Key points - Teaching As Leadership
advertisement
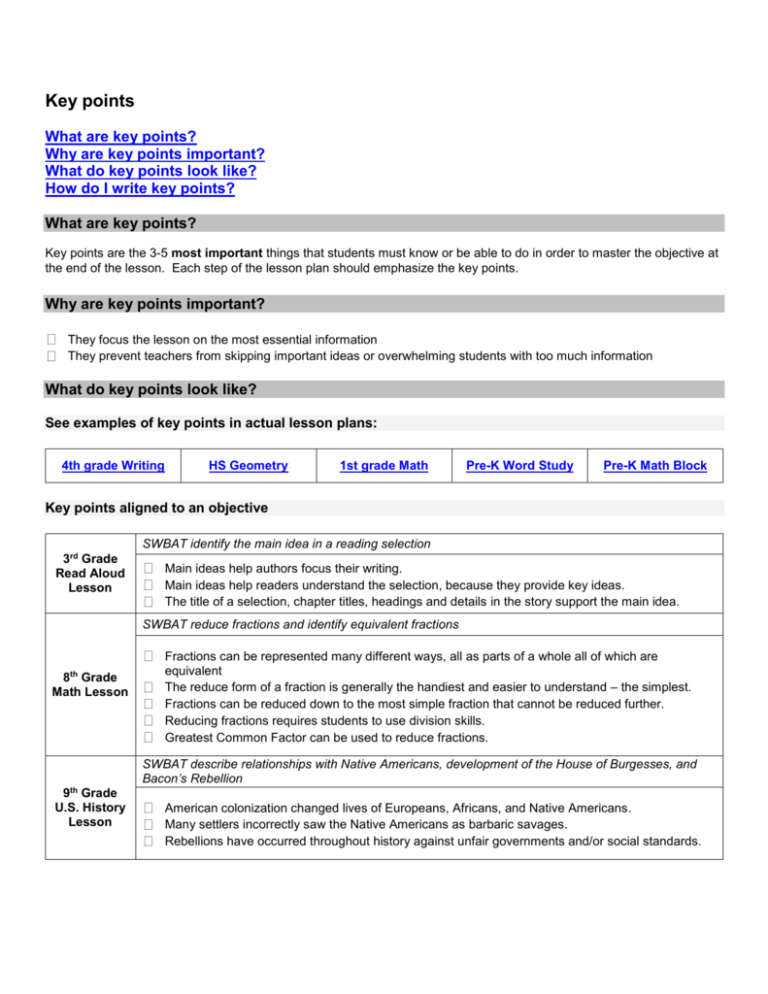
Key points What are key points? Why are key points important? What do key points look like? How do I write key points? What are key points? Key points are the 3-5 most important things that students must know or be able to do in order to master the objective at the end of the lesson. Each step of the lesson plan should emphasize the key points. Why are key points important? They focus the lesson on the most essential information They prevent teachers from skipping important ideas or overwhelming students with too much information What do key points look like? See examples of key points in actual lesson plans: 4th grade Writing HS Geometry 1st grade Math Pre-K Word Study Pre-K Math Block Key points aligned to an objective SWBAT identify the main idea in a reading selection 3rd Grade Read Aloud Lesson Main ideas help authors focus their writing. Main ideas help readers understand the selection, because they provide key ideas. The title of a selection, chapter titles, headings and details in the story support the main idea. SWBAT reduce fractions and identify equivalent fractions th 8 Grade Math Lesson Fractions can be represented many different ways, all as parts of a whole all of which are equivalent The reduce form of a fraction is generally the handiest and easier to understand – the simplest. Fractions can be reduced down to the most simple fraction that cannot be reduced further. Reducing fractions requires students to use division skills. Greatest Common Factor can be used to reduce fractions. SWBAT describe relationships with Native Americans, development of the House of Burgesses, and Bacon’s Rebellion 9th Grade U.S. History Lesson American colonization changed lives of Europeans, Africans, and Native Americans. Many settlers incorrectly saw the Native Americans as barbaric savages. Rebellions have occurred throughout history against unfair governments and/or social standards. Example of key points in an outline SWBAT explain the process of global warming (key points follow the Roman numerals) I. The atmosphere traps heat like a greenhouse. a. A greenhouse serves to trap heat. b. The sun’s rays hit the Earth and are often “trapped” by the atmosphere’s gases. c. Trapping is important to maintain a temperate climate. i. If there were no atmosphere, like on Mars, we’d freeze. II. Human processes are creating an overabundance of gases in the atmosphere. a. Manmade reasons for the production of gases: carbon dioxide emissions, burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, deep plowing of fields, CFC-filled refrigerators and air conditioners. b. We use the word “overabundance” because fewer of the sun’s rays can escape, making the Earth dangerously warm. Example of key points of a skill SWBAT apply the order of operations to complete calculations Mathematical operations must be performed in a specific order: 1. Parenthesis 2. Exponents 3. Multiplication 4. Division 5. Addition 6. Subtraction top How do I write key points? Ask yourself – what are the 3-5 most important things students need to know or be able to do by the end of the lesson in order to show mastery? Create an outline of your objective’s main ideas and supporting points see example above If you are teaching a skill, outline the key steps you need to take to complete the skill see example above Check alignment of your key points to the objective and assessment - are the key points on the same cognitive level as your objective? Important Note: as you write the rest of your lesson, remember to always emphasize these key points in all parts of the plan top