Topic 3: Patterns and algebra
advertisement

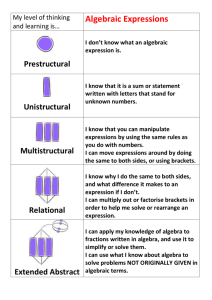
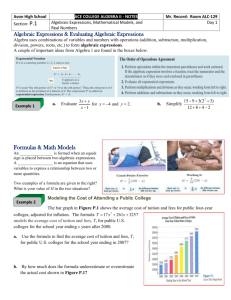
HEATHCOTE HIGH SCHOOL YEAR 8 MATHEMATICS PROGRAM 2004 TOPIC: Patterns and Algebra SUGGESTED TIME: At least 3 weeks CONTENT Key Ideas for Stage 2 1. Generate, describe and record number patterns using a variety of strategies Key Ideas for Stage 3 1.Build simple geometric patterns involving multiples 2.Complete a table of values for geometric and number patterns 3.Describe a pattern in words in more than one way Heathcote High School OUTCOMES: Stage 2: PAS2.1 Generates, describes and records number patterns using a variety of strategies (p 79) Stage 3: PAS 3.1a Records, analyses and describes geometric and number patterns that involve one operation using tables and words (p 80) Stage 4: PAS4.1 Uses letters to represent numbers and translates between words and algebraic symbols (p 82) PAS4.2 Creates, records, analyses and generalises number patterns using words and algebraic symbols in a variety of ways (p 83) PAS4.3 Uses the algebraic symbol system to simplify, expand and factorise simple algebraic expressions (p 85) Stage 5: PAS5.1.1 Applies the index laws to simplify algebraic expressions (p 87) KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS RESOURCES TERMINOLOGY Signpost 8 Second Edition Number pattern identifying and describing patterns when counting Chapter 5 Geometric pattern forwards or backwards by threes, fours, sixes, Table of values sevens, eights or nines Term creating, with materials or a calculator, a variety of Equal sign patterns using whole numbers, fractions or decimals Number sentence finding a higher term in a number pattern given the Rule first five terms Variable describing a simple number pattern in words Pronumeral Constant using the equals sign to record equivalent number Sum relationships and to mean ‘is the same as’ rather Product than as an indication to perform an operation Algebraic expression eg 4 3 6 2 Algebraic symbols completing number sentences involving one Simplify operation by calculating missing values Expand transforming a division calculation into a Factorise multiplication problem eg find so that 30 ÷ 6 = Substitute becomes find so that 6 = 30. Like terms Grouping symbols working through a process of building a simple geometric pattern involving multiples, completing a table of values, and describing the pattern in words. This process includes the following steps: - building a simple geometric pattern using materials - completing a table of values for the geometric pattern - describing the number pattern in a variety of ways and recording descriptions using words - determining a rule to describe the pattern from the YR8 program 3 patterns & algebra Page 1 of 4 table - using the rule to calculate the corresponding value for a larger number working through a process of identifying a simple number pattern involving only one operation, completing a table of values, and describing the pattern in words. This process includes the following steps: - completing a table of values for a number pattern involving one operation (including patterns that decrease) - describing the pattern in a variety of ways and recording descriptions using words - determining a rule to describe the pattern from the table - using the rule to calculate the corresponding value for a larger number Key Ideas for Stage 4 1.Use letters to represent numbers 2.Translate between words and algebraic symbols and between algebraic symbols and words 3.Recognise and use simple equivalent algebraic expressions 4.Create, record and describe number patterns using words 5.Use algebraic symbols to translate descriptions of number patterns 6.Use the algebraic symbol system to simplify, expand and factorise simple algebraic expressions 7.Substitute into algebraic expressions using letters to represent numbers and developing the notion that a letter is used to represent a variable using concrete materials such as cups and counters to model: - expressions that involve a variable and a variable plus a constant eg a, a 1 - expressions that involve a variable multiplied by a constant eg 2a, 3a - sums and products eg 2a 1, 2 (a 1) - equivalent expressions such as x x y y y 2x 2 y y 2 ( x y ) y - and to assist with simplifying expressions, such as (a 2) (2a 3) (a 2a) (2 3) 3a 5 recognising and using equivalent algebraic expressions y y y y 4y eg w w w2 a b ab a a b b Heathcote High School YR8 program 3 patterns & algebra WORKING MATHEMATICALLY WMS3.1 Asks questions that could be explored using mathematics in relation to Stage 3 content WMS3.3 Describes and represents a mathematical situation in a variety of ways using mathematical terminology and some conventions WMS4.1 Asks questions that could be explored using mathematics in relation to Stage 4 content WMS4.3 Uses mathematical terminology and notation, algebraic symbols, diagrams, text and tables to communicate mathematical ideas DIAGNOSIS/ASSESSMENT Page 2 of 4 translating between words and algebraic symbols and between algebraic symbols and words recognising like terms and adding and subtracting like terms to simplify algebraic expressions eg 2n 4m n 4m 3n recognising the role of grouping symbols and the different meanings of expressions, such as 2a 1 and 2a 1 simplifying algebraic expressions that involve multiplication and division 12a 3 eg 4x 3 2ab 3a simplifying expressions that involve simple algebraic fractions eg a a 2 3 2x x 5 3 expanding algebraic expressions by removing grouping symbols (the distributive property) 3( a 2) 3a 6 eg 5( x 2) 5 x 10 a ( a b) a 2 ab factorising a single term eg 6ab 3 2 a b factorising algebraic expressions by finding a common factor eg 6a 12 6(a 2) x 2 5 x x( x 5) 5ab 10a 5a(b 2) 4t 12 4(t 3) distinguishing between algebraic expressions where letters are used as variables, and equations, where letters are used as unknowns substituting into algebraic expressions generating a number pattern from an algebraic expression replacing written statements describing patterns with equations written in algebraic symbols translating from everyday language to algebraic language and from algebraic language to everyday Heathcote High School YR8 program 3 patterns & algebra Page 3 of 4 language Key Ideas for Stage 5 1.Apply the index laws to simplify algebraic expressions (positive integral indices only) using the index laws previously established for numbers to develop the index laws in algebraic form eg 2 2 2 3 2 2 3 2 5 a m a n a mn 2 5 2 2 2 5 2 2 3 a m a n a mn 2 2 (a m ) n a mn 2 3 6 establishing that a0 1 using the index laws eg a3 a3 a33 a0 and a3 a3 1 a0 1 simplifying algebraic expressions that include index notation eg 5x 0 3 8 2 x 2 3x 3 6 x 5 12a 6 3a 2 4a 4 2m 3 (m 2 3) 2m 5 6m 3 Heathcote High School YR8 program 3 patterns & algebra Page 4 of 4