Reaction Time Test
advertisement

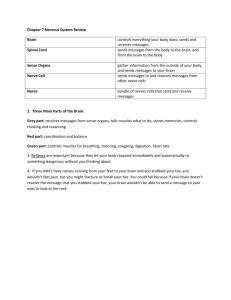
PPT Reaction Time Name Period Date For each problem, choose the best answer and, on multiple choice questions, mark the Scantron sheet (match the question number) or fill in the blank(s) or follow the instructions for that problem. Don’t forget the units in your answers! Show your work for partial credit. 1. N=D/T Solve for T. 2. A person who has been given cold medicine has a slower reaction time than a person who has not been given cold medicine. What is the independent variable? a. Cold medicine b. Reaction time c. Gravity d. Illness 3. Which of these is a complete definition of reaction time? a. The time it takes your brain to tell your muscles to move b. The time it takes for your brain to realize something has happened, and for your muscles to move c. The time it takes to move d. The time it takes for your brain to realize something has happened, for your nerves to communicate the brain’s orders to your muscles, and your muscles to move. 4. Improving reaction time through learning or practice is what? a. Reflex arc b. Habituation c. Conditioned response d. Dynamic time 5. Which one of these is NOT under the control of the autonomic nervous system? a. Heart beat b. Breathing c. Liver function d. Snapping your fingers 116097001 1 PPT Reaction Time 6. Nerve impulses in the squid Loligo travel at about 200 meters per second. One especially large specimen of Loligo is about .8 meters long from brain to tentacle tip. How long is nerve time for this Loligo? a. .4 seconds b. .025 seconds c. .004 seconds d. .025 seconds 7. A reflex arc is faster than normal reaction time because… a. the autonomic system controls it. b. the nerves speed up. c. the signals only have to travel to the spinal cord and back, not all the way to the brain and back. d. the brain processes faster during a reflex arc. 8. We measured reaction time using a ruler. If the ruler dropped 0.20 meters, what is reaction time? a. .2 seconds b. .4 seconds c. .1 seconds d. .02 seconds 9. What does the Central Nervous System do? a. Processes information and tells the rest of the body what to do. b. Controls only involuntary functions, like heart rate. c. Carries the signal back and forth between the brain and the rest of the body. d. Builds new blood cells. 10. Which one of these is an example of habituation? a. Becoming a better guitar player by practicing. b. Jerking your hand away from a hot stove very quickly. c. Ignoring or not noticing a fly buzzing around the room after a few minutes. d. Reacting more quickly to a ruler dropping after several tries. 11. Processing time is… a. the time it takes a signal to travel from the brain to the muscles. b. the time it takes the brain to realize something has happened. c. the time it takes the muscles to move. d. the time it takes to react to something. 116097001 2 PPT Reaction Time 12. If Mr. Kleinjans is sitting under a tree, and an elephant falls out of the tree from 20 meters above him, how much time does he have to react and avoid being squashed by the elephant? a. .2 seconds b. 1 second c. 4 seconds d. 2 seconds 13. If his nerve time is .02 seconds and his dynamic time is .12 seconds, how long does he have to realize that the elephant is falling on him? a. 1.06 seconds b. .06 seconds c. .14 seconds d. 2.14 seconds 14. A charging rhino is moving toward you at a constant velocity of about 40 miles per hour. How fast does your total reaction time have to be to dodge the rhino when it is 2 miles away? (Rhinos don’t corner very well, so you can assume if you move to one side, the rhino will miss you.) a. 3 minutes b. 5 minutes c. 20 minutes d. 40 minutes 15. On the line of scrimmage, the Center snaps the ball after he hears the Quarterback call out the snap count. It takes him about 0.2 seconds total to snap the ball after the count is given. If processing time is 0.07 seconds and nerve time is 0.05 seconds, how long is dynamic time? a. .12 seconds b. .08 seconds c. .2 seconds d. .04 seconds 116097001 3 PPT 116097001 Reaction Time 4 PPT Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 116097001 Reaction Time Answer T = D/N A D C D C C A B C B D A A B Concept 3 variables Independent variable Definition of rxn time Conditioned response Parts of nervous system Nerve time Reflex arc Rxn time & acceleration Central nervous system Habituation Processing time Acceleration Parts of rxn time Speed Parts of rxn time 5 PPT 116097001 Reaction Time 6