Urban zones - Shawlands Academy
advertisement

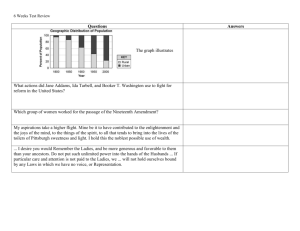
Urban zones Urban areas have a wide range of activities that take place throughout them. These activities can be grouped in to zones were particular types of activities are found predominantly in one area. The main zones found within an area are as follows: Central Business district (CBD) Nineteenth century housing Nineteenth century industry Twentieth century housing Twentieth century industry Greenbelts Dormitory or satellite settlements. CBD The Central Business District (CBD) in the city centre is where most business and commerce is located. It is the geographical centre. The CBD is easily identified by the following features: High/multi-storey buildings Expensive land values Shops are department stores or specialist shops, like jewellers Modern shopping malls and pedestrian precincts Cultural/historical buildings, museums and castles Offices, finance, banks, administration, town hall (business sector) Bus and railway stations (transport centres) Multi-storey car parks The CBD is located in the centre because it is: A central location for road/railways to converge The most accessible location for workers Accessible to most people for shops and businesses Nineteenth Century Housing This is part of the inner city and is found in the areas around the inner city. This area grew rapidly during industrialisation in the nineteenth century. The nineteenth century housing is easily identified by: A mixture of high density tenement/terraced housing Rectangular ‘grid iron’ pattern Busy roads pass through the housing Often near nineteenth century industry Lack of open space These areas can often be described as slum areas. In recent years these areas have seen large changes. (See future notes) Nineteenth century housing is located here because: Workers needed to be near the industries Land is cheaper outside the CBD Nineteenth century industry This is also part of the inner city area, which surrounds the CBD. It grew rapidly during industrialisation. The nineteenth century industry is easily identified by: Next to transport – railways, canals or rivers Near to nineteenth century housing (Labour) Large buildings, densely packed Very little open space This area has often become run down and derelict in recent years and some areas may be undergoing redevelopment. Nineteenth century industry is located here because: Needs good transport links for transporting raw materials Needed a near by labour force Land is cheaper outside the CBD Twentieth century housing Twentieth century housing can be both private estates and local authority housing. Twentieth century housing is easily identified by: Lower density housing (semi-detached, detached and low rise flats) Street patterns are more varied, with cul de sacs and curved roads. Far more open space Busy roads avoid housing estates. On the outskirts away from industry. Twentieth century housing is located here because: There is more space to build on Land prices are cheaper Twentieth century industry This is usually found on the very outskirts of a city. Twentieth century industry is easily identified by: Twentieth century industry is located here because: Land values are lower on the outskirt Easily accessible due to high ownership of cars Room for expansion Sites have room for expansion Good transport links – major roads and motorways Nearby labour force Open green areas which are often landscaped Greenbelts These are areas used by planners to control the spread of urban areas in to the rural landscape. It is found at the edge of urban areas on the rural- urban fringe. It is an area of open green space characterised by golf courses, country parks, airports and market gardens. The development in green belt areas is heavily restricted. The stated objectives of green belt policy are to: protect natural or semi natural environments; improve air quality within urban areas; ensure that urban dwellers have access to countryside, with consequent educational and recreational opportunities; and protect the unique character of rural communities which might otherwise be absorbed by expanding suburbs. Dorimotory or satelitie settlements. Small rural settlement which have good transport links (rail, motorway). They are used as commuter settlements and have a large resident population, but as very few of them actually work in the village, there is nobody to support any services. The commuters will do their shopping and banking in the city where they work. This means that these settlements will have fewer services than their population suggests they should have. Some commuter settlements are changing their services to cater for the different residents, with restaurants and cafes replacing the traditional village services. Task Answer the following questions in sentences. 1) What is the CBD? 2) Explain the growth and conditions of the zone containing nineteenth century industry. (Where did it grow up, why did it grow up here and what would the environment be like ?) 3) What is the green belt and why is it important? 4) Get a a copy of the table from your teacher and complete it. 5) Give the sheet with the table on a title.