Boscastle flash flood 2004
advertisement

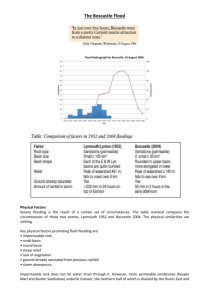
On 16 August 2004, a devastating flood swept through the small Cornish village of Boscastle. What were the physical factors responsible for this flash flood? (Flash flood: A flood caused by heavy or excessive rainfall in a short period of time, generally less than 6 hours.) They were mainly heavy rainfall and catchment characteristics that promoted rapid surface run-off. Drainage basin characteristics: o The village is located at the output point of a tiny drainage basin, whose size is just 21.5 km² in area. Small drainage basins tend to react rapidly to inputs, often giving rise to quick flow processes. o Three rivers – the Valency, Jordan and its tributary Paradise - converge on the village of Boscastle. Their confluence is in the centre of the village. o The three river valleys are very steep and narrow. As a result, surface runoff is rapid. A broader floodplain would have helped to soak up excess water and to dissipate energy more effectively (through an increased hydraulic radius). Furthermore, the steep valley sides mean that soils are thin, as a result of mass movement, with limited infiltration capacity. o The drainage basin is made of is hard sandstone with limited permeability and, therefore, percolation. High intensity rainfall: o 185mm arrived in just five hours, the majority falling in the first two hours. Under such conditions, the rate of input of rainwater greatly exceeding the infiltration capacity of any soil type. Overland flow was inevitable. o In total, an input of 3 million tonnes of water was added to this steep, tiny drainage basin in a few hours. Antecedent conditions: The soils were already saturated from previous rainfall during July and earlier in the week, encouraging overland flow as the additional input of water was unable to infiltrate the ground. Short-term conditions: o A high tide in the bay restricted the rate of exit of water leaving the basin at the river’s mouth. o A small landslide in the upper basin temporarily blocked the basin, leading to a build-up of water that suddenly burst free. What were the human factors? o Changes in farming practice in the area possibly contributed, with a reduction of trees and hedges higher up the valley (reducing interception) causing water to flow through more quickly than would have been the case in the past. o Old, small drainage systems were insufficient to cope with the high intensity rain. o A tarmac-surfaced park at the top of the village caused rapid surface runoff due to its impermeable surface.