Palliative Care Symptom Management Guidelines
advertisement

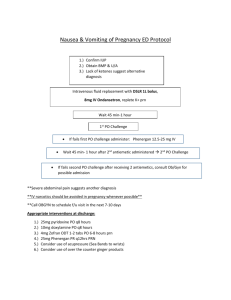
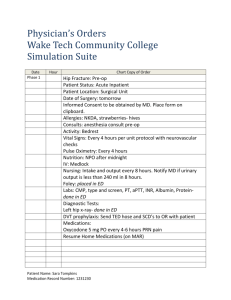
LifeCare Palliative Care Symptom Management Guidelines Agitation, anxiety, delirium and depression management: Nursing interventions: Reduce sensory stimulation Restore/re-orient routines Use client/patient/resident’s adaptive devices (glasses, hearing aids, etc.) Calm fears for agitation and anxiety Educate the client/patient/resident and family about the use of guided imagery CDs and relaxation techniques Consult spiritual care Medical interventions: Alprazolam (Xanax) 0.25-0.5mg TID PO PRN for anxiety Citalopram (Celexa) 10mg to 40 mg daily PO for depression or anxiety Haloperidol (Haldol) 0.5 mg PO/IV/subcutaneous, titrate up to 5 mg every hour a daily requirement is established and then administer in 2-3 divided doses daily PRN for agitation, anxiety, physical aggression with the potential to cause harm and/or hallucinations or delusions that are causing the client/patient/resident distress. Maximum daily dose is 30 mg/24 hours. Evaluate after each dose. Mirtazapine (Remeron) 7.5-15 mg daily PO for depression Sertraline (Zoloft) 25-200mg daily PO for depression or anxiety Refer to Social Services Refer to Behavioral Health Anorexia/cachexia management: Nursing interventions: Education with client and family including: o Exploration of the meaning of feeding o Types of appealing food and drinks o Use of small portions on small plates o Artificial hydration/nutrition considerations o Minimizing odors that suppress appetite o Use of essential oils that stimulate appetite Consult dietary Medical interventions: Dexamethasone (Decadron)2-6 mg PO daily maximum dose 6 mg/24hours. Metoclopramide (Reglan) 10-20 mg PO 30 minutes before meals and HS Medical interventions: Docusate sodium 100-400 mg PO BID, maximum dose 800mg/24hours Senna 1-4 tabs PO BID Docusate/senna 1-4 tablets PO BID Magnesium hydroxide (MOM) 30 ml PO daily PRN Page Nursing interventions: Educate family and client including: o Increasing fluids and high fiber foods o Encouraging more activity o Ensuring privacy for bowel movements 1 Constipation management/Bowel care Ensure orders have been obtained for constipation/bowel care if opioids are prescribed. Polyethylene Glycol (Miralax) 17 grams PO daily mixed in 8 oz of liquid PRN Cough Management Nursing interventions: Elevate head of bed to 30° Add room humidifier Medical interventions: Benzonatate (tessalon) 200mg PO TID PRN Guaifenesin & dextromethorphan (Robitussin DM) 5 ml PO every 2 hours PRN Guaifenesin with codeine 5 ml PO every 2 hours PRN Diarrhea management Medical interventions: Loperamide (Imodium) 4 mg initially then 2 mg after each loose BM to a maximum of 16 mg/24 hours Dry eyes/nose management Nursing interventions: Add humidification to room Medical interventions: Artificial tears 1-2gtts each eye PRN Eye lubricant (artificial tears) ¼ to ½ inch in lower lid BID PRN Saline nasal spray in each nostril PRN Dyspnea management Nursing interventions: Semi-fowlers positioning as comfortable for client Add a fan to room Open a window Oxygen at 2 liters via nasal canula PRN, may titrate up for comfort, using caution with clients with COPD Pulse oximetery if it will result in a change in treatment or therapy plan Medical interventions: Albuterol 2.5mg/3ml by nebulizer every 4 hours Albuterol/ipratropium (Duoneb) in 3 ml by nebulizer every 4 hours Alprazolam 0.25-0.5mg TID PO PRN Furosemide 5-40 mg PO every hour PRN for dyspnea and rales Morphine 2.5 mg PO/SL every hour PRN, evaluate after each dose Morphine 0.5 mg IV every 15 minutes PRN Oxycodone 2.5-10 mg PO/SL every hour PRN, evaluate after every dose Fatigue Management 2 Medical interventions Prednisone 7.5-10mg PO daily Page Nursing interventions Educate client and family including: o Promote adaptation and prioritization of activities o Encourage mild exercise and activity o Schedule rest periods Fever Management Nursing interventions: Tepid sponge baths Cool clothes to groin, armpits and forehead Minimal covers Medical interventions: Acetaminophen 650mg every 6 hours PO/rectally PRN Acetaminophen 1000 mg every 4 hours PO/Rectally PRN. Not to exceed 4 gm/24 hours. Ibuprofen 400-800mg every 4 hours PO PRN. Not to exceed 3200mg/24 hours May alternate ibuprofen dose with acetaminophen 650 mg every 4 hours PRN Hiccup Management Nursing interventions: Educate family and client on nonpharmacological interventions, such as: o Soft palate massage o Holding ice water in the oropharynx o Swallow 2 teaspoons of sugar o Swallow dry bread o Tongue traction enough to trigger gag reflex Medical interventions: Chlorpromazine 25-50 mg PO every 6 hours PRN Baclofen 5 mg PO every 8 hours PRN, reduce dose for clients with renal dysfunction Nausea & Vomiting Management Nursing interventions: Educate client and family o Avoidance of smells that trigger nausea o Incorporate relaxation techniques o Use of essential oils such as ginger Medical interventions: Dexamethasone 1-20 mg PO daily, may be given in divided doses, reevaluate in 7 days Prochlorperazine 25 mg suppository rectally every 12 hours PRN Haloperidol 2 mg PO/SQ/IV BID PRN Lorazepam 0.5 – 1.5 mg PO every 4 hours Metoclopramide (Reglan) 10-20 mg PO/IV QID 30 minutes before meals and at hs Medical interventions: Artificial saliva every hour PRN Topical viscous lidocaine 2% 5 ml every 4 hours PO PRN, swish and spit Miracle mouth wash (equal parts viscous lidocaine 2%, disphenhydramine 12.5 mg/2ml, and antacid 200/200/20 mg/5ml) 5 ml every hour PRN, swish and spit or swish and swallow Candid treatment: Nystatin (100 000units/ml) 5 ml swish and swallow QID x 7 days, then reevaluate Fluconazole 200 mg PO initially then 100 mg PO for 7 days, then reevaluate Page Nursing interventions: Educate family and client including: o Use of a soft toothbrush or toothette o How to clean dentures o Food preparation: lukewarm, nothing too hot/cold, mildly spiced, soft foods o Lip balm as needed to keep lips moist o Salt solution, 1 tsp salt in 1 c H2O, 15-30 ml. Swish and spit 4 times daily as needed 3 Oral Care Management Pain Management Neuropathic pain: Amitriptyline10-25 mg daily PO HS PRN (avoid use in elderly clients) Gabapentin 100 mg PO daily at HS, titrate up to 300mg BID , then 300mg TID Gabapentin ( for elderly population) 100 mg PO daily at HS, titrate up to 100mg BID then 100mg TID Pregabalin 50 mg PO TID, evaluate in 7 days (decrease dose for clients with renal dysfunction) Transdermal lidocaine patch (1-3 patches), apply for 12 hours then remove for 12 hours 4 Medical interventions: Mild pain: Acetaminophen 1000 mg every 6 hours PO PRN Acetaminophen 650 mg every 4 hours PO PRN, not to exceed 4 gm /24 hours Ibuprofen 400-800 mg PO every 4 hours PRN, not to exceed 3200 gm/24 hours Naproxen 250 mg PO BID PRN Tramadol 25-100 mg PO QID PRN (reduce dose in clients with renal dysfunction; not to exceed 400 mg/24 hours) Hydrocodone/APAP 5/500mg 1-2 tabs PO every 4 hours PRN Oxycodone/APAP 5/500mg 1-2 tabs PO every 4 hours PRN Malignant Bone Pain: Ibuprofen 400-800mg PO QID Naproxen 250 mg PO BID Dexamethasone 3-12 mg PO TID Opioid medication for moderate to severe pain Hydromorphone (Dilaudid) 2 mg PO every 1 hour PRN Hydromorphone 0.1 mg IV every 15 minutes PRN Morphine 0.5 mg IV every 15 minutes PRN Morphine 10 mg PO every hour PRN Morphine SR (MS Contin)15 mg PO every 12 hours Oxycodone IR 5-10 mg every hour PRN Oxycodone SR 10 mg PO every 12 hours Page Nursing interventions Educate client and family of nonpharmacological interventions including: o Guided imagery CDs o Essential oils such as Pam Away, ginger o Diversional techniques o Massage o Social work referral PRN to teach relaxation techniques Secretion Management Medical interventions: Atropine 1% ophthalmic solution 1-4gtts every 2 hours PRN Scopolamine 1.5 mg transdermal patch behind ear, change every 72 hours PRN. May increase to 3 patches changed every 72 hours PRN Seizure Management Nursing intervention: Educate family o Not to put anything in mouth of client, especially fingers o How to place client in a recovery position. Medical interventions: Lorazepam 2-4mg IV/SQ PRN, may repeat in 15 minute intervals if seizure continues, maximum 8 mg/ 12 hours Diazepam 5-10 mg IV/Buccal/IM every 15 minutes to a maximum of 30 mg PRN Diazepam 0.2 mg/kg rectally for seizures, may repeat one time in 4 hours PRN, maximum of one course of treatment every 5 days. Medical interventions: For wound pain: Hydromorphone 2-4mg PO every hour PRN Morphine 1 mg in 1 gram hydrogel applied to cover wound surface daily To control odor: Metronidazole 500 mg PO TID x 7 days, reassess Metronidazole 500mg crushed and sprinkled into wound daily x 7 days. Reassess Silver sulfadiazine cream 1% applied to wound surface daily, assess in 7 days For Pruritus: Hydroxyzine 10-25 mg PO every 6 hours PRN Doxepin 10-25 mg PO daily HS, use for 7 day and evaluate Paroxetine 10-20 mg PO daily Diphenhydramine 25 mg every 4 hours PO PRN Hydrocortisone 1% cream or lotion applied TID PRN Triamcinolone 0.1% cream topically TID PRN Pressure ulcers and malignant wounds: Cleanse wound with NS or non-cytotoxic Page Nursing interventions: Do a Braden skin risk assessment, if warranted start safety protocol Over the counter moisturizing lotion as needed for dry skin and discomfort of itch Peppermint oil for odor, on bed linen or in room, not on ulcer Kitty litter, coffee grounds or activated charcoal placed in dish under bed to absorb odor Lavender oil mixed in carrier oil apply to skin for itch Use of pressure reducing mattress, where available Heel protection Evaluate chairs, wheelchairs, etc., for appropriate pressure relieving surfaces Educate family and client including: o Causes and risks for pressure areas o Mobilization o Minimizing friction and sheer o Moisture control on skin o Nutrition and hydration o Techniques for odor control o Wound cleansing and irrigation Administer PRN pain med ½ hour prior to dressing change 5 Skin and Wound Management wound cleanser For low to moderate amounts of exudates in stage 2-3 ulcers: o Hydrocolloid dressing; change every 2-5 days o Foam dressing, change every 3-5 days For copious exudates: o Alginate (avoid in bleeding wounds). Apply topically within wound borders, change every 2-4 days o Ostomy appliance to contain drainage from fungating wounds To prevent bleeding: o Use non adherent absorbing dressings o Moisten dressings with NS before removal To manage active bleeding: o Apply gauze saturated with 1:1000 solution of epinephrine o Apply firm pressure to wound Sleep Disturbance/Insomnia Management Nursing interventions: Educate client and family including: o Good sleep environment o Relaxation therapies o Avoidance of stimulants such as caffeine o Use of essential oils such as Peace & Calm or lavender Medical interventions: Alprazolam 0.25 to 0.5mg may repeat dose in 1-2 hours Temazepam 15 mg PO at HS PRN may repeat x 1 dose Trazodone 25-100 mg PO HS PRN, may repeat x 1 dose Zolpidem 5-10 mg PO HS PRN Urinary Incontinence and/or Retention Management 6 Medical interventions: Oxybutynin 2.5mg PO2-4 times daily PRN for bladder spasms Straight/indwelling catheter PRN Page Nursing interventions: Bladder scan PRN to confirm retention Rectal exam to rule out fecal impaction