Micropipeting SOP
advertisement

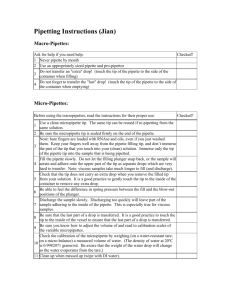
LABORATORY SKILLS TRAINING TITLE: MEASURING SMALL VOLUMES USING MICROPIPETTES PURPOSE: The purpose of this Skills Training is to train the student in the basic techniques of pipetting using a variable automatic micropipette. PREREQUISITES: N/A REFERENCES: Gutzman, K., Pipetting: A Practical Guide, The American Biology Teacher, Vol. 63, NO. 2, February 2001. MATERIALS: Variable automatic pipets Variable pipet tips Waste disposal container for used pipet tips SAFETY EQUIPMENT: Safety glasses and gloves PROCEDURE: Pipetting Small Volumes of Liquids 1. CHOOSE THE CORRECT MICROPIPETTE Each micropipette has a range of volumes for which it is accurate and reliable. This range is stamped on the pipette below the display window and should never be exceeded. The range of variable volumes pipettes you may encounter include: P10 (1-10 μl), P200 (20- 200 μl) and P1000 (200-1000 μl). Selection of the correct pipette is crucial to accurately pipetting the desired volume. Each type of pipette requires a tip that fits the end of the pipette correctly. Determine the volume you need to pipet and then select the correct pipette for the task. Set the pipette to the desired volume by rotating the plunger button on the end until the correct numbers appear in the display. CAUTION: Do not rotate the volume in the display beyond the minimum or maximum numbers stamped on the micropipette. Select and fit the appropriate size tip for the pipette selected. CCCLST0031 Approved: 23July2014 Revision: 30July2014 2. PIPETTING THE DESIRED VOLUME BEFORE immersing the tip into the liquid, you must push out the same amount of air out by pressing the plunger button to the first stop slowly and smoothly. While still holding the plunger button down, hold the pipette vertically and immerse the tip into the liquid and hold it at a constant depth below the surface of the liquid. Slowly release the plunger button so that the pipette will draw the liquid into the tip. As the depth of liquid lowers, so must the tip of the pipette. Once the plunger button has completed been released, hold the pipette in the liquid for 1 additional second to complete aspiration. Remove the pipette and tip from the solution and continue to hold the pipette vertically. 3. DELIVERING THE LIQUID SAMPLE To deliver the sample, place the tip against the inside wall of the tube that is receiving the sample at a slight angle. Press the plunger button slowly and smoothly to the first stop. Wait at least one second as it dispenses and then press the plunger button further to the second stop to expel any residual liquid from the tip to deliver (TD) the desired volume. DO NOT release the button until the tip is out of the tube to which the sample was delivered. Keep the plunger button pushed down as you withdraw your sample from the tube so as not to re-aspirate any of the transferred sample. Release the plunger button slowly and smoothly. 4. TIP REMOVAL The tip may be ejected from the tip holder by pressing the tip ejector button while holding the pipette tip over a waste container. Tip changes are required only if aspirating a different liquid, sample or reagent. If contamination of the tip is a concern, then a tip change is always appropriate. TRAINING ASSESSMENT: The laboratory technician is considered skills trained in the use of micropipettes when they have successfully completed the training assessment. 1. Receive 95% on all assessments in the use of variable automatic micropipettes. DOCUMENTATION: Evaluations recorded in Skills Training Assessment Log placed in the laboratory notebook. DOCUMENTATION OF SKILLS TRAINING: Student Name: ________________________ Date: __________________________ Approved By: _________________________ Date: __________________________ CCC Science Department Instructor CCCLST0031 Approved: 23July2014 Revision: 30July2014








![1_Metrics_and_Measurements[1].](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007631401_2-8c00297193e8f35a27d21d00f521096c-300x300.png)
