Name ______ per. _____ Meta Lessons Lesson 1
advertisement

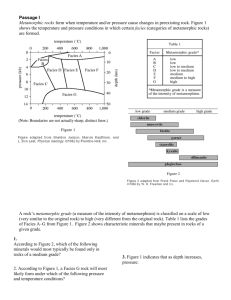
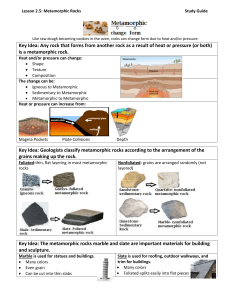
Name ______________________________________________ Meta Lessons per. _____ Lesson 1 - Formation of Metamorphic Rocks 1. Metamorphic rocks show what? 2. Why are they best seen in nature? 3. What two variables affect the formation of metamorphic rocks? 4. Instead of melting, what happens when the rock changes? 5. Explain the term metamorphosed? 6. Explain the intermediate steps between shale and gneiss. a. . b. . c. . d. . e. . 7. What igneous rock can also metamorphose into gneiss? 8. Besides temperature and pressure, what other variable also affects metamorphic rock formation? 9. What are three facts about Serpentine? a. . b. . c. . 10. Differentiate between the following metamorphisms: a. Contact b. Regional c. Burial d. Cataclastic Name ______________________________________________ Meta Lessons per. _____ e. Low-grade f. Intermediate-grade g. High-grade 11. What types of rocks would you find in each condition above? a. Contact b. Regional c. Burial d. Cataclastic e. Low-grade f. Intermediate-grade g. High-grade Lesson 2 - Metamorphic Rock Classification Chart 1. Differentiate between the terms foliated and nonfoliated. 2. How would you tell slate from phyllite? 3. How would you tell schist from gneiss? 4. How would you tell marble, quartzite, serpentine, and hornfels from each other? 5. Use the chart to answer the following questions. a. List the metamorphic rocks that have a foliated texture. b. List the metamorphic rocks that have a nonfoliated texture. Name ______________________________________________ Meta Lessons per. _____ 6. Use the chart to determine what minerals are found in each metamorphic rock in the table below: Lesson 4 - The Many Facies of Metamorphic Rocks 1. When a rock metamorphoses, what else matters besides the amount of temperature and pressure? 2. What did George Barrow do? 3. What are metamorphic facies? 4. Use the Metamorphic Facies graph to complete the following table: Name ______________________________________________ Meta Lessons 5. Provide two additional facts about each of the following facies. a. Zeolite i. . ii. . b. Hornfels. i. . ii. . c. Blueschist i. . ii. . d. Greenschist i. . ii. . e. Amphibolite i. . ii. . f. Granulite i. . ii. . g. Eclogite i. . ii. . Lesson 5 - Michelangelo and Marble 1. What is the country rock (original rock) of marble? 2. What happened to this country rock when it turned to marble? 3. What gives marble its color? 4. What are three reasons Michelangelo used Carrara marble? per. _____