Lab - Week One: The Scientific Method
advertisement

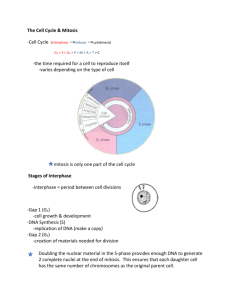
Biology 211 - Lab Six: Cell Division and Introduction to Mendel Reminder: Bring your textbook, a calculator, and goggles! Pre-Lab Homework: 1. Define mitosis, explain mitotic products using G1 cells that have 2n=2, 4, 6. Now define meiosis, explain meiotic products using G1 cells that have 2n=2, 4, 6. 2. What living thing are you staining? What kind of cell division will you be seeing? 3. Define CROSSING OVER, including when it happens (kind of division, phase?). 4. Understand Mendel’s laws, relating each to cell division (which kind, phase?). In-Lab Activity Overview a. Modeling Key Steps of the Cell Cycle and Mitosis b. Observing Mitosis and Counting Phases in Plant Cells c. Modeling Meiosis, Including Crossing Over and Independent Assortment d. Mendel – Analyzing a One-Gene Mystery Cross Modeling Key Steps of the Cell Cycle and Mitosis For this exercise, you will use pop bead chromosomes to model the cell cycle and mitosis (G1 cell, 2n = 4). You will move your pop bead chromosomes through a series of chalk-drawn cells that show (if present): cell membrane, nuclear envelope, spindle. Modeling Instructions – Work In Pairs 1. One pair of chromosomes will be LONG, made of 8 pop beads – 1 red, 1 blue 2. The other pair will be SHORT, made of 4 pop beads – 1 red 1 blue 3. Model S phase by replicating ALL your chromosomes – keep sisters together! 4. Model ALL phases of mitosis: pro-, prometa-, meta-, ana-, and telo-phase 5. Each pair member needs to practice for their partner until they get it 6. When ready, call your instructor over to check understanding, initial worksheet! Observing Mitosis and Counting Phases in Plant Cells These procedures were provided to us by a former student/now-high school teacher in rural Idaho. In this activity, pairs will stain and view their own root tips, using onions that have been growing in a beaker of water to promote root development. Procedures - Work in Pairs 1. Cut off 1 root tip (about 1 cm) – should be white, firm, and healthy! 2. Wearing gloves, fill test tube 3 cm full of fixative (strong acid!) and add tip 3. Incubate tubes at 50°C for 6 minutes – a bath will be set up in the fume hood 4. Still in the hood, dump contents into a watch glass and transfer tip to a slide 5. Carry slide back to bench, cut/remove all material EXCEPT 2 mm at the very tip! 6. Place 2 drops of aceto-orcein stain on the root tip and soak for 4 minutes 7. Place a coverslip flat on the tip and press gently STRAIGHT DOWN 8. View using 40X objective, surveying edges for cell division – show instructor! Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab Six, page 1 Modeling Meiosis, Including Crossing Over and Independent Assortment For this exercise, you will be using the same pop bead chromosome models, the same G1 cell, and the same general procedures as for mitosis. Modeling Instructions – Work In Pairs 1. Model prophase I, CROSSING OVER 1 set of beads on LONG pair only 2. Model metaphase I, including showing INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT! 3. Model anaphase I and telophase I, emphasizing final products 4. Model ALL phases of meiosis II, emphasizing final products 5. Each pair member needs to practice for their partner until they get it 6. When ready, call your instructor over to check understanding, initial worksheet! Mendel – Analyzing a One-Gene Mystery Cross A bean farmer has been doing some breeding experiments that got out of hand. Early on, though, he did discover that true-breeding white beans crossed with true-breeding purple beans yielded all white beans. He hands you a jar of beans that represent 200 offspring from a “mystery cross” and asks you to figure out what the original cross was. Logic – Set-Up Your Hypothesis/Predictions – Work In Tables 1. Write out ALL possible genotypes for all possible parents. There are THREE! 2. Using the 6-square box on your worksheet, determine and record EVERY possible cross using genotypes above and show a Punnett Square for each. 3. Given that “mystery offspring” are a mix of white and purple beans, place an X next to all outcomes that DO NOT GIVE white AND purple beans. From remaining crosses, CIRCLE the cross representing your hypothesis about parental genotypes. 4. Each PERSON needs to assess 50 beans, recording each phenotype. Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab Six, page 2 Lab Six: Cell Division and Mendel - Turn In As Pairs At End of Lab Pair Member Names: 1. Based on your MITOSIS modeling using pop beads, complete the following: a. 1 pt. Instructor Initials - students have correctly modeled mitosis _____ b. 1 pt. DRAW (use correct chromosome colors) the following: Anaphase All Product(s) of Mitosis 2. 1 pt. Based on your onion root tip staining and counting, complete the following: a. Instructor Initials - students stained and observed mitotic onion cells _____ b. How do you KNOW this is MITOSIS and not MEIOSIS? 3. Based on your MEIOSIS modeling using pop beads, complete the following: a. 1 pt. Instructor Initials - students have correctly modeled meiosis _____ b. 1 pt. DRAW (use correct chromosome colors) the following: Anaphase I Anaphase II All Product(s) of Meiosis II With crossing over! Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab Six, page 3 4. Complete the following idea problems about Mendel and Cell Division. a. 1 pt. Relate Mendel’s Laws to cell division (which Kind, which Step?) Define Law Division, Step Law of… Segregation Independent Assortment b. 1 pt. Draw (use correct chromosome colors) the following: Independent Assortment Version I Independent Assortment Version I 4. Mendelian Monohybrid Cross Experiment. a. 1.5 pts. Six Possible Crosses. Circle the one representing your hypothesis! b. 1 pt. Record your data here – both actual and expected. Purple Observed Counts White Hypothesis-Predicted Counts c. 0.5 pts. Do your data support your hypothesis? Explain. Biology 211 Lab Manual, Lab Six, page 4