unit plan - Achievement First
advertisement

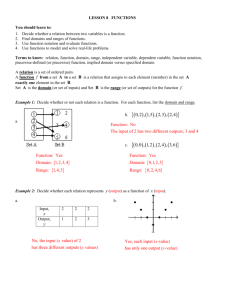
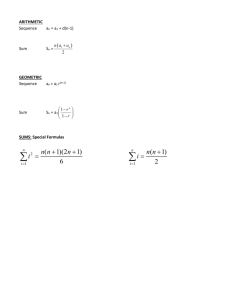
Algebra II - Unit #1 RELATIONS & FUNCTIONS UNIT OVERVIEW Unit Title Unit Designer Relations & Functions Duration IA Period 16 days #1 Stage 1: Identify Desired Results 1) Take standards from the AF Scope and Sequence. 2) Unpack the standards into Unit Aims Standard # Standard Unit Aims (SWBAT) Explain pattern relations, either for repeating patterns or A2.A.1 Describe, extend, and generalize from increasing patterns. patterns (including visual patterns as well as Predict future iterations of patterns (what would the fifth situations) increase look like?) A2.A.2 Explain why function rules used to generalize about patterns make sense given the situation. A2.A.3 Make conjectures about generalities by testing examples and by finding counter-examples. A2.A.4 Define a relation and function & determine when a relation is a function by analyzing its equation, graph, or table. A2.A.5 Determine the domain and range of a function from its equation and from its graph. Justify the domain and range using mathematical arguments. A2.A.6 Explain and use the procedure for finding xintercepts (roots) and y-intercepts algebraically. A2.A.7 Explain end behavior of a function and find the equations of asymptotes. A2.A.8 Describe the graph mathematically, including finding vertices, axes of symmetry, maximums and minimums, slopes of lines, and increasing and decreasing sections. A2.A.9 Sketch the graph of a function, given its equation (may use calculator). A2.A.10 Write functions using function notation and Create an incremental pattern relation and write their own generalization. Identify pattern relations that can be written in function form. Describe function rules and their applications to patterns. Write function rules based upon a given pattern. Write pattern identities based upon a given examples. Compare function rules against future patterns, to check for predicting ability. Define both a function and a non-function. Compare data in tables and determine whether the data represents a function. Use the vertical-line test to check for graphs of functions. Identify equations that represent functions. Define domain and range as the possible values for both the x and y values of a function. Identify the domain and range of a function using either a table or the graph. Use interval notation to describe mathematically the domain and range. Define x-intercept and y-intercepts as the point(s) where a function crosses each axes. Identify an intercept when given an equation’s graph. Solve equations algebraically to solve for the x-intercept or y-intercept. Define end behavior of a function and asymptotes. Determine end behavior of a function and describe a function’s end behavior using interval notation. Identify asymptotes of functions and write their equations. Define vertex, axis of symmetry, maximum, minimum, slope, increasing, and decreasing. Identify the vertex, axis of symmetry, slope, and maximum/minimums of a graph. Determine the sections of a graph that are increasing or decreasing. Identify and graph basic equations of graphs (y mx b, y x2 , y x3 , y x ). Use a data table to make a basic sketch of an equation. Compare and check sketches using a graphing calculator. Analyze data tables to describe functional relationships. Algebra II - Unit #1 explain why function notation is important. A2.A.11 Use function notation to evaluate functions for given values in the domain. A2.A.12 Explain whether a function is odd or even and whether a function is one-to-one, onto, or both. Translate verbal relationships to mathematical statements. Write mathematical statements in function notation. Compare the uses of function notation and tables. Describe the relationship between function notation and points on a graph. Evaluate functions for given domain values (x-values). Define odd and even functions and identify examples of each. Explain the differences between odd and even functions and give a non-example. Define “one-to-one” functions and “onto” functions. Explain the differences between one-to-one and onto functions and give an example of each. Enduring Understandings: What do you want students to know in 10 years about this topic? 1. Scholars will be able to identify pattern relations both in objects and real-life situations and apply algebraic reasoning. 2. Scholars will understand how graphs represent data and the different forms of a graph and their characteristics. 3. Scholars will be able to interpret functions and the relations they represent. Essential Questions: What questions will guide this unit and focus learning and thinking? 1. How can quickly explaining a pattern or event be useful? 2. Why are their relations in life and patterns? 3. Why do humans use graphical interpretations of data? Stage 2 : Assessment Summative assessment: Write the final unit exam that assesses all EUs and standards. Give a description of this assessment in the space below, but the write the final exam before moving onto stage 3. Exam: Unit Assessment will consist of a 60-minute exam. Exam questions will consist of analytical questions, which will ask scholars to think about the conceptual concepts they are learning and vocabulary, a multiplechoice section, and word-problems section. In each section, scholars will be expected to show their work and/or give explanations for their graphs. Formative assessment: How will you check for student understanding throughout the unit? (Quizzes, exit tickets, independent work products, etc) Exit Slips: At the end of each lesson, scholars will complete a short exit slip to check for understanding of the aims taught during the lesson. Information from these slips will be used to gage review time and practice problems. Quiz: Scholars will be given an announced quiz half-way through the unit to assess comprehensive Algebra II - Unit #1 understanding. A review session will be held the day before the quiz to allow for questions and clarifications. Homework: Each night, scholars will be assigned a selection of problems from the textbook to be completed and checked for effort the next day. Unit Vocabulary *Remember to include both new terms and cumulative review Pattern Relation Function Non-Function Function Rules Vertical Line Test Domain Range Interval Notation x-intercepts y-intercepts End Behavior Asymptote Vertex Axis of Symmetry Maximum Minimum Slope Increasing/Decreasing Odd Function Even Function Onto Function One-to-One Function Optional Sections Performance Tasks (optional) Determine product criteria and develop a rubric to evaluate student understanding. 1. Students will work collaboratively on the 48 Hour Project. During this project, students complete a large number of interrelated tasks in a short amount of time. This involves the skill of breaking up work into sub-tasks, negotiating equitable distributions of work, and helping each other by giving support and critical advice. 2. Students will improve their communication skills during the 48 Hour Project and the Seminar Problem. Algebra II - Unit #1 Over the course of the unit, they will work collaboratively on a poster, presentation, and write-up, and they will create one write-up on their own. Prior Knowledge and Prerequisite Skills (optional) List prior skills and knowledge that students would need to access to be successful in this unit. Common Misunderstandings (optional) Anticipate potential misunderstandings and incorporate this information in your lesson planning. Misconception Clarification Aim Lesson Plan Ideas (optional) Brainstorm potential activities, resources, and materials. Idea Reflections to Capture for the Future (optional) What would I do differently if I were to teach this again? Where do I need to go from here?