Calculus BC: Parametric Equations Worksheet
advertisement

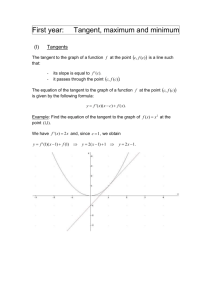
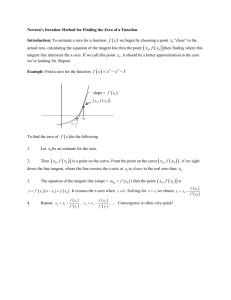
CALCULUS BC WORKSHEET ON PARAMETRICS AND CALCULUS Work these on notebook paper. Do not use your calculator. dy d2 y and On problems 1 – 5, find . dx dx 2 1. x t 2 , y t 2 6t 5 2. x t 2 1, y 2t 3 t 2 3. x t , y 3t 2 2t 4. x ln t, y t 2 t 5. x 3sin t 2, y 4cost 1 _____________________________________________________________________________ 6. A curve C is defined by the parametric equations x t 2 t 1, y t 3 t 2 . dy in terms of t. dx (b) Find an equation of the tangent line to C at the point where t = 2. (a) Find 7. A curve C is defined by the parametric equations x 2cost, y 3sin t . (a) Find dy in terms of t. dx (b) Find an equation of the tangent line to C at the point where t = . 4 ______________________________________________________________________________ On problems 8 – 10, find: dy (a) in terms of t. dx (b) all points of horizontal and vertical tangency 8. x t 5, y t 2 4t 9. x t 2 t 1, y t 3 3t 10. x 3 2cost, y 1 4sint ______________________________________________________________________________ On problems 11 - 12, a curve C is defined by the parametric equations given. For each problem, write an integral expression that represents the length of the arc of the curve over the given interval. 11. x t 2 , y t 3 , 0 t 2 12. x e2t 1, y 3t 1, 2 t 2 Answers to Worksheet on Parametrics and Calculus 3 2 dy 2t 6 3 d2y 3 1. 1 ; t 3 2 dx 2t t dx 2t 2t ______________________________________________________________________________ dy d2y 3 2. 3t 1; dt dx 2 2t ________________________________________________________________________________ 1 18t 2 1 2 dy 6t 2 d y 2t 36t 4 1 1 2 dx 1 2 dx 1 2 t t 2 2 ________________________________________________________________________________ 3 12t 2 3. 1 4t 2 ; 2 dy 2t 1 d 2 y 4t 1 2t 2 t; 4t 2 t 1 1 dx dx 2 t t ________________________________________________________________________________ 4 sec2 t 2 dy 4sin t 4 d y 4 5. tan t; 3 sec3 t 2 dx 3cos t 3 dx 3cos t 9 _______________________________________________________________________________ dy 3t 2 2t 6. (a) dx 2t 1 dy 312 2 1 8 , x 5, y 4 so the tangent line equation is (b) When t = 1, dx 2 1 1 5 8 y4 x5 5 ________________________________________________________________________________ dy 3cost 3 7. (a) cot t dx 2sint 2 4. (b) When t 4 , dy 3 3 3 2 so the tangent line equation is cot , x 2, y dx 2 4 2 2 3 2 3 x 2 2 2 ________________________________________________________________________________ dy 2t 4 8. (a) dx 1 dy dx (b) A horizontal tangent occurs when 0 and 0 so a horizontal tangent dt dt occurs when 2t 4 0 which is at t= 2. When t = 2, x = 7 and y = 4 so a horizontal dx dy tangent occurs at the point 7, 4 . A vertical tangent occurs when 0 and 0 dt dt Since 1 0 , there is no point of vertical tangency on this curve. y 9. (a) dy 3t 2 3 dx 2t 1 dy dx 0 and 0 so a horizontal tangent occurs when dt dt 3t 2 3 0 which is at t 1 . When t = 1 , x = 1 and y = 2, and when t 1, x = 3 and y = 2 so a horizontal tangent occurs at the points 1, 2 and 3, 2 (b) A horizontal tangent occurs when dx dy 0 and 0 so a vertical tangent occurs when dt dt 1 3 11 1 2t 1 0 so t . When t , x and y so a vertical tangent occurs at the 2 4 8 2 3 11 point , . 4 8 A vertical tangent occurs when ______________________________________________________________________________ dy 4cost 10. (a) dx 2sint dy dx (b) A horizontal tangent occurs when 0 and 0 so a horizontal tangent dt dt 3 occurs when 4cost 0 which is at t and . When t = , x = 3 and y = 3, and when 2 2 2 3 , x = 3 and y = 5 so a horizontal tangent occurs at the points 3, 3 and 3, 5 . t 2 dx dy A vertical tangent occurs when 0 and 0 so a vertical tangent occurs when dt dt 2sin t 0 so t 0 and . When t 0, x 5 and y 1 and when t , x 1 and y 1 so a vertical tangent occurs at the points 5, 1 and 1, 1 . _______________________________________________________________________________ 2 11. s b a 2 dx dy dt dt dt 2 0 2t 3t dt or 0 2 2 2 2 4t 2 9t 4 dt _______________________________________________________________________________ 2 12. s b a 2 dx dy dt dt dt 2 2 2e 3 dt or 2t 2 2 2 2 4e4t 9 dt