Word file (31 KB )
advertisement
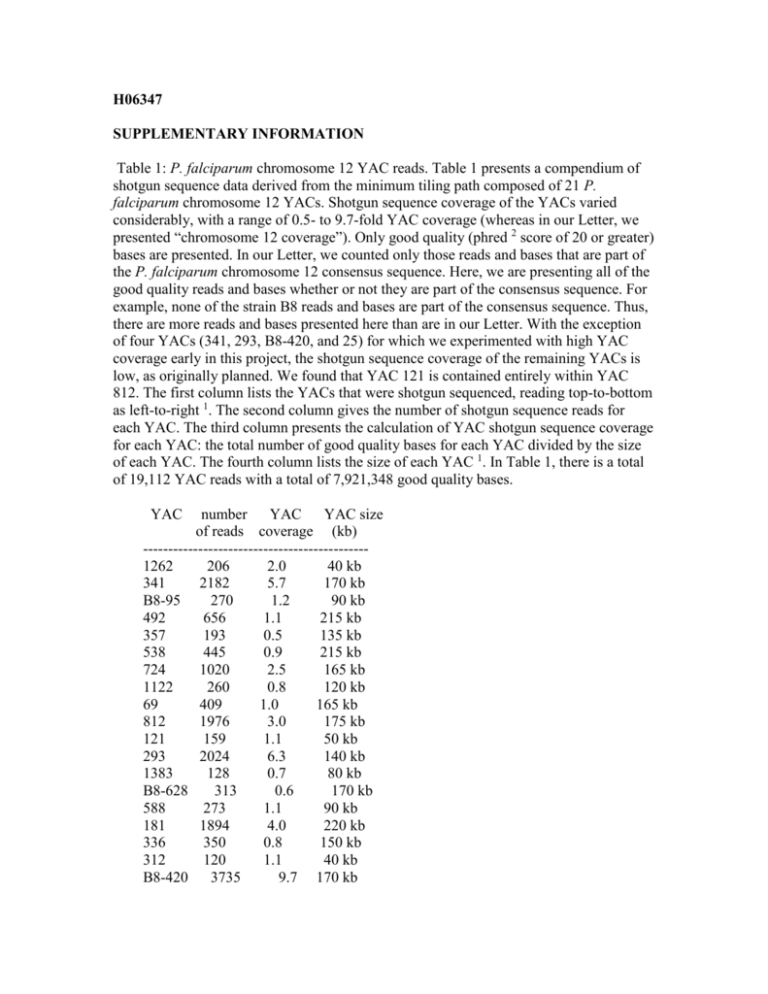
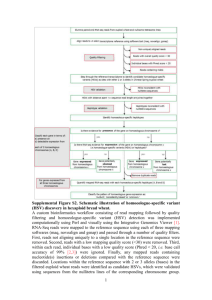
H06347 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Table 1: P. falciparum chromosome 12 YAC reads. Table 1 presents a compendium of shotgun sequence data derived from the minimum tiling path composed of 21 P. falciparum chromosome 12 YACs. Shotgun sequence coverage of the YACs varied considerably, with a range of 0.5- to 9.7-fold YAC coverage (whereas in our Letter, we presented “chromosome 12 coverage”). Only good quality (phred 2 score of 20 or greater) bases are presented. In our Letter, we counted only those reads and bases that are part of the P. falciparum chromosome 12 consensus sequence. Here, we are presenting all of the good quality reads and bases whether or not they are part of the consensus sequence. For example, none of the strain B8 reads and bases are part of the consensus sequence. Thus, there are more reads and bases presented here than are in our Letter. With the exception of four YACs (341, 293, B8-420, and 25) for which we experimented with high YAC coverage early in this project, the shotgun sequence coverage of the remaining YACs is low, as originally planned. We found that YAC 121 is contained entirely within YAC 812. The first column lists the YACs that were shotgun sequenced, reading top-to-bottom as left-to-right 1. The second column gives the number of shotgun sequence reads for each YAC. The third column presents the calculation of YAC shotgun sequence coverage for each YAC: the total number of good quality bases for each YAC divided by the size of each YAC. The fourth column lists the size of each YAC 1. In Table 1, there is a total of 19,112 YAC reads with a total of 7,921,348 good quality bases. YAC number YAC YAC size of reads coverage (kb) --------------------------------------------1262 206 2.0 40 kb 341 2182 5.7 170 kb B8-95 270 1.2 90 kb 492 656 1.1 215 kb 357 193 0.5 135 kb 538 445 0.9 215 kb 724 1020 2.5 165 kb 1122 260 0.8 120 kb 69 409 1.0 165 kb 812 1976 3.0 175 kb 121 159 1.1 50 kb 293 2024 6.3 140 kb 1383 128 0.7 80 kb B8-628 313 0.6 170 kb 588 273 1.1 90 kb 181 1894 4.0 220 kb 336 350 0.8 150 kb 312 120 1.1 40 kb B8-420 3735 9.7 170 kb 614 25 995 1504 5.1 8.4 80 kb 90 kb Table 2. P. falciparum chromosome 12 reads. Table 2 presents a summary of our P. falciparum chromosome 12 sequence reads. Only good quality (phred 2 score of 20 or greater) bases are presented. The top half of the table lists the data from shotgun sequencing chromosome 12. The first column lists the vector (M13 phage or pUC plasmid) and type of dye chemistry (dye-primer, dye-terminator, and BigDye-terminator) used for detection on polyacrylamide gels. The second column gives the number of reads. The third column presents the calculation of raw chromosome 12 coverage for each category: the total number of good quality bases divided by the size of P. falciparum chromosome 12. The lower half of the table gives the number of reads accumulated during the finishing process. In the first column, these reads are divided into groups based upon the sequencing template: PCR products (sequenced in whole or in part for physical gap filling, sequencing the complementary strand, or validation reaction product), existing M13 or pUC templates employed for primer-extension sequencing, and existing M13 templates for PCR to synthesize and sequence the complementary strand ("M13 reverses"). All finishing sequence reactions were conducted with BigDye-terminator chemistry. Whereas in our Letter we included only those reads/bases that support the chromosome 12 consensus sequence, here we are including all of our data. Therefore, the numbers in Table 2 are higher than the numbers in our Letter. At the beginning of this large-scale sequencing project, we achieved a combined total of 4.4-fold chromosome 12 coverage with dye-primer and dye-terminator chemistries. For the M13-based reads, the average good quality read lengths were 342 bases (b) for the dye-primer chemistry and 412 b for the dye-terminator chemistry. A comparison of these two numbers explains why we undertook such limited sequencing with dye-primer chemistry. With BigDyeterminator chemistry, the average good quality read length in the M13-based vector was 460 b. This considerable improvement in good quality read length explains why we switched from dye-terminator chemistry to BigDye-terminator chemistry as soon as BigDye-terminator chemistry became available commercially. Employing BigDyeterminator chemistry, we achieved 6.89-fold chromosome 12 coverage. Thus, in total, we achieved 8.7-fold shotgun sequence coverage of P. falciparum chromosome 12. However, the P. falciparum chromosome 12 preparations were approximately 80% pure 3 . Therefore, unsurprisingly, roughly 20% of our P. falciparum chromosome 12 shotgun reads did not assemble into chromosome 12. These reads are presumptive contaminants derived from other P. falciparum chromosomes. We imported the equivalent nonassembled reads from our colleagues at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute and the Institute for Genomic Research. Using a stringent standard, we conducted our matching procedure with those imported reads and our bins. As the result of this matching process, we found an additional 7,007 shotgun sequence reads ("imported" in Table 2). As we did not have phred scores for the bases, we could not calculate coverage for these reads. Shotgun Number of reads Coverage M13 dye-primer 1,857 0.17 M13 dye-terminator 12,389 1.64 M13 BigDye-term 41,898 6.89 pUC dye-term imported 13,388 7,007 2.58 --- Finishing PCR reads primer-extension M13 reverses 303 6,901 205 0.03 1.02 0.04 1. Rubio, J. P., Thompson, J. K. & Cowman, A. F. The var genes of Plasmodium falciparum are located in the subtelomeric region of most chromosomes. Embo J 15, 4069-77. (1996). 2. Ewing, B., Hillier, L., Wendl, M. C. & Green, P. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res 8, 175-85. (1998). 3. Su, X. Z. & Wellems, T. E. Plasmodium falciparum: assignment of microsatellite markers to chromosomes by PFG-PCR. Exp Parasitol 91, 367-9. (1999).