Townfield calc policy posters 2015
advertisement

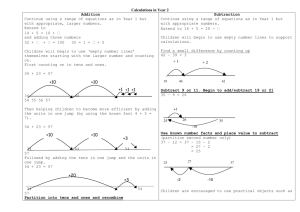
Calculation Policy from September 2014 Year 1 Addition Subtraction + = signs and missing numbers 3+4= 3+=7 +4=7 +=7 =3+4 7=+4 7=3+ 7=+ Promoting covering up of operations and numbers. 7+4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Recording by drawing jumps on prepared lines and constructing own lines. ( Teacher models number lines with missing numbers) Division Pictures and marks Pictures and marks Sam spent 4p. What was his change from 10p? There are 3 sweets in one bag. How many sweets are there in 5 bags? 12 children get into teams of 4 to play a game. How many teams are there? - = signs and missing numbers (Recording on a number line modelled by the teacher when solving problems) 7-3= 7-=4 -3=4 -=4 Number lines (numbered) Multiplication Pictures and marks =7-3 4=-3 4=7- 4=- Use of bead strings to model groups of. A bag of 12 sweets is shared among 4 children. How many sweets will each child get? (sharing) 12 sweets are placed in bags of 4. How many bags can I make? (grouping) Number lines (numbered) 11 – 7 (Counting back) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Number bonds to 10. The difference between 7 and 11 (counting on) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Experiencing division as sharing and as grouping. 9 10 11 12 Recording by drawing jumps on prepared lines and constructing own lines. ( Teacher models number lines with missing numbers) (Teachers model jottings appropriate for larger numbers) Calculation Policy from September 2014 Year 2 Addition Subtraction + = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 1 but with appropriate, larger numbers. Extend to 14 + 5 = 10 + 35 = + 5 Use Dienes blocks to support. Partition into tens and ones and recombine Use hundred square to consolidate mental image i.e. counting down adds 10 – counting up subtracts 10 12 + 23 = 10 + 2 + 20 + 3 = 30 + 5 = 35 Refine to partitioning the second number only: 23 + 12 = 23 + 10 + 2 = 33 + 2 = 35 Multiplication x = signs and missing numbers ÷ = signs and missing numbers 14 + 5 = 20 - 32 + = 50 Use Dienes blocks to support. 7x2= 7 x = 14 x 2 = 14 x = 14 6÷2= 6÷=3 ÷2=3 ÷=3 Find a small difference by counting on Arrays and repeated addition 42 – 39 = 3 +1 2x4 +2 =2x7 14 = x 7 14 = 2 x 14 = x =6÷2 3=6 ÷ 3=÷2 3=÷ Understand division as sharing and grouping 4x2 Sharing – 6 sweets are shared between 2 people. How many do they have each? or repeated addition 39 40 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 (or 4 + 4) 42 Subtract 9 or 11. Begin to add/subtract 19 or 21 35 – 9 = 26 +1 0 +10 +2 26 25 23 35 33 Add 9 or 11 by adding 10 and adjusting by 1 35 + 9 = 44 +10 Counting back where appropriate Use known number facts and place value to subtract (partition second number only) -1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 6 2 can be modelled as: Grouping – There are 6 sweets. How many people can have 2 each? (How many 2’s make 6?) 37 – 12 = 37 – 10 – 2 = 27 – 2 = 25 27 25 44 1 35 -10 35 Division - = signs and missing numbers 37 45 -2 -10 0 2 4 6 Calculation Policy from September 2014 Year 3 Addition Subtraction + = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 1 and 2 but with appropriate, larger numbers. 58 + = 100 35 = + 9 Division - = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year and 2 but with appropriate numbers. x = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 2 but with appropriate numbers. ÷ = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 2 but with appropriate numbers. Find a small difference by counting on Continue as in Year 2 but with appropriate numbers e.g. 102 – 97 = 5 Number lines Understand division as sharing and grouping 18 ÷ 3 can be modelled as: Sharing – 18 shared between 3 Grouping - How many 3’s make 18? Subtract mentally a ‘near multiple of 10’ to or from a two-digit number Continue as in Year 2 but with appropriate numbers e.g. 78 – 49 is the same as 78 – 50 + 1 Partition into tens and ones and recombine Partition both numbers and recombine. Refine to partitioning the second number only e.g. 36 + 53 = 53 + 30 + 6 = 83 + 6 = 89 +30 Multiplication Subtract 9 or 11 to whole numbers. Begin to add/subtract 19 or 21, 29 or 31. 6 Doubling multiples of 5 up to 50 Partition using grid method to present 87 30 60 x 97 2 -5 84 – 56 = 28 + 20 +4 60 20 + 10 = 30 Use known facts and place value to carry out simple multiplications. Use the Grid Method as above (partitioning) +4 80 7 14 = 60 + 14 = 74 OR Partition: 15 x 2 -10 Counting forward (complementary addition) 56 18 Arrays and repeated addition Continue to understand multiplication as repeated addition and continue to use arrays. 89 Add a near multiple of 10 to a two-digit number Continue as in Year 2 but with appropriate numbers e.g. 35 + 19 is the same as 35 + 20 – 1. 12 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 Remainders Sharing - 16 shared between 3, how many left over? Grouping – How many 3’s make 16, how many left over? 35 x 2 = 70 97 – 15 = 82 +6 83 0 Counting back in ‘jumps’ 82 53 6x3 84 X 3 30 90 e.g. 32 x 3 =96 2 6 = 90 + 6= 96 0 3 16 ÷ 3 = 5 r1 6 9 12 15 16 Calculation Policy from September 2014 Year 4 + = signs and missing numbers - = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 3 but with appropriate numbers. x = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 3 but with appropriate numbers Add the nearest multiple of 10 Continue as in Year 2 and 3 but with appropriate numbers e.g. 63 + 29 is the same as 63 + 30 - 1 Find a small difference by counting up e.g. 5003 – 4996 = 7 This can be modelled on an empty number line Pencil and paper: The Grid Method Expanded pencil and paper method To support the step towards column addition the children will be taught to partition within the standard written form. Use known number facts and place value to subtract mentally 3 + 6=93 82 20 7 140 8 -10 Pencil and paper procedures Complementary addition 754 – 86 = 668 +0.7 8.5 +600 +14 9.2 3 21 0 +6 6 +6 12 +6 18 +6 24 30 =140+21=161 Pencil and paper: Chunking 114 ÷ 6 92 -5 +3.0 +6 x 30 500 + 40+ 7 + 300+ 80+ 9 800+120+16 = 936 5.5 23 x 7 = x Adding decimal numbers 5.5 + 3.7= Grouping Recall methods from year 3 30 ÷ 6 can be modelled as: 92 – 15 = 77 77 547+389= ÷ = signs and missing numbers 86 100 2 2100 60 560 16 = 2160 = 576 Recombine using thousands, hundreds, tens and units: 2000 + 600 + 130 + 6 = 2736 Estimate and check. +54 700 70 754 x10 0 x9 60 114 Calculation Policy from September 2014 Year 5 + = signs and missing numbers Add the nearest multiple of 10, then adjust Continue as in Year 3 and 4 but with appropriate numbers e.g. 630 + 299 is the same as 630 + 300 - 1 Use formal methods of addition: - = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 4 but with appropriate numbers. Pencil and paper procedures: Counting back Pencil and paper: Grid method 920 – 150 = 770 372 x 24 is approximately 400 x 20 = 8000 820 770 920 358 + 73 = 3 5 8 + 7 3 4 3 1 1 1 x = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 4 but with appropriate numbers, including decimal numbers. -50 -10 0 x 300 70 2 20 6000 1400 40 = 7440 4 1200 280 8 = 1488 + 8928 Complementary addition Begin to use short multiplication 754 – 186 = 668 +500 +14 186 200 +54 700 754 ÷ = signs and missing numbers Recall methods from year 4 Remainders Quotients expressed as fractions or decimal fractions 61 ÷ 4 = 15 ¼ or 15.25 41÷ 4 = 10 r1 x10 0 41 OR 40 41 = (10 x 4) + 1 Remainders Quotients expressed as fractions or decimal fractions 676 ÷ 8 = 84.5 41÷ 4 = 10 r1 8006 – 2993 = 5013 Short Division Beginning to use decomposition 2 4 1 352 -178 174 +1 Calculation Policy from September 2014 Year 6 + = signs and missing numbers Continue using formal methods of addition - = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 5 but with appropriate numbers. x = signs and missing numbers Continue using a range of equations as in Year 5 but with appropriate numbers, including decimal numbers. Pencil and paper: decomposition Pencil and paper procedures Short Multiplication Add the nearest multiple of 10, 100 or 1000, then adjust Continue as in Year 2, 3, 4 and 5 but with appropriate numbers including extending to adding 0.9, 1.9, 2.9 etc Add the nearest multiple, then adjust Continue as in Year 5 but with appropriate numbers e.g. 6389 + 1299 is the same as 6390 + 1300 - 2 Pencil and paper procedures Extend to numbers with any number of digits and decimals with 1 and 2 decimal places. 124.9 + 117.25 = 242.15 124.90 (note the addition of a zero) + 117.25 242.15 11 Solve problems involving decimal numbers. Long Multiplication ÷ = signs and missing numbers Use formal method for division when appropriate: long division