Inventory Management Problems & Solutions
advertisement
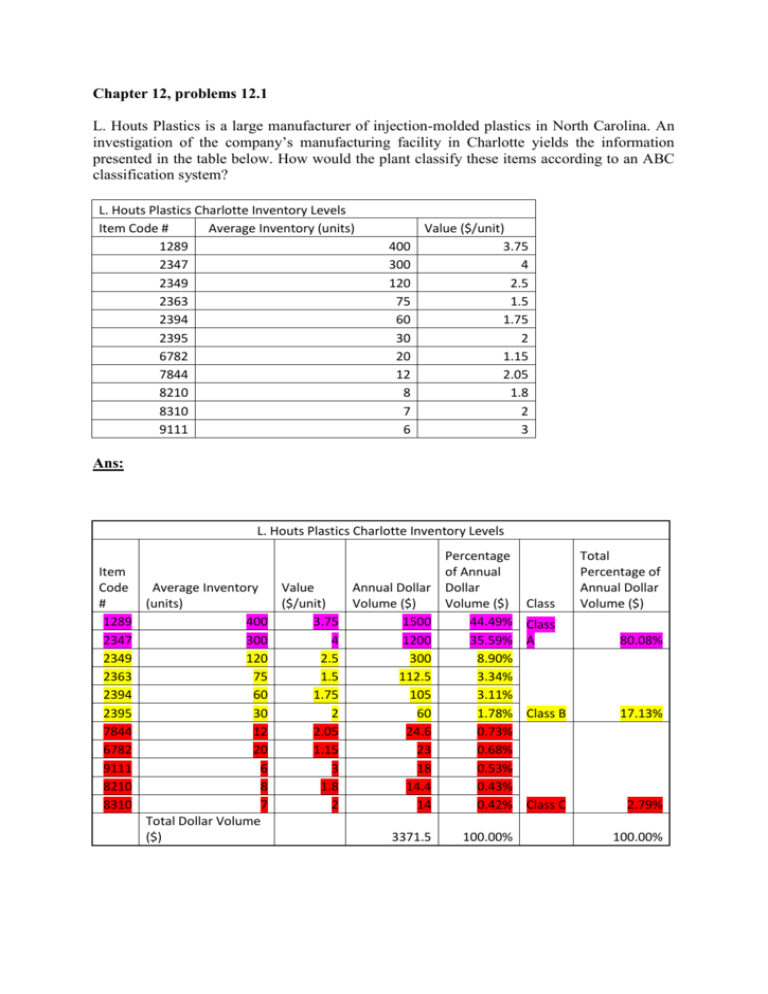
Chapter 12, problems 12.1 L. Houts Plastics is a large manufacturer of injection-molded plastics in North Carolina. An investigation of the company’s manufacturing facility in Charlotte yields the information presented in the table below. How would the plant classify these items according to an ABC classification system? L. Houts Plastics Charlotte Inventory Levels Item Code # Average Inventory (units) 1289 2347 2349 2363 2394 2395 6782 7844 8210 8310 9111 400 300 120 75 60 30 20 12 8 7 6 Value ($/unit) 3.75 4 2.5 1.5 1.75 2 1.15 2.05 1.8 2 3 Ans: L. Houts Plastics Charlotte Inventory Levels Percentage Item of Annual Code Average Inventory Value Annual Dollar Dollar # (units) ($/unit) Volume ($) Volume ($) Class 1289 400 3.75 1500 44.49% Class 2347 300 4 1200 35.59% A 2349 120 2.5 300 8.90% 2363 75 1.5 112.5 3.34% 2394 60 1.75 105 3.11% 2395 30 2 60 1.78% Class B 7844 12 2.05 24.6 0.73% 6782 20 1.15 23 0.68% 9111 6 3 18 0.53% 8210 8 1.8 14.4 0.43% 8310 7 2 14 0.42% Class C Total Dollar Volume ($) 3371.5 100.00% Total Percentage of Annual Dollar Volume ($) 80.08% 17.13% 2.79% 100.00% Chapter 12, problems 12.5 William Beville’s computer training school, in Richmond, stocks workbooks with the following characteristics: Demand D = 19,500 units/year Ordering cost S = $25/order Holding cost H = $4/unit/year a) Calculate the EOQ for the workbooks. b) What are the annual holding costs for the workbooks? c) What are the annual ordering costs? Ans: Data Demand rate, D Setup/order cost, S Holding cost, H Unit Price, P 19500 25 4 Results Optimal Order Quantity, Q* Maximum Inventory Average Inventory Number of Orders 493.71 493.71 246.86 39.50 Holding cost Setup cost 987.42 987.42 Unit costs Total cost, Tc $0.00 $1,974.84 a) Calculate the EOQ for the workbooks. = 493.71 ~ 494 units EOQ = SQRT (( 2* Demand * Order Cost)/ Holding Cost) EOQ = SQRT (( 2* 19500 * 25 )/4) = 493.71 Units ~ 494 Units b) What are the annual holding costs for the workbooks? Ans: Annual holding costs for the workbooks = (Quantity of items) * (Holding Cost) / 2 = 494 * 4/2 = $ 987.42 c) What are the annual ordering costs? Ans: Annual ordering costs for the workbooks = (Demand * Order Cost)/ Q Annual ordering costs for the workbooks = (19500 * 25) / 493.71 = $ 987.42 Chapter 12, problems 12.9 Southeastern Bell stocks a certain switch connector at its central warehouse for supplying field service offices. The yearly demand for these connectors is 15,000 units. Southeastern estimates its annual holding cost for this item to be $25 per unit. The cost to place and process an order from the supplier is $75. The company operates 300 days per year, and the lead time to receive an order from the supplier is 2 working days. a) Find the economic order quantity. b) Find the annual holding costs. c) Find the annual ordering costs. d) What is the reorder point? Ans: Data Demand rate, D Setup cost, S Holding cost, H Unit Price, P Daily demand rate Lead time in days Results Optimal Order Quantity, Q* Maximum Inventory Average Inventory Number of Setups Holding cost Setup cost Unit costs Total cost, Tc Reorder Point 15000 75 25 50 2 300 300 150 50 $3,750.00 $3,750.00 $0.00 $7,500.00 100 a) Find the economic order quantity. Ans: EOQ = SQRT (( 2* Demand * Order Cost)/ Holding Cost) EOQ = SQRT ((2* 15000 * 75) /25) = 300 Units b) Find the annual holding costs Ans: Annual holding costs for the workbooks = (Quantity of items) * (Holding Cost) / 2 Annual holding costs for the workbooks = (300 * 25) /2 = $3,750.00 c) Find the annual ordering costs. Ans: Annual ordering costs for the workbooks = (Demand * Order Cost)/ Q Annual ordering costs for the workbooks = (15000 * 75) /300 = $3,750.00 d) What is the reorder point? Ans: Reorder point = (Demand Per Day ) * (Lead Time for new order in Days) Reorder Point = (15000/300) * 2 = 50 * 2 = 100 units Chapter 12, problems 12.15 M. Cotteleer Electronics supplies microcomputer circuitry to a company that incorporates microprocessors into refrigerators and other home appliances. One of the components has an annual demand of 250 units, and this is constant throughout the year. Carrying cost is estimated to be $1 per unit per year, and the ordering cost is $20 per order. a) To minimize cost, how many units should be ordered each time an order is placed? b) How many orders per year are needed with the optimal policy? c) What is the average inventory if costs are minimized? d) Suppose that the ordering cost is not $20, and Cotteleer has been ordering 150 units each time an order is placed. For this order policy (of Q = 150) to be optimal, determine what the ordering cost would have to be. Ans: Data Demand rate, D Setup/order cost, S Holding cost, H Unit Price, P Results Optimal Order Quantity, Q* Maximum Inventory Average Inventory Number of Orders Holding cost Setup cost Unit costs Total cost, Tc 250 20 1 100 100 50 2.50 50 50 $0.00 $100.00 a) To minimize cost, how many units should be ordered each time an order is placed? Ans: EOQ = SQRT (( 2* Demand * Order Cost)/ Holding Cost) EOQ = SQRT ((2* 250 * 20) /1) = 100 Units b) How many orders per year are needed with the optimal policy? Ans: Number of Orders = Annual Demand / Q = 250 /100 = 2.50 c) What is the average inventory if costs are minimized? Ans: Average Inventory = 100/2 = 50 d) Suppose that the ordering cost is not $20, and Cotteleer has been ordering 150 units each time an order is placed. For this order policy (of Q = 150) to be optimal, determine what the ordering cost would have to be. Ans: EOQ = sqrt (( 2* Demand * Order Cost)/ Holding Cost) 150 = sqrt ((2* 250 * Order Cost)/1) Order Cost = 150 * 150 /( 2* 250) = 75 *3/5 = 45 $









