Vocabulary Chapter 2, Section A
advertisement

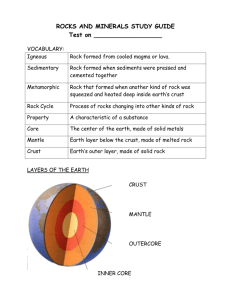
Vocabulary Chapter 3, Section A Rock: A naturally formed solid that is usually made up of one or more types of minerals. Rock cycle: The set or natural, repeating processes that form, change, break down, and re-form rocks. Igneous rock: Rock that forms as molten rock cools and becomes solid. Sedimentary rock: Rocks formed as pieces of older rocks and other loose materials get pressed or cemented together or as dissolved minerals re-form and build up in layers. Metamorphic rock: Rock formed as heat or pressure causes existing rock to change in structure, texture, or mineral composition. Sediment: Solid materials such as rock fragments, plant and animal remains, or minerals that are carried by water or by air and that settle on the bottom of a body of water or on the ground. Metamorphism: The process by which a rock’s structure or mineral composition is changed by pressure or heat. Recrystallization: The process by which bonds between atoms in minerals break and re-form in new ways during metamorphism. Foliation: The arrangement of minerals within rocks into flat or wavy parallel bands; a characteristic of most metamorphic rocks. Intrusive igneous rock: Igneous rock that forms as magma cools below Earth’s surface. Extrusive igneous rock: Igneous rock that forms as lava cools on Earth’s surface.