Reproduction and Genetics - Effingham County Schools
advertisement
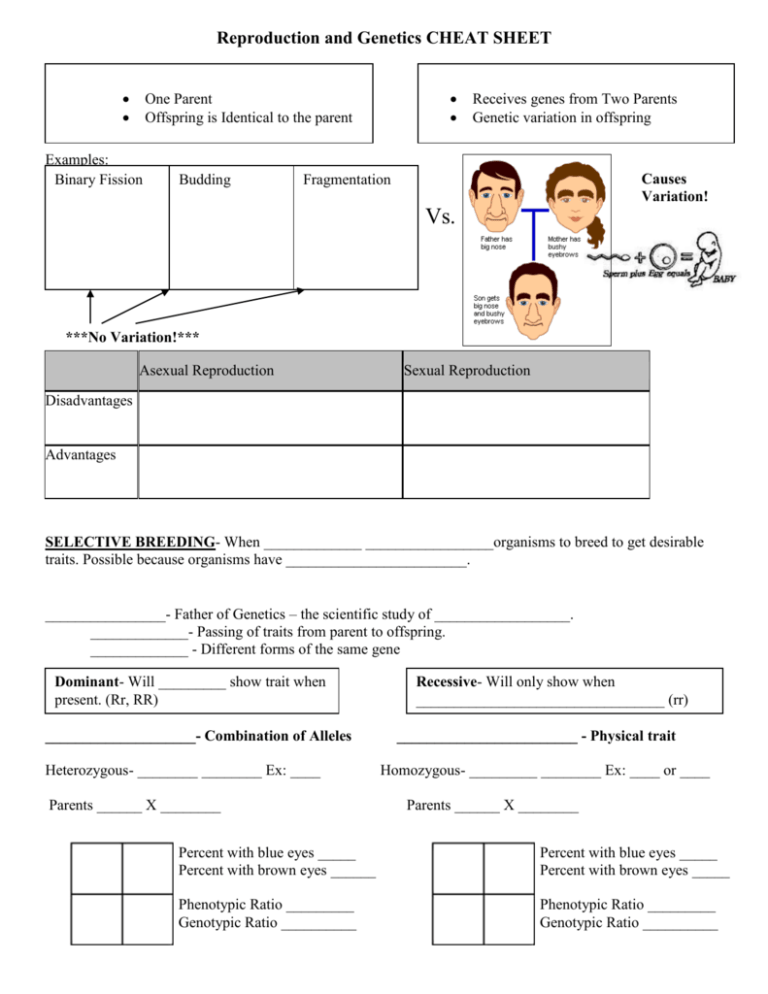
Reproduction and Genetics CHEAT SHEET One Parent Offspring is Identical to the parent Examples: Binary Fission Budding Receives genes from Two Parents Genetic variation in offspring Causes Variation! Fragmentation Vs. ***No Variation!*** Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Disadvantages Advantages SELECTIVE BREEDING- When _____________ _________________organisms to breed to get desirable traits. Possible because organisms have ________________________. ________________- Father of Genetics – the scientific study of __________________. _____________- Passing of traits from parent to offspring. _____________ - Different forms of the same gene Dominant- Will _________ show trait when present. (Rr, RR) ____________________- Combination of Alleles Heterozygous- ________ ________ Ex: ____ Parents ______ X ________ Recessive- Will only show when _________________________________ (rr) ________________________ - Physical trait Homozygous- _________ ________ Ex: ____ or ____ Parents ______ X ________ Percent with blue eyes _____ Percent with brown eyes ______ Percent with blue eyes _____ Percent with brown eyes _____ Phenotypic Ratio _________ Genotypic Ratio __________ Phenotypic Ratio _________ Genotypic Ratio __________ 1. For each genotype below, indicate whether it is heterozygous (one dominant allele + on recessive allele) or homozygous recessive (two recessive alleles) or homozygous dominant (two dominant alleles). Heterozygous = H, Homozygous Recessive = HR, Homozygous Dominant = HD AA ______ bb______ CC______ Dd_______ Ee _______ ff_______ GG______ hh ______ 2. Circle the Genotypes above that would express a Dominant Trait. 3. For Each of the Genotypes below, determine the phenotypes that would be expressed Big nose (N) is dominant to small nose (n) Brown hair (B) is dominant to blond (b) NN _______________ BB _______________ nn _______________ bb _______________ Nn _______________ Bb _______________ 4. 5. For each Phenotype, give the possible genotype(s) Straight hair (L) is dominant to Curly hair (l) Cleft chin (T) is dominant to a non-cleft chin (t) Straight _____________________ Curly ______________________ Cleft Chin ______________________ Non-cleft _______________________ 6. Set up the Punnet square for each of the crosses listed below. Round seeds (R) are dominant to wrinkled seeds (r). Rr x rr What percentage of the offspring will be round? ___ What is the phenotypic ratio? _________________ What is the genotypic ratio? __________________ RR x rr What percentage of the offspring will be round? ___ What is the phenotypic ratio? _________________ What is the genotypic ratio? __________________ 7. In pea plants purple flowers are dominant to white flowers. If two white flowered plants are cross, what percentage of their offspring will be white flowered? ______________ 8. A white flowered plant is crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for the trait. What percentage of the offspring will have purple flowers?___________ What percent will have white flowers? ___________ 9. Show how two purple flowers can cross and have offspring that have offspring with white flowers. What genotype would both parents need to be? _______ and _____ What percent of the offspring would have white flowers? ________











