Restricted antimicrobials
advertisement
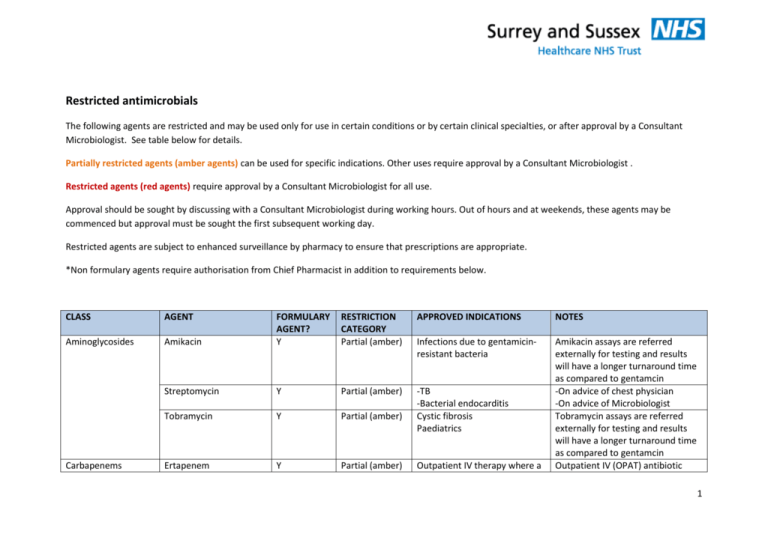
Restricted antimicrobials The following agents are restricted and may be used only for use in certain conditions or by certain clinical specialties, or after approval by a Consultant Microbiologist. See table below for details. Partially restricted agents (amber agents) can be used for specific indications. Other uses require approval by a Consultant Microbiologist . Restricted agents (red agents) require approval by a Consultant Microbiologist for all use. Approval should be sought by discussing with a Consultant Microbiologist during working hours. Out of hours and at weekends, these agents may be commenced but approval must be sought the first subsequent working day. Restricted agents are subject to enhanced surveillance by pharmacy to ensure that prescriptions are appropriate. *Non formulary agents require authorisation from Chief Pharmacist in addition to requirements below. CLASS AGENT Aminoglycosides Carbapenems RESTRICTION CATEGORY Partial (amber) APPROVED INDICATIONS NOTES Amikacin FORMULARY AGENT? Y Infections due to gentamicinresistant bacteria Streptomycin Y Partial (amber) Tobramycin Y Partial (amber) -TB -Bacterial endocarditis Cystic fibrosis Paediatrics Ertapenem Y Partial (amber) Amikacin assays are referred externally for testing and results will have a longer turnaround time as compared to gentamcin -On advice of chest physician -On advice of Microbiologist Tobramycin assays are referred externally for testing and results will have a longer turnaround time as compared to gentamcin Outpatient IV (OPAT) antibiotic Outpatient IV therapy where a 1 carbapenem is required Cephalosporins Imipenem Meropenem Y Y Partial (amber) Partial (amber) Cefotaxime Y Partial (amber) Ceftriaxone Y Partial (amber) Cefixime Y Partial (amber) Ceftazidime Y Partial (amber) See meropenem -Treatment of infections due to multiresistant gram negative bacteria -Severe hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) or ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP) if allergic to penicillin (not anaphylactic) -Severe sepsis if penicillin allergy or ESBL -Complex UTI – if recent ESBL -Haematology / Neutropenic sepsis -ICU -Bacterial meningitis -Typhoid fever -Epiglottitis -Paediatrics -Bacterial meningitis -PID -Gonorrhoea -Typhoid fever -Outpatient IV (OPAT) -Typhoid fever -Oral therapy of resistant organisms -Paediatrics -Pseudomonas infections (penicillin allergy or no choice should be discussed with Consultant Microbiologist prior to discharge Use in other conditions requires approval from Consultant Microbiologist -Use of 3rd generation cephalsosporins must be kept to a minimum in inpatients due to very high risks of C.difficile -Where ceftriaxone is planned to be used as outpatient parenteral antibiotic therapy (OPAT) in current inpatients, it should be started just prior to discharge. Inpatients should not receive ceftriaxone if discharge is not imminent due to high risk of C.difficile – use appropriate inpatient regimen 2 Cyclic polypeptide Daptomycin Y Restricted (red) Echinocandins Caspofungin N* Partial (amber) Fosfomycins Fosfomycin Partial (amber) Glycopeptides Teicoplanin Vancomcyin IV N* (unlicensed) Y Y Vancomycin PO Y Partial (amber) Tigecycline Y Restricted (red) Glycylcyclines Partial (amber) Partial (amber) alternative agents) Nil -Haematology -ICU -altenative to amphotericin for febrile neutropenia -alternative for invasive aspergillosis -candidaemia caused by nonalbicans or mfluconazoleresistant candida -Oral treatment of UTI due to ESBL producing coliforms -Treatment of infections caused by resistant gram positive organisms e.g. MRSA -Prophylaxis and treatment of infection in MRSA colonised patients -Prophylaxis and treatment of infection in penicillin-allergic patients and where other antibiotics are contraindicated Severe C.difficile associated disease Nil Reserved for serious gram positive infections where no suitable alternative agent is available Has no activity against Cryptococcus See relevant section of policy with regards to dosing and monitoring. Serum level monitoring may be required. This is the only indication for oral vancomycin See C.difficile care pathway for full details of C.difficile investigation and treatment Reserved for complicated skin and soft tissue infections and complicated intra-abdominal 3 infections, and other infections where no suitable alternative agent. NB This agent has no antipseudomonal activity Macrolides Azithromycin Y Partial (amber) -Chlamydial infections / GUM -Paediatrics -Typhoid fever Nil Oxazolidinones Linezolid (PO or IV) Y Restricted (red) Penicillins Co-amoxiclav IV / PO Y Partial (amber) -Pyelonephritis -Orbital/pre-septal cellulitis -Rhinosinusitis (persistent) -Diabetic foot infection -Animal/human bite -Severe community acquired pneumonia (CAP) -COPD exacerbation (severe, or no response to 1st line) -Hospital acquired pneumonia -Intra-abdominal sepsis Piperacillin-tazobactam Y Partial (amber) -ICU -Haematology / neutropenic sepsis -Cholangitis / liver abscess / spontaneous bacterial peritonitis/ other severe intraabdominal sepsis Used for serious gram positive infections caused by resistant organisms (e.g. MRSA, VRE) where no suitable alternative exists. Also PVL-producing S.aureus infections Use in other conditions requires approval by Consultant Microbiologist Use in other conditions requires approval by Consultant Microbiologist 4 Polyenes Polymyxins Pyrimidines Quinolones Pivmecillinam N* Partial (amber) Lipid associated Amphotericin B (e.g. Ambisome) Colistin (Colomycin) IV and by nebulisation Y Partial (amber) Y Partial (amber) Flucytosine Ciprofloxacin (IV) Y Y Partial (amber) Partial (amber) Ciprofloxacin (PO) Y Partial (amber) -Pseudomonas infections or other bacterial infections where narrower spectrum antibiotics are not active -Severe hospital acquired pneumonia (HAP) or ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP) -Severe sepsis -Necrotising fasciitis / Fournier’s gangrene -Oral treatment of UTI due to ESBL producing coliforms -Serious suspected or confirmed fungal infections -Haematology -severe gram negative infections resistant to other antimicrobial agents and where no other alternatives -chronic respiratory infection (Pseudomonas) – nebulised colistin -Cryptococcal meningitis -Haematology / neutropenic sepsis -ICU -Initial treatment for PO indications below if unable to take PO medication (switch to oral as soon as possible) -UTI where resistance to other May be combined with coamoxiclav 375mg tds po to enhance activity against ESBL producing coliforms. Used mainly in UTIs. IV Colistin has significant toxicity – it should only be used where no alternatives and where recommended by Consultant Microbiologist High risk for C.difficile – use alternative agents where possible High risk for C.difficile – use 5 Ofloxacin Y Partial (amber) Moxifloxacin (PO) Levofloxacin (PO,IV) Norfloxacin (PO) Y Y Y Partial (amber) Partial (amber) Partial (amber) Streptogramins Quinupristin/Dalfopristin Y Restricted (red) Triazoles Voriconazole Partial (amber) N* antibiotics -Prostatitis -ERCP prophylaxis -Malignant otitis externa -Typhoid and paratyphoid fever -Oral treatment of P.aeruginosa infections -Liver abscess (penicillin allergy) -Diabetic foot ulcer -Severe sepsis (penicillin allergy) -ICU -Haematology / neutropenic sepsis -Salmonella enteritis (Micro recommended) -Bacillary dysentery -Typhoid fever (only if fully sensitive) -Complex UTI in urology patients -Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) -Respiratory medicine -Pneumonia (penicillin allergy) -Prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis -Haematology alternative agents where possible For serious infections where no suitable alternative agent is available Cautions – drug interactions 6 Others Other agents used in specialist groups -Systemic Aspergillus infection or other invasive mycosis -Systemic Candida infection due to non-albicans candida Hydatid disease, strongloides Albendazole N* Restricted (red) Chloramphenicol N* Partial (amber) Clindamycin Y Partial (amber) Co-trimozaxole Y Partial (amber) Foscarnet Y Partial (amber) -Meningitis if severe cephalosporin allergy -Serious infections due to resistant bacteria -Staphylococcal infections of soft tissue and bone -Human and animal bites -Group B streptococcal prophylaxis (maternity) -Adjunctive treatment of severe soft tissue infection / streptococcal toxic shock / PVL staphylococcal infection -Pneumocystis pneumonia / infection -S.maltophilia infection -CMV infection Gancyclovir IV Y Partial (amber) -CMV infection Rifampicin Y Partial (amber) Anti-tuberculous agents e.g. capreomycin, cycloserine, ethambutol, Y Partial (amber) -Staphylococcal infection (in combination only) -Prosthetic joint infection (in combination only) -TB common Used on advice of Consultant Microbiologist Used on advice of Consultant Microbiologist On advice of Haematologist or Microbiologist On advice of Haematologist or Microbiologist On advice of Consultant Microbiologist On advice of chest physician 7 isoniazid, pyrazinamide, rifabutin, rifampicin, rifanah, rimactazid Antivirals (antiretrovirals) – see formulary for full list available Antivirals (hepatitis) see formulary for full list available Y Partial (amber) -HIV On advice of GUM physician Y Partial (amber) -Viral hepatitis B & C On advice of Gastroenterologist 8