Chemical Reactions, Chemical Equations, Electricity & Magnetism
advertisement

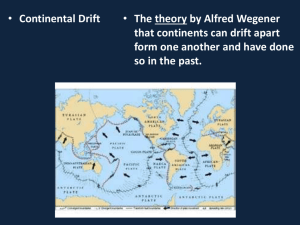
1 Evolutionary Theories Evolution – the process of change over time Pangaea – a supercontinent made up of all the world’s present landmasses joined together Natural Selection – the theory that explains how populations can eventually evolve into new species Adaptation – a trait or structure that improves an organism’s chance for survival and reproduction Continental Drift – the process by which the continents split apart from a single landmass Theory of Plate Tectonics – a theory that states that Earth’s lithosphere, or land, is broken into large sections called tectonic plates that move and change position over time Lithosphere – the uppermost layer of Earth, made up of crust and mantle Tectonic Plates – giant chunks of land or ocean floor Asthenosphere – the soft layer of the mantle made up of semisolid rock that flows slowly Convergent Boundary – the location where two tectonic plates push together Divergent Boundary – the location where two tectonic plates pull apart 2 Transform Boundary – the location where two tectonic plates slide past each other Subduction – the process in which one tectonic plate is pushed under another tectonic plate Volcano – an opening in Earth through which magma is released Magma – molten material beneath or within the Earth’s crust from which igneous rock is formed Lava – magma that reaches Earth’s surface Earthquake – the shaking of Earth’s surface that occurs when energy stored as pressure in rocks is released quickly Fault – a break or crack in Earth’s surface along which movement occurs Hot Spot – an area of volcanic activity in the middle of a tectonic plate Weathering – process in which rocks are broken down into smaller pieces through the action of wind, water, roots, and animals Mechanical Weathering – the process that breaks rocks apart without changing their chemical composition Chemical Weathering – a process that changes the chemical composition of rocks