Biology Midterm Review Continued
advertisement

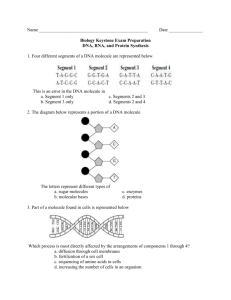
Biology Midterm Review Continued Protein Synthesis 1. Distinguish between transcription and translation. 2. Use the following DNA sequence to determine which amino acids are coded for: ACTGCA. Cell Transport Use the following illustrations to answer Questions 5-7. 3. The illustrations above demonstrate the transport of an ion across the plasma membrane, but they are out of sequence. In what order do they belong? i. D-C-B-A B. A-B-D-C C. C-B-D-A D. A-D-B-C 4. What statement is true about diagram D? i. The ion movement is random ii. Energy is required iii. The fatty acids in the plasma membrane could also move apart to allow the ion through iv. The concentration of ions is higher at the top of diagram D at the bottom 5. Which process is best represented by these diagrams? i. Diffusion B. Active Transport C. Endocytosis D. Passive Transport 6. Compare and contrast active transport and facilitated diffusion. 7. A Paramecium expels water when it is in fresh-water. What can you conclude about the concentration gradient in the organism’s environment? Carbon Cycle 8. Which of the following would most decrease the amount of carbon dioxide in the air? i. A growing maple tree B. A running dog C. A person driving a car D. A burning forest 14. Which 2 elements are important in the carbon cycle? A. oxygen and nitrogen B. hydrogen and nitrogen C. oxygen and carbon D. carbon and hydrogen Difference between RNA and DNA 15. Mark whether each of the following basic components is absent or present in DNA and RNA. Component Name DNA RNA Phosphate group Simple sugar Nitrogenous base Hydrogen bonds Adenine Thymine Guanine Cytosine Uracil Double helix Ribose Deoxyribose Cell Cycle 16. Which of the following indicates the correct order of mitosis in animal cells? i. A-B-C-D B. B-C-A-D C. C-A-D-B D. C-B-A-D Organelle Functions 17. Describe the differences between a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell. 18. Compare mitochondria and chloroplasts. Why are they referred to as energy transformers? 19. Choose the correct vocabulary words to fit the definitions below: ________________ Organelle that is the boundary between the cell and its environment ________________ Membrane-bound organelles that transform energy in all eukaryotic cells ________________ Highly organized structures within cells ________________ Organelles that are the sites of protein synthesis ________________ Basic unit of organization of both unicellular and multicellular organisms 20. Which of the following is NOT found in both plant and animal cells? A. Chloroplast B. cytoskeleton C. ribosomes D. mitochondria Ecology – Energy Flow 21. Order the following levels of biological organization from the broadest to the smallest categories: Biological community, Population, Biosphere, Ecosystem, Organism 22. Match the correct definition to each of the levels used in Question 28. __________________ A group of organisms, all of one species, which interbreed and live in the same place at the same time. __________________An individual living thing that is made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds, grows, and develops. __________________The portion of Earth that supports life. __________________ Populations of plants and animals that interact with each other in a given area and with the abiotic components of that area. __________________ All the populations of different species that live in the same place at the same time. 23. Why do autotrophs always occupy the lowest level of ecological pyramids? 24. Which of the following describes energy and matter in ecosystems? i. Both energy and matter are completely recycled. ii. Matter recycles, but some energy is transferred. iii. Energy is recycled, but most matter is lost. iv. Both matter and energy are completely lost. Use the following energy pyramid diagram to answer Questions 32 and 33. 25. In the pyramid of energy above, less energy is available in the second level because _______. i. There is more food that at the first level ii. Energy from the first level was given off as heat iii. The organism at the top doesn’t need very much energy iv. Producers don’t use as much energy 26. The amount of energy at each level is about ______ of what it was on the level before: i. 50% B. 25% C. 20% D. 10% Key 1. Transcription is the process of making an mRNA copy from a portion of a DNA strand. Translation is the process of converting the mRNA sequence into a sequence of amino acids in a protein. 2. UGA CGU AAA stop, arginine, lysine 3. mRNA takes the message from DNA to the ribosome, tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome in the correct order, rRNA is what the ribosome is made of and helps to put the amino acids in order to form a protein 4. changes the amino acid, thus the protein, thus the trait coded for. 5. C. C-B-D-A 6. B. Energy is required 7. B. Active transport 8. Both can use carrier proteins. Active transport uses energy, facilitated diffusion does not use energy, must go from high to low concentration 9. More water in the solution than in the paramecium, so hypotonic solution. Paramecium must expel water so it doesn’t explode 10. A 11. C 12. Component Name DNA RNA Phosphate group Present Present Simple sugar Present Present Nitrogenous base Present Present Hydrogen bonds Present Present Adenine Present Present Thymine Present Absent Guanine Present Present Cytosine Present Present Uracil Absent Present Double helix Present Absent Ribose Absent Present Deoxyribose Present Absent 13. Interphase: normal cell activities, Prophase: chromosomes get short and thick, spindle fibers form, centrioles migrate to poles; Metaphase: chromosomes line up at middle of cell, attaching to spindle fibers by the centromeres; Anaphase: chromosomes pull away on spindle fibers; Telophase: reverse of prophase 14. D. C-B-A-D 15. Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus. A prokaryotic cell has no membranebound organelles. Most of its metabolism takes place in its cyctoplasm. 16. Both mitochondria and chloroplasts are composed of two membranes, with the inner membrane being highly folded. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and other pigments used to capture light energy. Mitochondria and chloroplasts transform energy from one form to another. 17. Plasma membrane, mitochondria, nucleolus, organelle, ribosomes, vacuole, cell 18. A. cell wall 19. sun 20. Biosphere – Ecosystem – Biological Community – Population – Organism 21. Population – Organism – Biosphere – Ecosystem – Biological Community 22. Autotrophs capture light energy and create nutrients. When eaten, they provide nutrients for all other organisms. They have the most energy so must be at the bottom of the pyramid. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. B. Matter recycles, but some energy is transferred. B. energy from the first level was given off as heat Food chains have one producer, first order consumer, etc while food webs have multiple organisms at each level D. 10% Photosynthesis: Reactants = CO2 and H2O, Products = Glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen, Respiration: Reactants = Glucose and Oxygen, Products = H2O, Co2 and ATP B chloroplast Glycolysis – cytoplasm, citric acid or Krebs cycle – mitochondria, Electron Transport chain – mitochondria Stores energy Aerobic- uses oxygen, Anerobic – does not use oxygen A protein 2 only: pH and temperature Enzyme: 35. ATP 36. Energy is stored in the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate molecules, released when this bond is broken. 37. DNA polymerase: joins nitrogen bases, helicase: unzips the DNA, ligase: joins the phosphates and sugars 38. DNA 39. Carbohydrates: monosaccharides, glucose, energy Lipids: fatty acids and glycerol, oil, stores energy, insulation Proteins: amino acids, enzymes, structural (hair, etc) and functional proteins (hemoglobin) Nucleic acids: nucleotides, DNA, genetic information 40. Iodine: starch; Brown paper: lipid; Benedicts: glucose, Biuret’s solution: protein 41. Dependent: result of independent. Independent: controlled by researcher 42. State the problem. 43. Growth: 44. Acid rain: kills trees, destroys habitat. Non-native species: out-competes native species, overpopulation due to lack of natural predators. Deforestation: destroys habitat of animals, erosion, CO2 buildup in the atmosphere. 45. Growth and develop, reproduce, made of cells, use energy, respond to environment 46. Maintaining internal balance. 47. Habitat: where an organism lives. Niche: role of an organism in the environment 48. Predator-prey: lynx and hare. Commensalism: barnacle and whale. Mutualism: lichen = algae and fungi. Parasite: tick on a dog.