Bio K Study Guide – Early earth and evolution
advertisement

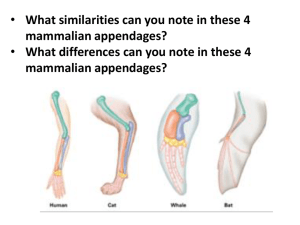
Bio A – Evolution Bio A Study Guide – Early earth and evolution 1. The Big Bang Theory describes the creation of _________________________________ a. Does it describe the first living things? b. Has our universe stopped changing? 2. What is spontaneous generation? (Yes this is review from past units! Look it up!) - name three scientists whose work disproved the possibility of spontaneous generation - What is biogenesis? 3. What is the Primordial soup? Why is it significant? What allowed the primordial soup to form? What was the purpose of Stanley Miller’s experiment? 4. What is continental Drift? What was the problem with it? 5. What alternative did the idea of Plate Tectonics introduce? 6. What evidence exists to support the idea that the continents move? 1 Bio A – Evolution 7. Complete the following table: Scientist Linneaus What was his contribution? How did this contribution influence Darwin? Lamarck Mendel Malthus 8. Define the following terms in your words: a. Adaptation b. Natural Selection c. Evolution d. Survival of the fittest (make sure your description is complete!) 9. How do Darwin’s finches support his ideas on evolution? Describe their genetic variation. Describe how they show adaptation. Describe how they demonstrate evolution 2 Bio A – Evolution 10. What do evolutionary biologists mean when they say an organism is “fit”? It has adaptations that work well in the current environment 11. Describe how each of the following can be used to support Darwin’s theories: Sedimentary rock and fossils: Sedimentary rock is formed in layers over time. Layers closer to the “bottom” are older. Fossils are a partial record of life forms. Their location within the sedimentary rock gives us an idea of their age. Locations of the same fossils on different continents supports continental drift Comparative Anatomy: Similar anatomical structures (homologous and vestigial organs) provide evidence of common ancestor with divergence . - Homologous structures Similar structures (even if the function is no longer the same, offer proof of common ancestry and divergence. - Analogous structures Parts of two organisms which have the same function, but did not arise from a common ancestor (very different structures are said to be analogous (and their evolution is convergent. - Vestigial structures Structures which had a function in an earlier ancestor, but serve no purpose now. Comparative Biochemistry: A comparison of the similarities in the sequences of DNA or amino acids (in proteins). Higher similarity indicates a closer relationship Comparative Embryology: Embryos that look more similar to each other (ie frog and a turtle or a salamander and a fish are more closely related to each other. 12. For each of the following statements, identify whether gradualism or punctuated equilibrium is being described: a. Happens relatively quickly in small populations Punctuated Equilibrium 3 Bio A – Evolution b. Results in the accumulation of tiny changes over a long period of time Gradualism c. A population of pre-horse animals starting off short and getting taller and taller over time until they reach the height of modern horses. Gradualism d. A population of butterflies going from dark brown to white without passing through light brown along the way. Punctuated Equilibrium e. Supported by the fossils that we find in sedimentary rock Punctuated Equilibrium and some Gradualism f. Supported by Darwin Gradualism g. Supported by Jay Gould Punctuated Equilibrium 13. Describe the conditions necessary in order for natural selection to occur. Explain why each is necessary. PHENOTYPIC VARIATION must exist Over production; Limited resources, Competition, survival of the fittest, differential reproduction Selection cannot occur without variation and and environmental stressor (struggle to survive). With these two things present, all others fall into place. 14. What two organelles are explained by the “endosymbiont theory” (aka endosymbiosis) - Mitochondria and chloroplasts how did they get to be part of our cells? - Either engulfed (eaten) or burrowed into a larger organism and were not digested What is the evidence that supports this theory? Both Mitochondria and chloroplasts have unique DNA (different from each other and different from the nucleus. Both are the size of prokaryotes, both have double membranes like prokaryotes, both produce new organelles via fission. 15. How does variation appear in a population? (for example: how did all the different hair colors in humans appear?) Mutations, genetic recombination (crossing over, independent assortment, segregation during sexual reproduction) 4 Bio A – Evolution 16. Fill in the chart below to compare divergent and convergent evolution. Does it suggest the two organisms are closely related? Is it caused by sharing a common environment? Does it create homologous or analogous structures? Provide an example of each Convergent Divergent NO YES NO YES ANALOGOUS HOMOLOGOUS Butterfly wing and bat wing Bat wings and a cat forelimb and a human arm Digging paws on two organisms that arise from different structures but have the same function in the same environment All have similar base structures (bone structure), but how they function is very different. Under what conditions does evolution NOT occur? Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium (no mutations, no migration or immigration, no natural selection, random mating) How would we mathematically tell whether a population is evolving? If the allele frequencies are changing over time in a population How do we know whether a population has evolved to the point of being a new species? They are no longer able to interbreed (can be due to physical, sexual, temporal, geographic issues) - What has to occur in order for a species to diverge into two different species? Isolation in one of the above ways, coupled with mutations or genetic drift What are cladograms and phylogenetic trees? What can they tell us? Graphical illustrations of how related two organisms. They can be based on a few attributes or many 5 Bio A – Evolution - Describe what the following tells us: Dog and wolf are closely related Skunk and otter share a common ancestor further back intime than the dog and wolf All are carnivores Skunk and otter are in the same family 6