02_SWP_BCA protein assay_JC
advertisement

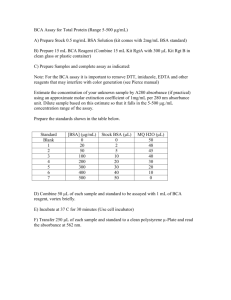
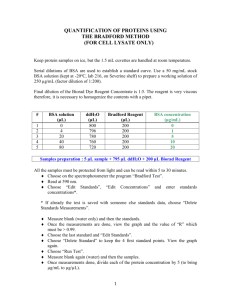
OHS026 Safe Work Procedure Faculty/Division: Medicine School/ Divisional Unit School of Medical Sciences ORU/NRM Document number SOMS.CGM.SWP002 Initial Issue date 26-6-09 Current version 1.0 Current Version Issue date 26-6-09 Next review date 26-6-12 The Writing Safe Work Procedures Guideline (OHS027) should be consulted to assist in the completion of this form. Safe Work Procedure Title and basic description Title: BCA Protein Assay Description: Quantifies amount of protein in samples of lysed cell extracts Associated risk assessment title and location: 02_RA_BCA Protein Assay_JC Describe the activity or process The BCA Protein Assay is a complete kit supplied by Thermo Scientific (formerly Pierce). The procedure is as per the instructions supplied by the manufacturer. The assay can be performed in test-tube volumes to be read via cuvette in a spectrophotometer, or scaled-down to microplate volumes to be read on a plate reader. Preparation of Standards and Working Reagent (required for both assay procedures) Preparation of Diluted Albumin (BSA) Standards Use Table 1 as a guide to prepare a set of protein standards. Dilute the contents of one Albumin Standard (BSA) ampule into several clean vials, preferably using the same diluent as the sample(s). Each 1 ml ampule of 2.0 mg/ml Albumin Standard is sufficient to prepare a set of diluted standards for the working range suggested in Table 1. There will be sufficient volume for three replications of each diluted standard. Table 1. Preparation of Diluted Albumin (BSA) Standards Dilution Scheme for Standard Test Tube Protocol and Microplate Procedure (Working Range = 20–2,000 μg/ml) Vial Volume of Diluent Volume and Source of BSA Final BSA Concentration A 0 300 μl of Stock 2,000 μg/ml B 125 μl 375 μl of Stock 1,500 μg/ml C 325 μl 325 μl of Stock 1,000 μg/ml D 175 μl 175 μl of vial B dilution 750 μg/ml E 325 μl 325 μl of vial C dilution 500 μg/ml F 325 μl 325 μl of vial E dilution 250 μg/ml G 325 μl 325 μl of vial F dilution 125 μg/ml H 400 μl 100 μl of vial G dilution 25 μg/ml I 400 μl 0 0 μg/ml = Blank Test-tube Procedure (Sample to Working Reagent (WR) ratio = 1:20) 1. Pipette 0.1 ml of each standard and unknown sample replicate into an appropriately labelled test tube. 2. Add 2.0 ml of the WR to each tube and mix well. 3. Cover and incubate tubes at selected temperature and time: Standard Protocol: 37°C for 30 minutes (working range = 20-2,000 μg/ml) RT Protocol: RT for 2 hours (working range = 20-2,000 μg/ml) NB: Increasing the incubation time or temperature increases the net 562 nm absorbance for each test and decreases both the minimum detection level of the reagent and the working range of the protocol. Using a forced-air incubator can introduce significant error in colour development because of uneven heat transfer. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ Page 1 of 3 Safe Work Procedure Date Effective: 01/01/2007 Uncontrolled document when printed Current Version: 1.2, 15/08/2007 4. Cool all tubes to RT. 5. With the spectrophotometer set to 562 nm, zero the instrument on a cuvette filled only with blank from standard curve. Subsequently, measure the absorbance of all the samples within 10 minutes. 6. Subtract the average 562 nm absorbance measurement of the Blank standard replicates from the 562 nm absorbance measurement of all other individual standard and unknown sample replicates. 7. Prepare a standard curve by plotting the average Blank-corrected 562 nm measurement for each BSA standard vs. its concentration in μg/ml. Use the standard curve to determine the protein concentration of each unknown sample. Note: If sample size is limited, 10 μl of each unknown sample and standard can be used (sample to WR ratio = 1:20). However, the working range of the assay in this case will be limited to 125-2,000 μg/ml. Microplate Procedure (Sample to WR ratio = 1:20~1:8) 1. Pipette 10-25 μl of each standard or unknown sample replicate into a microplate well (working range = 20-2,000 μg/ml). It will probably be necessary to dilute your samples in order to fit into the detectable range of the assay. For tissue culture samples this dilution may be between 1:5 – 1-20; for organ tissue samples higher dilutions such as 1:50 may be necessary. This dilution factor will have to be accounted for when inferring concentrations from your standard curve. 2. Add 200 μl of the WR to each well and mix by gently shaking. 3. Cover plate and incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes. Incubation at RT for 1 hr also works well. 4. Cool plate to RT. 5. Measure the absorbance at or near 562 nm on a plate reader. Notes: Wavelengths from 540-590 nm have been used successfully with this method. Because plate readers use a shorter light path length than cuvette spectrophotometers, the Microplate Procedure requires a greater sample to WR ratio to obtain the same sensitivity as the standard Test Tube Procedure. If higher 562 nm measurements are desired, increase the incubation time to 2 hours. Increasing the incubation time or ratio of sample volume to WR increases the net 562 nm measurement for each well and lowers both the minimum detection level of the reagent and the working range of the assay. As long as all standards and unknowns are treated identically, such modifications may be useful. 6. Subtract the average 562 nm absorbance measurement of the Blank standard replicates from the 562 nm measurements of all other individual standard and unknown sample replicates. 7. Prepare a standard curve by plotting the average Blank-corrected 562 nm measurement for each BSA standard vs. its concentration in μg/ml. Use the standard curve to determine the protein concentration of each unknown sample. List all resources required including plant, chemicals, personal protective clothing and equipment, etc BCA Protein Assay Kit (Pierce) Microplate reader Disposable Face Mask Gloves Safety Glasses Lab Coat/Gown List potential hazards and risk controls including specific precautions required BCA protein assay kit: Reagents A and B can cause irritation by eye and skin contact, and inhalation. Wear gloves and gown and safety glasses when handling the kit. Must read MSDS FOR KITS before the start of the experiment. Eye wash and shower station if contact occurs ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ Page 2 of 3 Safe Work Procedure Date Effective: 01/01/2007 Uncontrolled document when printed Current Version: 1.2, 15/08/2007 List emergency shutdown instructions In the event of inhalation or ingestion the first aid officer should be consulted immediately. First Aid Officer: Renee Szokolai ext 58497 List clean up and waste disposal requirements Plastic tubes and plates should be disposed in correct biological waste bags. List legislation, standards and codes of practice used in the development of the SWP NSW OHS Act 2000 NSW OHS Regulation 2001 Code of Practice for the Labelling of Workplace Substances AS/NZS 2243.2:2006. Safety in laboratories. Part 2: Chemical aspects AS/NZS 2243.3: 2006 Safety in laboratories Part 3: Microbiological aspects and containment facilities AS/NZS 1336:1997 Recommended Practices for Occupational Eye Protection AS/NZS 2161.1:2000 Occupational Protective Gloves – Selection, Use and Maintenance Supervisory approval, training, and review Supervisor: Peter Gunning Signature: Plant custodian: n/a Signature List competency required – qualifications, certificates, licencing, training - eg course or instruction: Training as per Training Needs Analysis, Induction to Lab, Training in this SWP ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ Page 3 of 3 Safe Work Procedure Date Effective: 01/01/2007 Uncontrolled document when printed Current Version: 1.2, 15/08/2007