Pharmaceutical Microbiology I
advertisement

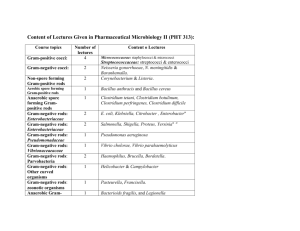
Pharmaceutical Microbiology I PHT 313 وصف المقرر يتناول ه ذا المق رر رراة ا المروروت ال المة للا لض را و يش م المق رر ى ال أف رر رسرة را وه ت اللوتريول ويت و المروول ويت وال ررولويت ويع ا اللوترريول ويت ى ث الموورال العنقوريا ونختص تاراة ا ف اص ر المقرر و يتناول اللوترريا المةللا لض را المروروب ث شو ه وخ اس ه والعوا الممرضا المج ور ف ت المرو روب الت ت فة اىا ى ال ث األنتجرن الةطحت والةموم واألنزيمال الخ واأل را الت ت فح ا توي ور حاو المر ر وطريق ا انتش ارت وفت ر ح انته ورر ر ا فش خرص الم ر المرو روب ووص ف ر أ ا تالنة لا لع إر رنرور ا و عم ر ا وط را الوااي ا والتطع ر ووتاسر ال وط را ى ن الم ر ال طريال فرشم فقةرمه لةطا ل طريال ورراةا ال طريال المةللا لض را المهم ا طلر ا PHT226 أ ا ى ال رروةال فارس فت Course description: Topics of this course cover the fundamentals of organisms causing infections to humans for undergraduate pharmaceutical students. This course includes three major topics "bacteriology, mycology and virology". Medical bacteriology covered the important micro-organism causing disease. Each micro-organism is studied from the following topics: Morphology and characters, virulence factors "surface antigen, toxins and enzymes", pathogenesis, the disease caused by infectious micro-organism, clinical and laboratory diagnosis, prophylaxis, epidemiology, vaccination and treatment. Medical mycology involved introduction and classification of fungi. In addition, study of medically important fungi that caused human disease. Medical virology was previously studied under PHT226. Prerequisite: PHT226 Credits: Three credits distributed as 2+1 (Lectures + Laboratory) Course Proficiencies: The students at the end of the course must be able to: 1- Define of causative agents causing human diseases 2- Define Role of virulence factors to established the diseases 3- Describe the of mode of transmission of the infectious diseases, incubation period of pathogenic micro-organisms, and signs and symptoms of the disease 4- Define the basis of diagnosis of micro-organism-causing infection 5- Describe the fundamentals of epidemiology of diseases, in addition their prophylaxis, prevention and control, vaccination and treatment of infectious diseases Course Assessments: 1st theoretical quiz 15% 2nd theoretical quiz 15% 1st practical examination 15% 2nd practical examination 15% Final theoretical examination 40% Total marks 100% Required Readings 1- Practical and theoretical textbooks in medical microbiology for pharmacy undergraduate students. 2- Many websites such http://www.cehs.siu.edu/fix/medmicro/INDEX.htm. as 3- "Mackie and McCartney": Practical medical microbiology 3rd ed, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, London, Melbourne, and New York". 4- "Bailey and Scott's: Diagnostic Microbiology (Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology)". 5- Tovar's Online Textbook of Bacteriology is available as a free electronic reference in this course. The Table of Contents page has a searchable index. 6- Check the Medical and Diagnostic Microbiology textbooks in the university library. Content of Lectures Given in Pharmaceutical Microbiology II (PHT 313): Course topics Gram-positive cocci: Number of lectures 4 Content o Lectures Gram-negative cocci: 2 Non-spore forming Gram-positive rods 2 Streptocococcaceae: streptococci & enterococci Neisseria gonorrhoeae, N. meningitidis & Baranhemalla. Corynebacterium & Listeria. Aerobic spore forming Gram-positive rods 1 Bacillus anthracis and Bacillus cereus Anaerobic spore forming Grampositive rods Gram-negative rods: Enterobacteriaceae Gram-negative rods: Enterobacteriaceae Gram-negative rods: Pseudomonadaceae Gram-negative rods: Vibrionaceaeaceae Gram-negative rods: Parvobacteria Gram-negative rods: Other curved organisms Gram-negative rods: zoonotic organisms Anaerobic Gramnegative rods Acid fast bacteria 1 Clostridium tetani, Clostridium botulinum, Clostridium perfringenes, Clostridium difficile 2 E. coli, Klebsiella, Citrobacter , Enterobacter" 2 Salmonella, Shigella, Proteus, Yersinia" " 1 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1 Vibrio cholorae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus 2 Haemophilus, Brucella, Bordetella. 1 Helicobacter & Campylobacter 1 Pasteurella, Francisella. 1 Bacterioids fragilis, and Legionella 1 branched bacteria Cell wall deficient organisms Spirochates Obligate intracellular bacteria Medically important fungi 1 1 Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium bovis, Mycobacterium leprae & Nocardia Actinomyces Chalamydiae & Mycoplasma 1 1 Treponema, Borrelia, Leptospira Rickettsia, coxiella, Ehrlichia 2 Candida albicans & Cryptococcus neoformans Microcococcaceae: staphylococci & micrococci Laboratory Exercises for Pharmaceutical Microbiology II (PHT 313): (3hours/Lab): Week Topic Lab description 1 Staphylococci Use of catalase test to differentiate between staphylococci and streptococci. Laboratory diagnosis of staphylococci by gram stain and biochemical tests as coagulase, DNase, Mannitol fermentation on Mannitol salt agar and novobiocin sensitivity tests to differentiate between S. aureus, S. epidermidis and S. saprophyticus using 2 Streptococci Use of blood agar to differentiate between , , haemolytic streptococci. Use of bacitracin to identify Strepococcus pyogenes. Use of CAMP test to identify Streptococcus agalactiae. Use of optochin and bile soloubility tests to differentiate between viridans streptococci and Streptococcus pneumoniae. 3 Corynebacterium Use of Gram stain to characterize the morphology of Corynebacterium. Use of Loefflers serum agar medium as growing medium for corynebacteria. Elek's test and sucrose fermentation to differentiate between Corynebacterium diphtheriae and diphtherioids. 4 Bacillus Gram stains to characterize Gram-positive bacilli. Spore staining to characterize the spores of Bacillus. Motility test and hemolysis on blood agar to dipherntiate between Bacillus anthracis and Bacillus cereus 5 Clostridium 6 Enterobacteriaceae Gram stains to characterize Gram-negative bacilli. Oxidase test, nitrate reductase test and oxidative fermentative test to identify Enterobacteriaceae. Use of common selective and differential media to differentiate between lactose and non-lactose fermenters. 7 Enterobacteriaceae Use of Indole, methyl red, voges proskauer, and citrate "MViC" test to differentiate between members of Enterobacteriaceae. Also use of urease test, motility test and TSI agar test to differentiate between Enterobacteriaceae. 8 1st examination 9 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10 Vibrio cholorae Gram stains to characterize Gram-positive bacilli. Spore staining to characterize the spores of Clostridium. Nagler's reaction and Sormy clot formation to identify Clostridium. Gram stains to characterize Gram-negative bacilli. Oxidase test, nitrate reductase test and oxidative fermentative test to identify Pseudomonas. Use of selective "Cetermide" media to grow of Pseudomonas and exhibition of exo-pigments on nutrient agar. Liquefaction of gelatin. Gram stains to characterize Gram-negative curved bacilli. Oxidase test, nitrate reductase test and oxidative fermentative test to identify Vibrionaceae. Use of common selective and differential media "TCBS" to identify Vibrio cholorae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. 11 Haemophilus influnzae Gram stains to characterize Gram-negative bacilli. Use of enriched media "Chocolate agar" to grow Haemophilus. X and V factor test and satalletism to identify Haemophilus. 11 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Acid fast stains to charactize acid fast bacteria "Mycobacterium". Use of Lowenstein Jensen medium to grow of Mycobacterium 12 Medical Mycology 13 Applied Microbiology 14 2nd examination Examination of yeasts and moulds (Candida & Asperigullus) Microbiological examination of water and Milk Spots Laboratory exercises will start after starting of lecturers Laboratory exercise must be start at Sunday, Monday and Tuesday. Laboratory exercises must not be start at Saturday and Wednesday. Requirements for the Laboratory Exercises: I- Organisms: - Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus viridans, Enterococcus faecalis, Bacillus subtilus, Clostridium tetani, Clostridium perfringenes, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Corynebacterium xerosis, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter diversus, Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella sonneii, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio cholorae non O1, Haemophilus influnzae, Mycobacterium phili, Candida albicans. II- Equipments Required for All Microbiological Laboratory: Equipment Number Autoclave 2 Hot air oven 2 Incubator 2 Digital balance 1 Water bath 2 Distillator 1 pH meter 1 Spectrophotometer 2 Microscope One per each student Bacterial filter 2 Laminar flow 1 III- Glassware and disposables: - Flasks, beakers, bottles, and measures with different sizes. - Screw caped glass tubes (different sizes) - PJ tubes, universal tubes, - 1 ml, 5ml and 10 ml sterile pipettes and pasture pipettes - Sterile disposable Petri-dishes. - pipump (green and blue) - Membrane filters 0.22 um. - Wattmann filter paper, lens paper, - Microscopic glass slides and covers. IV- Media and chemicals 1- Media: Nutrient agar, nutrient broth, blood agar base, mannitol salt agar, deoxyribonuclease agar, bile esuline agar, litmus milk, macConkey agar, Eosin methylene blue agar, Salmonella Shigella agar, Selenite broth, peptone water, methyl red-voges proskauer medium, simmone,s citrate agar, urea agar base, cetermide agar, oxidative fermentative medium, thiosulfate citrate bile salts sucrose agar, Lowenstein-Jensen medium, Loefller;s serum medium, Mueller Hinton agar, MacConkey broth. 2- Chemicals: Immersion oil, liquid paraffin, crystal violet, safrannin, iodine, potassium iodide, malachite green, carbol fuchsin, methylene blue, p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, amyl alcohol, xylene, absolute ethanol, concentrated hydrochloric acid, bacitacin disc, optochin disc, novobiocin disc, methyl red, alpha-naphthol, potassium hydroxide, urea, oxidase reagent, hydrogen peroxide, X, V and XV factor, Sheep blood and rabbit plasma. Different antibiotic discs" Ampicillin, amoxicillin, amoxicillin/clavulanic, ceftazidime, cefotaxime, ceftazidime/clavulanic acid, imipenem, meropenem, cefoxitin, cefipime, pipercillin, aztreonam, ciprofloxacin, nalidixic acid, gentamicin, amikacin, tobramycin, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprime, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, penicillin G, oxacillin, vancomycin.