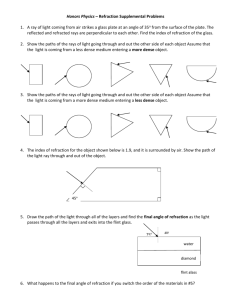
Index of Refraction
advertisement
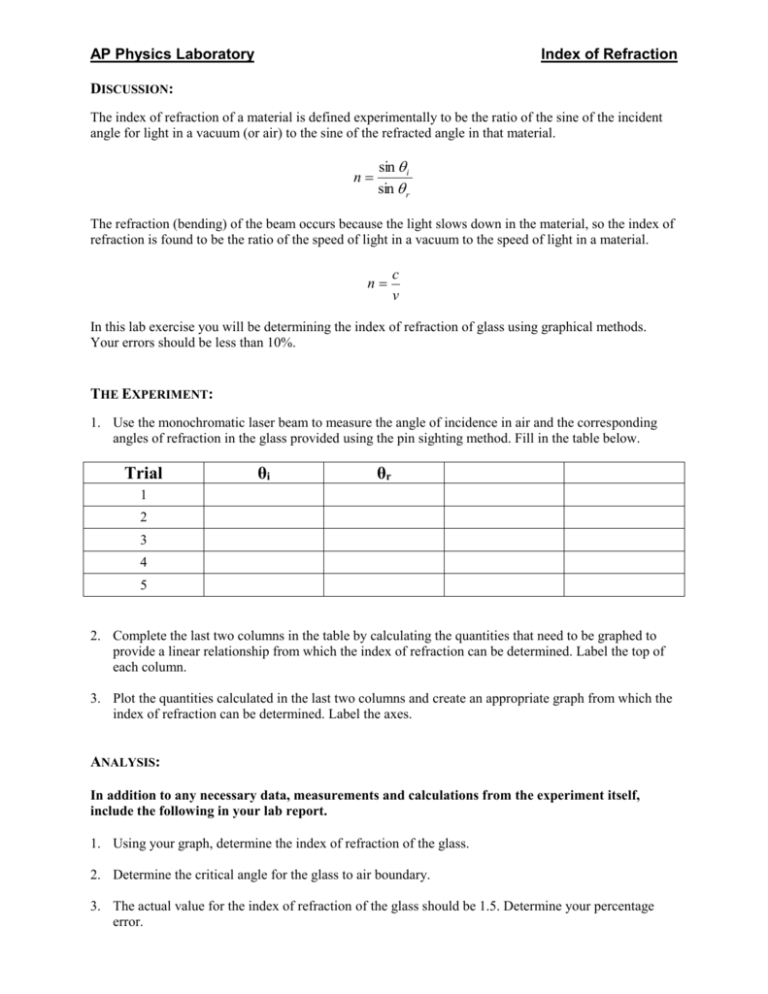
AP Physics Laboratory Index of Refraction DISCUSSION: The index of refraction of a material is defined experimentally to be the ratio of the sine of the incident angle for light in a vacuum (or air) to the sine of the refracted angle in that material. n sin i sin r The refraction (bending) of the beam occurs because the light slows down in the material, so the index of refraction is found to be the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a material. n c v In this lab exercise you will be determining the index of refraction of glass using graphical methods. Your errors should be less than 10%. THE EXPERIMENT: 1. Use the monochromatic laser beam to measure the angle of incidence in air and the corresponding angles of refraction in the glass provided using the pin sighting method. Fill in the table below. Trial θi θr 1 2 3 4 5 2. Complete the last two columns in the table by calculating the quantities that need to be graphed to provide a linear relationship from which the index of refraction can be determined. Label the top of each column. 3. Plot the quantities calculated in the last two columns and create an appropriate graph from which the index of refraction can be determined. Label the axes. ANALYSIS: In addition to any necessary data, measurements and calculations from the experiment itself, include the following in your lab report. 1. Using your graph, determine the index of refraction of the glass. 2. Determine the critical angle for the glass to air boundary. 3. The actual value for the index of refraction of the glass should be 1.5. Determine your percentage error.