in ADP and ATP? ADP has two phosphate groups and ATP has three phosphate groups—ATP has more stored energy than ADP. ADENINE PHOSPHATE GROUPS RIBOSE 2. How is energy released from ATP? Energy is released from ATP when a chemical bond is broken and a phosphate group is released. 3. What is the ultimate original source of energy for all living things on Earth? The sun is the ultimate original source of energy for most living things on Earth. 4. What is the process that plants use to capture energy and make complex molecules such as glucose? Plants use photosynthesis to capture solar energy and produce food. 5. Write the equation for photosynthesis? 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6. What is raised to a higher energy level (gets excited) and leaves the pigment to travel along a series of proteins in the thylakoid membrane when pigment molecules such as chlorophyll absorb light energy? When a chlorophyll molecule absorbs light energy, some of its electrons are raised to a higher energy level. What is the series of proteins along which it travels called? The electrons are passed from protein to protein in an electron transport chain. 7. NADP+ is important in photosynthesis because the energy it carries is used to produce organic molecules such as glucose. The molecule carries energy when a hydrogen ion and a high energy electron are attached to NADP+, producing NADPH. 8. What substance in the atmosphere enters the food chain through photosynthesis and provides the carbon that is used to make all organic molecules? All organic molecules contain carbon atoms that ultimately can be traced back through the food chain to the carbon dioxide plants take in from the atmosphere. 9. Define autotroph and heterotroph. Organisms, such as plants and algae, that make their own food are called autotrophs, while organisms that do not make their own food are called heterotrophs. 10. Consider the formula for photosynthesis. What gas is produced by plants? Plants give off oxygen when they undergo photosynthesis. 11. Consider the formula for photosynthesis. If carbon dioxide is removed from a plant's environment, what would happen to the plant's production of high-energy sugars? If carbon dioxide were removed from a plant’s environment, it would not have one of the reactants needed for photosynthesis, and the production of highenergy sugars by photosynthesis would slow and eventually stop. What other environmental factors might affect photosynthesis? Temperature, the amount of water available, and the intensity of sunlight are all environmental factors that might affect photosynthesis. SB3a Respiration – Final Review Explain the cycling of energy through the process of photosynthesis and respiration 1. Write the correct equation for cellular respiration. 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy 2. Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are almost opposite processes: Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it back into the atmosphere. 3. What is broken down to release energy during cellular respiration? Food molecules (glucose) are broken down to release energy during cellular respiration. 4. List the correct sequence of events in cellular respiration: GLYCOLYSIS KREBS CYCLE ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN 5. During which part of cellular respiration is the most energy released? The part of respiration that releases the most energy is the Electron Transport Chain. 6. Define aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic means that oxygen is required. Anaerobic means that oxygen is not required. Is cellular respiration aerobic or anaerobic? Cellular respiration requires oxygen, so it is an aerobic process. 7. During cellular respiration in eukaryotes, where does electron transport take place? Electron transport occurs in the mitochondrial membranes of eukaryotes. 8. What is the name of the process that takes place when organic compounds are broken down in the absence of oxygen? When organic compounds are broken down in the absence of oxygen, the process is known as fermentation. 9. What step occurs in both fermentation and cellular respiration? Both fermentation and cellular respiration begin with the process of glycolysis. 10. Which type of fermentation occurs when muscles are exercised extensively in the absence of sufficient oxygen? Lactic acid fermentation occurs when muscles are exercised extensively in the absence of sufficient oxygen. What is the product that builds up in muscles and causes soreness following exercise? Lactic acid builds up in the muscles, causing muscle soreness following exercise. SB1a Organelles– Final Review Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction 1. All cells contain cytoplasm, which is surrounded by a cell membrane (plasma membrane) What are the functions of this structure? The plasma membrane acts as a boundary between the cell and the environment, controls ehat enters and leaves the cell, and provides support and protection for the cell. 2. Eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus. Eukaryotes are generally much larger, and the DNA of eukaryotes is contained within a nucleus. In addition, they contain membrane-bound organelles that carry out various functions for the cell. 3. Are cell walls found in prokaryotes? Prokaryotes do have cell walls. 4. Organelles help to maintain stable conditions within a cell. What is the process of maintaining stable internal conditions called? The maintenance of stable internal conditions is called homeostasis. How does the cell membrane help to maintain stable conditions within a cell? The cell membrane controls what enters and leaves a cell; the concentration of various solutes is maintained at a constant level by the cell membrane. 5. Which organelle contains enzymes that help to break down food and worn-out organelles? Lysosomes function to break down food particles and worn-out organelles. 6. Which organelle found in plants and algae functions to convert the energy of the sun into chemical energy that is used as food? The chloroplast is the organelle that functions to convert solar energy to chemical energy. What is this process called? The process in which the sun’s energy is used to make chemical compounds is called photosynthesis. 7. What are saclike structures that that cells often use to store materials such as water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates called? Vacuoles are saclike structures that are used to store a variety of materials within a cell. 8. What is the main function of the cell wall? The cell wall provides support and protection for the cell. 9. What kingdom of organisms contains only organisms that lack cell walls? The animal kingdom does not contain any organisms that have cell walls. 10. On what organelle are proteins made, and where in the cell are these organelles located? Proteins are made by the ribosomes. Ribosomes are found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) or floating free in the cytosol. 11. The nucleus of eukaryotic cells is important because it contains DNA. Why is DNA important to cells? The DNA within the nucleus contains information needed to make proteins. DNA is the hereditary material used to pass traits from parent to offspring. 12. What organelle converts food into compounds that the cell uses for growth, development, and movement? The mitochondrion is the powerhouse of the cell, converting food molecules into chemical compounds that the cell can use. Do all eukaryotic cells undergo this process of converting food into different chemical compounds? All eukaryotes (Plants, Fungi, Protists, Animals) contain mitochondria to convert their food into useable energy. What is the name of the process, and what chemical compound is produced and used by the cell to start most chemical reactions? Cellular Respiration is the name of the process used by cells to release the energy of food and store that energy in ATP, which can be used by cells to start many chemical reactions. 13. What organelle that is found in animals (but not plants) functions during cell division to separate the chromosomes? The centrioles in animal cells are involved in cell division. 14. What structures do plant cells have that are not found in animal cells? Structures that are found in plant cells but not in animal cells include cell walls, chloroplasts, and central vacuoles. Mitochondrion Endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus Golgi body Plasma membrane 15. Identify and name the numbered structure in the diagram above which immediately identifies this cell as a eukaryote. Nucleus (2) 16. Identify and name the numbered structure in the diagram above which helps to break down glucose into ATP? mitochondrion (3) 17. Identify and name the numbered structure in the diagram above which contains enzymes that attach carbohydrates and lipids to proteins and sends them to their final destinations. Golgi body (5) 18. Identify and name the numbered structure in the diagram above which assembles components of the cell membrane and modifies some proteins. Endoplasmic reticulum (1) 19. Identify and name the numbered structure in the diagram above which controls what enters and leaves the cell. Plasma membrane (4) 20. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? All livingthings are composed of cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells come from pre-existing cells. 21. In multicellular organisms, cells exhibit cellular specialization in which cells are specialized to perform particular functions. The cells of unicellular organisms (all prokaryotes, most protists, and yeasts) are not specialized and must carry out all of the functions of life. 22. List the levels of specialization found in multicellular organisms: cells → tissues → organs → organ systems → organism SB3c, SB3b, & SB3d Taxonomy/ Kingdoms & Viruses – Final Review Examine the evolutionary basis of modern classification systems Compare how structures and function vary between the six kingdoms Compare and contrast viruses with living organisms 1. Taxonomy is defined as the science of grouping organisms according to their characteristics and evolutionary history. 2. Which word in the scientific name Dermacenter variablis is the genus? Dermacenter Which word is the speciesvariablis 3. List the biological hierarchy of taxons in the correct order from most diverse to least diverse: KINGDOM, PHYLUM, CLASS, ORDER, FAMILY, GENUS, SPECIES 4. A genus is composed of a number of related species. An order consists of a number of related families. A class is composed of a number of related orders. A kingdom is composed of a number of related phyla. 5. The most general and largest category in Linnaeus’s system is the kingdom. The most specific and smallest category in Linnaeus’ system is the species. 6. Scientists assign each kind of organism a universally accepted name in the system known as binomial nomenclature. 7. Today, biologists classify organisms not only by their physical similarities, but also by chemical and behavioral similarities. 8. A diagram such as the one to the right is called a cladogram. In this diagram, tissue formation and vascular bundles are traits that are shared by some species but are not present in others. These traits are called derived characters and indicate close evolutionary relationships among the organisms that share the traits. 9. Define autotrophic, heterotrophic, prokaryotic, & eukaryotic derived characters 10. List the kingdoms that contain eukaryotes: The kingdoms in domain Eukarya contain eukaryotes. They are Protista, Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia 11. List the kingdoms that contain prokaryotes: Kingdom Archaebacteria (Domain Archaea) and Kingdom Eubacteria (Domain Bacteria) contain prokaryotes, cells that do not have a nucleus. 12. An organism that is unicellular, heterotrophic, has cell walls containing peptidoglycan, and does not contain a nucleus belongs to the kingdom eubacteria. You know that it is in one of the bacterial kingdoms because it doesn’t have a nucleus. Kingdom eubacteria is identified by the presence of peptidoglycan in the cell walls of its many species. 13. Which prokaryotic kingdom contains organisms that are often found in extreme environments? Kingdom archaebacteria contains many species that are found in extreme environments such as hot springs or thermal vents, and in environments that are extremely acidic or have a very high salt content. 14. Which kingdoms contain organisms with cell walls? All kingdoms except Animalia contain some organisms with cell walls. All bacteria, fungi, and plants have cell walls. Plant-like and Fungus-like protists have cell walls, but animal-like protists do not have cell walls. Which kingdom contains no organisms with cell walls? Animalia 15. What carbohydrate is found in the cell walls of plants? Cellulose is found in the cell walls of plants. In the cell walls of fungi? Chitin is found in the cell walls of fungi. 16. In which two kingdoms might a newly discovered organism that is multicellular, nucleated, and photoautotrophic be placed? Such an organism might be placed in either Protista or Plantae. To which of these two kingdoms do MOST multicellular, nucleated, photosynthetic organisms belong? Most multicellular photosynthetic organisms belong to kingdom Plantae. 17. You are exploring the deciduous forest and discover a new species that is multicellular, nucleated, and has cell walls made of chitin. You also observe that it is a heterotroph that obtains food by absorbing nutrients from the environment. You make your name in biological circles by placing it in the kingdom Fungi and naming it after yourself! 18. To which kingdom would single-celled eukaryotes that are either heterotrophic or photosynthetic most likely belong? These organisms would be placed in Kingdom Protista. 19. Eukaryotic, photoautotrophic, multicellular organisms with cell walls of cellulose belong to which kingdom? Kingdom Plantae 20. The little kid next door is always bringing you organisms and asking you what they are. One day, he brings you a really weird-looking specimen. After examining and observing it for several weeks, you have placed it into one of the six kingdoms. Based on the following information, into what kingdom should it be placed? contains nuclei, consists of more than one cell, moves, consumes other organisms for food, its cells do not have walls The organism very clearly belongs in Kingdom Animalia. 21. Viruses are composed of protein and nucleic acid (either RNA or DNA). Fill in the blanks to describe how these two macromolecules are organized to form a virus: Viruses are composed of RNA or DNA surrounded by a protein coat. 22. List three ways that we know viruses are not alive. Viruses are not composed of cells. They do not make their own proteins or DNA. They do not use energy. They cannot reproduce independently of a cell. SCSh Characteristics of Science – Final Review 1. Biology is the study of life 2. How many variables are isolated and tested in a controlled experiment? A single variable is isolated and tested in a controlled experiment. 3. In science, a hypothesis is useful only if it can be tested 4. What tool is used by biologists to produce magnified images of structures that are too small to see with the unaided eye? In biology, a microscope is used to enlarge images. 5. What safety rule is the most important rule to follow when you are working with chemicals in general but especially with volatile chemicals? It is essential that goggles be worn when working with dangerous chemicals. 6. Controlled experiments are designed in science. You must be able to recognize and identify the manipulated (independent) variable, the responding (dependent) variable and the control group in an experiment. Define: manipulated variable—the condition which is deliberately changed in an experiment, responding variable—the data you collect; the condition that changes as a result of the changes you instituted, controlled variables—the conditions in an experiment that are kept constant. Several graphs and tables will be on the final exam. You must be able to interpret them. Be sure to read all information that accompanies the graph or table, examine the data carefully, and answer the specific question that is being asked.








