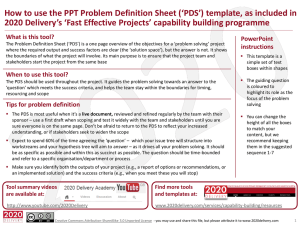
TPJ_4714_sm_FigsS1-S4-TableS1

Supplementary Figures
Figure S1. Phenotypes of PDS silencing induced at the seed-germination stage in different silencing mutant genotypes. ( A ) PDS silencing in PTGS mutant progeny from the crosses, dcl4/PDSi, rdr6/PDSi and sgs3/PDSi . (B) PDS silencing in
TGS mutant progeny from the crosses, nrpd1 /PDSi, dcl3-1/PDSi , ago4-1/PDSi , drm1.2/PDSi , rdr2-1/PDSi, drd1/PDSi, nrpd2/PDSi and nrpe1/PDSi.
Seedlings were geminated on media containing inducer, and PDSi seedlings geminated on media with (PDSi) or without (PDSi-un) inducer were used as control. Photography was taken at 10 days post germination.
Figure S2. Detection of primary and secondary siPds production along the endogenous PDS target gene. (A) Diagram illustrates endoPDS genomic structure and probes corresponding to each region. pds-U, 5’ UTR of endoPDS
. Pds, 5’-end of
PDS coding region, which was also used for the pX7-Pdsi construction. pDs, middle region of the PDS coding region. (B) RNA gel blot analysis of Pds -derived siRNAs
(siPds) with 32 P-labeled sense Pds RNA probe, miR159 accumulation and U6 RNA hybridization loading control as shown in Figure 4C. siRNAs in the reduced silencing line nrpd1/PDSi were also analyzed (lane 6). (C) Secondary siRNAs with sequence homology corresponding to upstream (upper panel) or downstream sequences of Pdsi targeted region. Membrane of (B) was stripped and rehybridized with a
32
P-labeled
RNA pds-U or pDs.
Figure S3. Analysis of DNA methylation and RNA expression of the endogenous
PDS gene. (A) Methylation-sensitive restriction-PCR (Chop-PCR) analysis of DNA methylation. DNA from indicated genotype was digested with the methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme AluI or HaeIII. PCR amplification was then carried out with related primers (Supplemental table 1). PCR fragments corresponding to endoPDS target, Pdsi silencer, or internal controls (Tubulin and one long-terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposon (solo LTR)) are shown on the left. Sequence lacking
AluI and HaeIII sites in endoPDS ( PDS control) served as controls to show that equivalent amounts of DNA were tested in all reactions. Restriction enzymes sites along each selected regions were illustrated on the right of gels. (B) Bisulphite sequencing of the endoPDS genomic region in PDSi line with or without induction of silencing. Sequenced region includes the first exon (E1) and a portion of the first intron. Cycle: CG site, square: CNG and triangle: CNN. Methylated cytosines were symbolized with related solid shapes. Positions of cytosines are indicated at the bottom. (C) DNA gel blot analysis of endoPDS DNA methylation. Genomic DNA of indicated samples was digested with the methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme
PvuI+SphI, HpyCH4IV, Sau3AI, Sau96I or ScrFI, and gels were probed with the
32
P-labeled endoPDS promoter sequence. Fragments resulting from complete digestion with the indicated enzyme, which could be detected by the probe are illustrated bellow. (D) RNA gel blot detection of endoPDS mRNA accumulation.
Total RNAs were extracted from mutant genotypes and their progeny from crosses, as well as WT (Col-0) and PDSi without induction of silencing as indicated on the top.
Gel was hybridized with
32
P-labeled Pds DNA probe. rRNAs stained with methylene blue were used as a loading control.
Figure S4. Methylation analysis of the primary pX7-Pdsi transgene (A) and exo-Pdsi silencer (B). Sequenced regions are illustrated with blue lines below the related diagrams. Samples from different genotypes are indicated. Different shapes represent different cytosine methylation as described in Figure S3B. Corresponding conversion charts and percentage of CG, CNG and CNN methylation of G
10-90-loxP
-Pds or G
10-90-loxP
region in the indicated genotypes were shown in Figure 7.
Supplementary Table
Table S1. Primers used in this study
Target mame Sequence (5’ – 3’) endo-
PDS pX7-
Pdsi
G
10-90
Pdsi
BG035
BG036
BG057
BG005
BG038
PDS 5'
PDS 3'
BG007
BG120
BG046
BG049
BG050
P1
P2
P3
P4
BG113
BG138
BG135
BG120
BG114
BG121 tubulin BX161
Application
ATGGTTGTGTTTGGGAATGTTTC
Probe preparation of Pds
CTTCCATGCAGCTATCTTTCCA
GAAGAGAAAAGGGGAAGAGAAG
Probe preparation of PDS promoter
(BG057/pPDSi-2R)
ACAAGACCATATGGGCACTCGAATACTC
Probe preparation of
TTTCTCCAACTTAACTCACAACTG pds-U
ATAGCTGCATGGAAGGA
CTGAAGAAACCGGTTCA
Probe preparation of pDs
CATTGAAGCAGTTGTGAGTTAAGTTG
ACCARCAATTACAACTTTCAAA
TATACCCTAACCCACCTTATATTTAAC
GAAAATGGTTGTGTTTGGGAATG
TTCCTCTCTTTAATCAAAATTACACTTAT
ACACTA
GCCGCCACGTGCCGCCACGTGCCGCC
CTCGTCAATTCCAAGGGCATCGGT
CTGGACACAGTGCCCGTGTCGGA
GGAATTCTGCAAACACACAAGACAAT
AGGATATYGTGGATYYAAGYTTG
Chop-PCR target
Bisulfite sequencing for
E1 region
Genotyping for PDS
AGATCAAACACCTCTTGTTGCCT
Bisulfite sequencing
(BG113/BG138) for
G
10-90
region
GTTATTTATGAGATGGGTTTTTATGATTA
GAG
Bisulfite sequencing for
Pdsi region
ACCARCAATTACAACTTTCAAA
CATTCCCAAACACAACCA
ATTTGGAGAGGAYAYGYTGG
CTCACTCACTCACACTTTTATTC
Chop-PCR. bisulfite sequencing
(BG113/BG114)
G
10-90
region for
Chop-PCR. bisulfite sequencing
(BG121/BG120) for Pdsi region
Chop-PCR
BX162
BX163
BX164
A211 solo
LTR
A212
T-DNA of Salk lines
LBa1
DCL3
DCL4
RDR2
RDR6
SGS3
DRD1
NRPD1
NRPD2
NRPE1
DRM1
DRM2
BG102
BG033
BG012
BG025
BG026
BG029
BG030
BG015
BG016
BG017
BG018
BG039
BG040
BG019
BG020
BG021
BG022
BG101
BG075
BG076
BG059
BG060
AAGTTATCAGGTCGAAAGGTCTG
TTTGGAGCCTGGGACTATGGAT
ACGGGGGAATGGGATGAGAT
ATAAAACTCGAAACAAGAGTTTTCTTATT
GCTTTC
TAATGGTATTATTTTGATCAGTGTTATAA
ACCGGA
Chop-PCR
Chop-PCR
TGGTTCACGTAGTGGGCCATCG
Genoityping of T-DNA insertion lines
TTCAAGAGTTGGGAAAAGACAG
GCTTTGGAGATACATGCCCAG
GGAACTGCTACGGTCTGGA
CCACTAGAAACGCATATTCAGAC
TCCACCTCGGCGAAGATACTG
GAAGCGTCACCATTAACACAACAA
TACTGTCCCTGGCGATCTCT
CCACCTCACACGTTCCTCTT
CAAAAAACCTGTGGTGGT C TG C A
ACAACCTTGGCACGTTCCTGC
TATGGGTTATGTTTGCCGTGTCT
TCTTCTTCTCCATCCACTGTTTC
GGGTTCGAATACGGGTCACTTGA
TGTTACATACTGAGAAGCATGCT
AGTGCCTCCATCTGTATTTGTTT
TGGAGATTTTCCACAACCAAG
TCTCTTCAAGCGCTTCGGGTG
AGTTAGCAGCCACTTCCTTCACT
TTATTGCTATGGGGTTTCCTGAG
CGAACTGCCGTGCCATCT
TCTAGAGGAAGTGGCATAAGC
AGGGCGACATTCTCATAGTAG
Genoityping
Genoityping
Genoityping
Genoityping
Genoityping
Genoityping
Genoityping
Genoityping
Genoityping
Genoityping
Genoityping