DRAINAGE BASINS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT REVISION GUIDE
advertisement

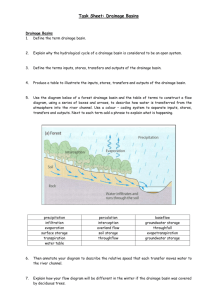
DRAINAGE BASINS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT REVISION GUIDE TOPIC KEY CONCEPTS/ KEY QUESTION you should be able to answer/ HINTS and suggestions a) The concept of the drainage basin as a system b) Processes in a drainage basin c) Mechanics of a drainage basin LOOK IN….. TOPIC OUTLINE. KEY WORDS MAKE YOUR OWN! Use the TOPIC OUTLINE THE DRAINAGE BASIN KEY WORDS: Define and delineate (draw the boundaries of ) a drainage basin and its features (e.g. watershed) on diagrams and maps Define the terms watershed, perimeter, catchment, drainage density, stream order and bifurcation ratio. Calculate drainage density, stream order and bifurcation ratio and use these measures to compare drainage basins. Identify different types of drainage patterns. KEY WORDS: Define and describe the interaction of the processes in the hydrological cycle. Interpret diagrams showing these processes on a flowchart. Discuss factors that influence the amount of runoff versus infilitration in a drainage basin and how they affect the shape of the hydrograph. Interpret hydrographs Define river channel variables (e.g. cross sectional area, depth etc) and other variables which affect channel flow (e.g. hydraulic radius, Manning’s equation to measure friction) and describe how these processes interact with each other (relationships between them). Explain different ways a river erodes, transports and deposits its load. Name and define the types of erosion and types of load. a) Landforms produced by erosion and deposition b) Flooding as a hazard FLUVIAL FEATURES IN THE LANDSCAPE Interpret the Hjulstrom graph showing the relationship between velocity and particle size. Describe (with the aid of diagrams) how the following landforms are formed by erosion and/or deposition: Waterfalls and rapids Meanders and oxbow lakes Floodplains and levees Deltas Describe the conditions which give rise to braided and meandering channels and compare them. Describe and recognize the characteristic landforms at the 3 stages of fluvial development (upper/middle/lower stages) Describe the impact of changing base levels on a river and the resultant landforms (e.g. rejuvenation, knickpoints and terraces) Define the two types of flooding and the impacts of flooding. Know recent examples of both types of floods. Using case studies show how humans increase the hazard of flooding (e.g. by urbanization, changes in land use and deforestation) Describe the hazards associated with flooding and how the hazard can be reduced. Refer to two case studies in detail. KEY WORDS: CASE STUDY 1 : Name 2 examples of flash flooding and slow flooding CASE STUDY 2: Name examples of where humans have increased the hazard of flooding. ***CASE STUDY 3: Describe the hazards associated with flooding and how these hazards can be been reduced in TWO areas (MEDC and LEDC) LEDC: Bangladesh MEDC: Mississippi Floods a) Managing the Supply and Demand for Water b) Issues with water utilization MANAGING THE WATER SUPPLY AND WATER UTILISATION What does drainage basin management involve? Describe this ***CASE STUDY 4: The by using at least one case study. Merjedba Drainage Basin Describe different water management strategies in a one drainage basin (Case study) Discuss some issues using water as a resource on a Global scale Local scale (Tunis) Regional scale (Tunisia) ***CASE STUDY 5 : Local: Water Use in greater Tunis Regional: water Management in Tunis