socal - Ocean Acoustics Library
advertisement

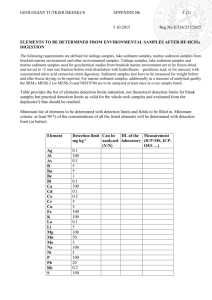
Matlab Function socal_sed.m to generate bottom properties for the South California Bight Region This program generates sediment parameters for the South California Bight region which was chosen as the test site in the last ESME workshop. The location lies between latitudes 32 N and 34.5 N and 117 W and 120 W. The program is written in such a way that given the location and the frequency of interest, the sediment properties are estimated using all the available data. The sediment information available include core data, sediment maps, sediment type information etc. For this location we were able to find some historical data which is listed below. 1. Bathymetry: Bathymetry is directly interpolated from the Navy Database (DBDBV1). 2. Core data: Deep Sea Drilling Program core data. Sites include : 467, 468, 469 (Leg 63) and 1012,1013,1014,1015 and 1017 (Leg 167). 3. Sediment type information: Emery2 gives a description of the type of sediments in the continental shelf. 4. SWellEx data: Musil et. al3 . and Bachman et. al.4 gives sediment information (type of sediment and layer thickness) at the SWellEx-96 site. 5. Sediment and geoacoustic models: Bachman5: Used for predicting the properties in the Catalina Basin. Hamilton model6: Used for predicting the compressional and shear wave speeds as well as attenuation as function of frequency for different sediment types. Bowles7: Used for predicting attenuation as a function of frequency and shear speeds for known sediment types . 6. Sediment layer thickness maps8: Used for predicting the sediment thickness. The program uses these data to arrive at the sediment parameters at a given location. The sediment compressional speed is estimated using the core data, sediment type information and the Hamilton’s values for these sediment types. Sediment thickness is estimated based on the core data and sediment thickness map. Shear speed, and Compressional and shear attenuation are determined mainly using the sediment type information and predictions by Hamilton and Stoll. The bottom properties are specified for a simple two layer model. Sediment Basement Compr. Speed, Shear Speed Attenuation, Density Compr. Speed, Shear Speed Attenuation, Density Some of the properties (compressional and shear speeds in the basement) are assumed constant throughout the area. The output parameters are also written in a text file sediment_par. They are written in the order as shown in the Appendix 1. References 1) DBDB-V : Digital Bathymetric Database – Variable resolution, http:// 128.160.23.42/dbdbv/database-doc.html. 2) Emery. K. O, “Continental shelf sediments of Southern California,” Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. Vol. 63, (1962). 3) Musil, M, Chapman, N. R and Wilmut M. J, “Range dependent matched field inversion of SWellEX-96 data using the downhill simplex algorithm,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 106 (6), (1999). 4) Bachman R. T, Schey P. W, Booth N. O and Ryan F. J, “Geoacoustic databases for matched field processing: Preliminary results in shallow water off San Diego, California, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 99(4), (1996). 5) Bachman R. T, “A Three-dimensional geoacoustic model for Catalina Basin,” Version 1.0, NraD Technical Report 1669, www.nosc.mil/sti/publications/pubs/tr/1669/ 6) Hamilton E. L, “Geoacoustic modeling of the sea floor,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 68(5), (1980). 7) Bowles F. A, “Observation on attenuation and shear-wave velocity in fine grained marine sediments,” J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101 (6), (1997) 8) Winterer E. L, “Sediment thickness map of the Northeast Pacific,” The geology of North America, Vol. N, The eastern Pacific Ocean and Hawaii, The Geological Society of America, 1989. Appendix 1. Inputs to socal_sed.m are as follows: 1. location : location specifies the location where the sediment properties are desired. It is specified as [latitude, longitude] using the latitude and longitude of the location. Currently the program can only handle only one location at a time. 2. freq : Frequency (Hz) at which the attenuation values are desired. The outputs of this function are listed as follows: The outputs of this function is written into a file sediment_par as a text file in the following order. 1. Bathymetry at the location (m) 2. Compressional wave speed in the sediment layer (m/s). 3. Thickness of the sediment layer (m). 4. Compressional speed in the basement layer (m/s). 5. Compressional wave attenuation (db/m) 6. Shear wave speed in the sediment (m/s) 7. Shear wave speed in the basement (m/s) 8. Shear wave attenuation (db/m) 9. Density in the sediment layer (g/cc) 10. Density in the basement (g/cc) Example: Let location=[33 –119] and freq=3000. Then socal_sed(location,sed) will output Sediment Properties: At location (lat,long) 33 -119 bathymetry at the location (m) 1800 Sediment Compr. Speed (m/s) 1546.7587 Depth of sediment (m) 34.86197 Compr. speed - basement (m/s) 1750 Compr. wave attenuation (dB/m) 0.1897541 Shear speed - sediment (m/s) 206.8277 Shear speed - basement (m/s) 400 Shear wave attenuation (dB/m) 45.6 Density - sediment (g/cc) 1.65 Density - basement (g/cc) 1.8