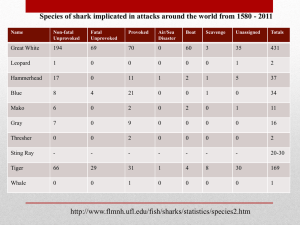
Carcharhinidae

Carcharhinidae
Requiem sharks
Carcharhinidae characteristics
5 gill slits
2 dorsal fins
No fin spines
Caudal fin w/ strong ventral lobe
Mouth behind eyes
Round eyes w/ nictitating eyelids
Long arched mouth w/ bladelike teeth
Short labial furrows
Mostly unpatterned
Mostly medium to large
100-300 cm
Some smaller
~100
Active strong swimmers
More nocturnal
Ram ventilators & buccal breathers
Behavior
Some solitary
Some socialize in small groups
Some social schooling spp.
Clear hierarchical dominance b/t spp.
Oceanic whitetip (Carcharhinus longimanus) dominate silky sharks
Silky sharks (Carcharhinus falciformis) dominate grey reef sharks
(Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos)
Taxonomy
Order Carcharhiniformes
Family carcharhinidae
12 genera (8 monotypic)
~50 spp. (31 are in genus Carcharhinus
)
Examples include
Tiger shark
(Galeocerdo cuvier)
Bull shark ( Carcharhinus leucas
)
Blacktip reef (
Carcharhinus melanopterus)
Sharpnose sharks ( Rhizopriondon spp.)
Lemon Shark ( Negaprion brevirostris
)
Distribution
Temperate and tropical seas
Majority tropical continental shelves & offshore
Some coral reefs
Some deep water
Benthopelagic
Pelagic-Blue Shark ( Prionace glauca) , Oceanic Whitetip ( Carcharhinus longimanus ), Silky Shark ( Carcharhinus falciformis )
All over the world
Feeding
Wide variety
Teleosts
Crustaceans
Mollusks
Elasmobranchs
Seabirds
Reptiles
Marine mammals
Reproduction
Most placental viviparous
Galeocerdo cuvier is ovoviviparous
Biennial or triennial reproductive cycle
Status
Important in commercial, subsistence and sports fisheries
used for
Food
Liver oil
Fins-especially blue shark
Skin
Ecotourism
Have bitten people
Caught as bycatch
Red list mixed from data deficient; threatened to endangered; many near threatened
Literature cited
Compagno, L.M. Dando, and S. Fowler. 2005. Sharks of the world. Princeton University
Press, Princeton, NJ. Pp288-322
Whitney NM, Crow GL. 2007. Reproductive biology of the tiger shark ( Galeocerdo cuvier ) in Hawaii. Marine Biology . 151 (1).pp63-70
Yokota K, Kiyota M, Minami H.2006.Shark catch in a pelagic longline fishery:
Comparison of circle and tuna hooks. Fisheriess Research. 81.pp 337-341.
Clarke SC, McAllister MK, Milner-Gulland EJ, et al.2006.Global estimates of shark catches using trade records from commercial markets .Ecology Letter 9.pp 1115-1126
Campana SE, Marks L, Joyce W, et al. Effects of recreational and commercial fishing on blue sharks (Prionace glauca) with inferences on the North Atlantic population . CANADIAN JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND AQUATIC SCIENCES 63. pp 670-682
IUNC 2006. 2006 IUCN red list of threatned species. At http:// www.iuncnredlist.org