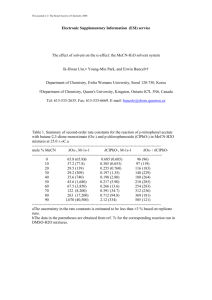
3. Program(s) in which the course is offered.
advertisement

National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Course Specification Institution: Salman Bin Abdel-Aziz University College/Department : Sciences and Humanitarian Studies College Al-Aflaj Female Sections, Chemistry Department. A Course Identification and General Information 1. Course title and code: Qualitative analysis, Chem2210 2. Credit hours 3 )1,0,2( 3. Program(s) in which the course is offered. (If general elective available in many programs indicate this rather than list programs) Chemistry Program 4. Name of faculty member responsible for the course Dr/ Mai Mostafa Ahmed Hassan 5. Level/year at which this course is offered 3ed level 6. Pre-requisites for this course (if any) 7. Co-requisites for this course (if any) 8. Location if not on main campus Sciences and Humanitarian Studies College Al-Aflaj Female Sections, Chemistry Department 1 B Objectives 1. Summary of the main learning outcomes for students enrolled in the course. Over aims of the course upon successful completion of this course: - The student should have knowledge about the concept, principles and theories qualitative analysis. - Define of general framework to study the analytical chemistry. - Gain the scientific information about the different reaction to separate the mixtures. - Understanding in depth deriving the equilibrium constant of the reactions. - Acquire familiarity with laboratory equipments and work safely in lab. 2. Briefly describe any plans for developing and improving the course that are being implemented. (eg increased use of IT or web based reference material, changes in content as a result of new research in the field) - Will convert parts of the course to electronic. - Use of web sites to illustrate some concepts in practical course. C. Course Description (Note: General description in the form to be used for the Bulletin or Handbook should be attached) Lectures'' outlines 1 Topics to be Covered List of Topics - General introduction in analytical chemistry - importance of studying qualitative analytical chemistry - Principles of qualitative analysis. - The principle of chemical equilibrium - Law of mass action - A base for L'Chethelet Law of Astewald dilution -Application on acid base reactions - Equilibrium in solutions of acids and bases - Water - the pH -Indicators acids and bases - Buffer solutions. -Solubility and solubility product - Applications of solubility product in precipitation of sulfides - precipitation of hydroxides - Equilibrium and the complexes reaction - Precipitation reactions - The theoretical principles for separating and analysing mixtures 2 No of Weeks Contact hours 2 4 2 4 2 4 6 3 2 4 2 4 Laboratory Experimental outlines 1 Topics to be Covered List of Expérimental General Introduction in Qualitative analysis and brief description of equipment used in analytical chemistry. Test of basic radicals in mixtures Group I (Ag, Pb, Hg) Test of basic radicals in mixtures Group III (Al, Fe, Cr) Test of basic radicals in mixtures Group IV (Ca, Ba, Sr) Test of basic radicals in mixtures Group VI (K, Na, Mg, NH 4) Scheme of the basic radicals in mixtures No of Weeks Contact hours 1 2 1 1 1 2 7 2 2 2 4 14 2 Course components (total contact hours per semester): Lecture: Tutorial: 13x2=26 Laboratory 12x2=24 Practical/Field work/Internship Other: 3. Additional private study/learning hours expected for students per week. (This should be an average :for the semester not a specific requirement in each week) 39 hours (3hours per week) 4. Development of Learning Outcomes in Domains of Learning For each of the domains of learning shown below indicate: A brief summary of the knowledge or skill the course is intended to develop; A description of the teaching strategies to be used in the course to develop that knowledge or skill. The methods of student assessment to evaluate learning outcomes in the domain concerned. a. Knowledge (i) Description of the knowledge to be acquired The student should be able to: -Acquires the knowledge and information about the importance of analytical chemistry and the different types and related fields. - Knowledge of the principles and foundations of qualitative analysis and the devices used in it. 3 – Define the basic concepts of chemical equilibrium constant for some reactions neutralization (such as a weak acid with a strong base - weak base with strong acid - Illustrate the theoretical bases for separating and analyzing mixtures. (ii) Teaching strategies to be used to develop that knowledge Theoretical lectures - small discussion groups - Preparation of research papers. (iii) Methods of assessment of knowledge acquired Quarterly written tests - discussions during the lectures – Final exam at the end of semester. b. Cognitive Skills (i) Description of cognitive skills to be developed - Develop the ability to analysis and scientific interpretation via training and identify the deferent basic radicals - Use scientific thinking to solve problems and solve overlaps in the separation of Basic radicals and that depending on the different solubility product. - The ability to derive useful information from data through to reach the best way to analyse the different samples. - Using of ideas and evidence from qualitative analysis to solve problems. (ii) Teaching strategies to be used to develop these cognitive skills Problem solving and exercises in analytical chemistry - practical exercises on the chemical analysis qualitative (iii) Methods of assessment of students cognitive skills Evaluation exercises solution - practical tests - Analysis of the unknown c. Interpersonal Skills and Responsibility (i) Description of the interpersonal skills and capacity to carry responsibility to be developed - Improve the ability to work in a team and solve some special exercise in chemical equilibrium, solubility product and the pH of a weak acid or strong base. - Training for the discussion of effective exercises and resolve issues within the lecture - Opinion, and get used to the inquiry and debate - Respect for colleagues and accept their opinions -Gain the ability to leadership team work. 4 (ii) Teaching strategies to be used to develop these skills and abilities Working in groups - the representation of roles - participate in the activities of the annual forum of Chemistry and seminars (iii) Methods of assessment of students interpersonal skills and capacity to carry responsibility Direct observation – collect assessment of performance and duties. d. Communication, Information Technology and Numerical Skills (i) Description of the skills to be developed in this domain. - The student used different methods to calculate the different concentrations of acids and bases and salts miscellaneous. - The link between the numerical value and the concentrations of materials.- Use the idea of buffer solutions to separate the elements and divided into groups - convert the numerical value of the equivalent weight of a substance to the mass weighted (ii) Teaching strategies to be used to develop these skills The use of e-learning - applications and practical exercises . (ii) Methods of assessment of students numerical and communication skills -Practical tests - solve exercises - During the discussion of work teams. e. Psychomotor Skills (if applicable) (i) Description of the psychomotor skills to be developed and the level of performance required - Procedure student of some tests for the detection of basic radicals of the unknown salt -The ability to revealed radicals in the base mixture - Development of applicant's ability of dealing with theoretical concepts and practical then collected in the summary schematic (ii) Teaching strategies to be used to develop these skills Lectures - laboratories and practical applications 5 (iii) Methods of assessment of students psychomotor skills Practical exercises - direct observation 5. Schedule of Assessment Tasks for Students During the Semester Assess ment Assessment task (eg. essay, test, group project, examination etc.) Week due Proportion of Final Assessment 1 Homework Assignments All along 5% 2 Pop Quizzes and Research papers All along 5% 3 Exam 1 6th 15% 4 Exam 2 11th 15% 5 Practical Exam 13th 20% 6 Final Exam 15th 40% D. Student Support 1. Arrangements for availability of teaching staff for individual student consultations and academic advice. (include amount of time teaching staff are expected to be available each week) - Laboratory assistance. - The two hour office per weak E Learning Resources 1. Required Text(s) -Qualitative analysis of inorganic, Salah Al-Din Mustafa, Mohamed Abdelaziz 2. Essential References -Principles of practical chemistry, Ahmed M. Eslam, Elsaide A. Hassan, Dar Alfager Alarabie, 2004. 3- Recommended Books and Reference Material (Journals, Reports, etc) (Attach List) -"Analytical chemistry" Hassan M. Al-Swaidan, Dar Al-Kheriji for publishing and distribution, Latest Edition. -"Dean's Analytical Chemistry Hand book" P. Patnaik, McGraw-Hill Hand books , Latest Edition. 6 4-.Electronic Materials, Web Sites etc Saudi Digital Library www.learnertv.com 5- Other learning material such as computer-based programs/CD, professional standards/regulations www.youtub.com/separation and identification of group F. Facilities Required Indicate requirements for the course including size of classrooms and laboratories (ie number of seats in classrooms and laboratories, extent of computer access etc.) 1. Accommodation (Lecture rooms, laboratories, etc.) - Lecture hall equipped with modern teaching technology (projector – interaction board – computer and internet) for all students. Lab is equipped in accordance the rules of safety and security 2. Computing resources - The presence of computer in classrooms 3. Other resources (specify --eg. If specific laboratory equipment is required, list requirements or attach list) - The presence of pure Chemical used in analytical. The presence of quantitative analytical equipments. - G Course Evaluation and Improvement Processes - 1. Strategies for Obtaining Student Feedback on Effectiveness of Teaching: - Student's questionnaires Analysis to specify the positive and negative views of them. E- suggestion. 1. Other Strategies for Evaluation of Teaching by the Instructor or by the Department Revision course description by the department committee. Self evaluation. 1. - Processes for Improvement of Teaching Updating the course material regularly. Increase the using modern technology methods in teaching like PowerPoint presentation. 7 4. - Processes for Verifying Standards of Student Achievement (eg. check marking by an independent member teaching staff of a sample of student work, periodic exchange and remarking of tests or a sample of assignments with staff at another institution) Checking a sample of the student's work, exams and assignments by other staff member in the department. 5. Describe the planning arrangements for periodically reviewing course effectiveness and planning for improvement. - Collecting all reports and evaluations at the end of the year for a reviewing purpose. - Conducting a meeting with the departmental committee for discussing the evaluation reports and share knowledge. - Reviewing results of reports and evaluations with inside and outside reviewers. -Designation the suitable improvement plane for the course 8