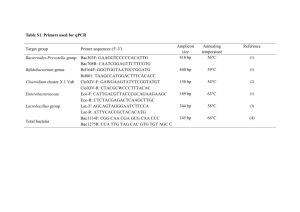
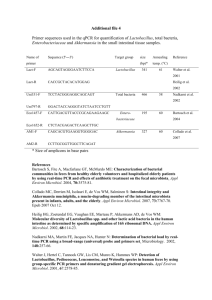
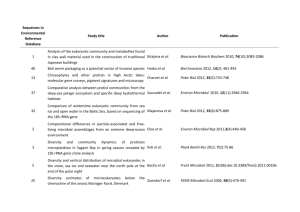
Curriculum Vitae - USC Dana and David Dornsife College of Letters
advertisement

CURRICULUM VITAE KENNETH H. NEALSON – WRIGLEY PROFESSOR OF GEOBIOLOGY, USC PERSONAL: Work: Home: University of Southern California Dept. of Earth Sciences, 117 Zumberge Halll of Science 3651 Trousdale Parkway Los Angeles, CA 90089-0740 phone: 213-821-2271 651 Andalusia Ave Los Angeles, CA 90065 phone: 323-227-6018 email: knealson@usc.edu EDUCATION: B.S. Biochemistry, University of Chicago, 1965 Ph.D. Microbiology, University of Chicago, 1969 Thesis Topic: Biochemical Genetics of Luminous Bacteria Thesis Advisor: Prof. Alvin Markovitz Postdoctoral Study, Harvard University, 1969-1972; Laboratory of Prof. J.W. Hastings EMPLOYMENT: Univ. Cal. San Diego, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, Assistant Professor, 1973-1978 Associate Professor, 1978-1984, Full Professor, 1984-1985 Univ. Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Center for Great Lakes Studies, Distinguished Professor, 1985-1997 Jet Propulsion Laboratory -- Senior Scientist; and Caltech -- Faculty Associate 1/98 – 9/01 Univ. of Southern California – Wrigley Professor of Geobiology – 10/01 – present HONORS & AWARDS: Hutchinson Fellowship for Graduate Studies in Botany, 1966 NSF Pre Doctoral Trainee, Univ. of Chicago, 1966-1969 NSF Post Doctoral Fellowship, 1969-1970 NIH Post Doctoral Fellowship, 1970-1972 Guggenheim Fellowship for Sabbatical Leave, 1981 Distinguished Visiting Professor, Univ. Wash., Summer, 1981 Elected Fellow, American Academy of Microbiology, Nov. 1993 NRL Distinguished Visiting Researcher Award, Jan., 1996 Nat. Acad. Sciences: Distinguished Leader in Life Sciences Award, October, 1998 Amer. Soc. Microbiology: Divisional Lecture Award, May, 1999 Amer. Soc. Microbiology: Divisional Lecture Award, May, 2000 NASA Special leadership award: JPL ($2,500 prize), June, 2000 Carnegie Institution Fellow – Cecil and Ida Green Fellow, December, 2000 (5 year award) Chair, Gordon Research Conference: Origin and Evoution of Life, Jan. 2001 Burroughs Wellcome Visiting Prof. in Microbiol. – Distinguished Lecture (Univ. Mo.), May, 2001 Society for Industrial Microbiol. – MDS Fermentation Technology Award – October, 2002 Amer. Soc. Microbiology. – Proctor and Gamble Award for Excellence in Environmental Microbiology Award Presented at ASM Meeting, Wash. D.C., May 2003. Society for Industrial Microbiol – Waksman Outstanding Educator Award, October, 2004 Recipient of the D.C. White Award for Research and Mentoring, Amer. Soc. Microbiol., 2009 Award to be presented at ASM meeting, San Diego, June 2010 1 PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES: American Society for Microbiology Society for General Microbiology American Association for Advancement of Science American Society for Limnology and Oceanography American Geophysical Union Society of Photochemistry and Photobiology The Oceanography Society American Society for Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology Geological Society of America International Society for Microbial Ecology NATIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL SERVICES: Grant Review Panels: National Science Foundation Biological Oceanography Environmental Protection Agency Basic Research Panel NASA Planetary Biology and Chemical Evolution Panel Exobiology Panel DOE Chairman, Subsurface Microbiology Panel Editor: Applied and Environmental Microbiology Member of Editorial Board of Journals: Geobiology Journal Environmental Microbiology FEMS Microbial Ecology Geomicrobiology Journal Symbiosis Outside Reviewer of Journals: Journal of Bacteriology, Science, Nature Biological Bulletin, Biochemistry, Journal of Biological Chemistry Limnology and Oceanography, Journal of Great Lakes Research Chairman, Nat. Acad. Sciences Task Group on Planetary Protection, 1993 Produced NAS Document for Public Distribution entitled: "Biological Contamination of Mars" Member Scientific International Advisory Board: Japanese Marine Biotechnology Institutes (MBI) Chairman, Nat. Acad. Sciences Task Group on Issues in Sample Return, 1996 Produced NAS Document for Public Distribution entitled: “Issues in Sample Return” Appointed Member, Space Studies Board of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 1996-98 Member, Space Science Exploration Subcommittee (Congressional Committee) 1996-99 Co-Chair, NAS Committee on Origin and Evolution of Life (COEL) 2005 - 2008 Member, Scientific Board, Venter Institute -- 2005 – 2008 Member, Space Studies Board of NRC – 2006 – 2008 Member, Mars Exploration Science Working Group, NASA 1998-present Member, Science Advisory Board, Max Planck Inst. Marine Microbiology, Bremen, Germany Member, Science Advisory Board, Synthetic Genomics, Inc., La Jolla, CA Member, Board of Trustees, J. Craig Venter Institute, San Diego, CA Member, Science Advisory Board, Japanese Marine Science & Technology (JAMSTEC) 2 AREAS OF RESEARCH: Biogeochemistry of Manganese and Iron: For several years we have been studying the laboratory and field activities of bacteria that oxidize and reduce metals, primarily manganese and iron. Past studies involved the development of methods to measure metal oxidation rates in the field, and the characterization of Mn and Fe oxidizing bacteria from a variety of marine and freshwater environments. Recent studies have involved the development of methods to measure the reduction of Mn and iron oxides by bacteria, and the relationship of these processes to other anaerobic processes in sediments. During this work, we described for the first time bacteria that grow anaerobically by coupling the oxidation of carbon to the reduction of iron and manganese oxides. These bacteria represent a new and novel metabolic group, which have been shown to couple their metabolism of metals to the extrusion of protons. They will be a major focal point of study for the near future. Present work with these organisms involves the molecular studies of their metal metabolism, and the relationship of this metabolism to other metabolic pathways within the metal reducing bacterium Shewanella putrefaciens. The studies range all the way from ecological studies of the distribution and activity of S. putrefaciens, to biochemical studies of the enzymes involved in reductive processes, to comparative gene studies of reductases involved in anaerobic metabolism. Development of Methods for Life Detection: During my time at JPL, I directed a group in the general area of Astrobiology. This group was composed of about 20 people, and had as its goal the development of search strategies for life detection, the development and testing of technologies to test these strategies in the laboratory or at other laboratories where the technologies exist, and eventually the use of these approaches and techniques for the search for life, both on Earth, in samples returned to Earth, and in situ on Mars and other sites off of our planet. This group and the work was decidedly interdisciplinary, including chemists, physicists, mathematicians, and engineers, as well as biologists, and involved a strong connection with national labs, such as the synchrotron facilities at Argonne and Berkeley, and with the group at Oak Ridge. Extreme environments on Earth: Recently, our laboratory has begun the investigation of extreme environments on Earth, utilizing the methods that we have been developing for life detection. These include the investigation of Mono Lake, CA. (high pH and salinity), deep subsurface environments (deep sea drilling cores), cold environments like the Antarctic and Siberian permafrost, and deserts, both hot and cold. One site of great interest is that of the Cedars in northern California, a site at which the pH reaches 12 and above, and the Eh is routinely minus 500 mV and lower. Geology of Mars, and the possibility of past or present life on Mars: I am presently involved with the Odyssey Mission to Mars, being a PI of the Themis imaging team. This work involves several students and postdocs in the lab, and focuses on the search for water and specific mineral types on the surface of Mars. It focuses on the properties of Mars that might be consistent with them being habitats for past life, and thus good sites to look for the evidence of past or even extant life when future Mars missions are flown. Microbial Fuel Cells for energy and education: Our lab has been working on the development and testing of microbial fuel cells (MFCs), with three goals in mind. First, to utilize these systems as teaching tools for microbial physiology and ecology; second, to improve power consumption to the point that useful power can be gained from the conversion of organic biomass; and, third, to engineer the systems for the processing of municipal and industrial waste. The latter would have the goal of both supplying energy and reducing the amount of sludge output from waste treatment plants via more efficient cycling of the waste during MFC operation. 3 MAJOR RESEARCH ACCOMPLISHMENTS: I list below what I feel are the major accomplishments of my own research, and that of my students and postdocs while working with me. The papers leading to these accomplishments are indicated in the publications list by being in bold. 1. Quorum Sensing (1970s) My thesis work, postdoctoral work, and early professorial research (at Scripps Institution of Oceanography) involved the biochemistry and physiology of light emitting bacteria. During these studies I discovered a mechanism the bacteria used to control their light emission that I called autoinduction. We purified the “autoinducer” (a homoserine lactone), and showed that it was used by the bacteria to communicate with each other in a process that was later renamed “quorum sensing”. This mechanism is now recognized as a major mechanism involved with microbial ecology, especially as regards biofilm formation, and pathogenesis. 2. Cloning of genes from marine bacteria (1980s) During the work with luminous bacteria, we successfully cloned the genes for bacterial luciferase. This was the first successful attempt at cloning and expressing genes from marine bacteria. During this work, we also cloned the genes for autoinduction (quorum sensing) discussed above. 3. Deployment of microelectrodes in the deep sea to measure oxygen flux (1980s) Claire Reimers, a postdoc in my lab, developed microelectrode methods, and worked to miniaturize the electronics, ultimately resulting in the measurement (for the first time) of oxygen profiles in deep sea sediments, and opening up an area of marine Geobiology formerly impossible. 4. Isolation of bacteria capable of manganese (and iron) reduction (1980s) In studies of the metal cycling of Oneida Lake, NY, while at the University of Wisconsin’s Center for Great Lakes Studies, we isolated, for the first time, an organism capable of “solid state respiration”, in which solid metal oxides of iron and/or manganese could be used for respiration (as electron acceptors). These bacteria, in the group Shewanella have been a model organism for the study of extracellular electron transport by bacteria. 5. Cloning of the first “environmental bacterium” (1990s) Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 was the first environmental bacterium (i.e., not a medical isolate) that was cloned, opening up a vast change in the way bacteria could be studied in the laboratory. 6. Metagenomics of the Marine Environment (2000s) Working with scientists from the Venter Institute, we succeeded, for the first time, in metagenomics analysis of the ocean. This work focused on the Sargasso Sea, and resulted in the first look at what turned out to be a surprisingly diverse and complex community. This was followed by a far more complex, large study, of the North Atlantic to the mid-Pacific, revealing a surprising and huge diversity not previously appreciated (or expected). 7. Identification of genes involved with electricity production in microbial fuel cells (MFC) Work at USC has revealed a number of genes from Shewanella that are essential for current production in MFC systems, and opened the door to the possibility of producing bacteria capable of producing electricity from domestic, industrial, and agricultural waste, while simultaneously producing clean water. This work is recently published, and in progress, and a major part of the laboratory’s focus at the present time. 4 RESEARCH FUNDING I have been continuously funded in the areas described above for about 30 years, and details of current funding are available on request. For the past 20 years, funding has been at a level of about $1M per year. A general summary is given below, with the amounts to my lab given in rough amounts. Extracellular electron electron transport: Uranium bioremediation -- ~ 100 K/year Microbial physiology/genetics -- ~ 300 K/year Chromium bioremediation -- ~ 125/year DOE DOE NSF Microbial Fuel Cell: Mechanisms of current production – 300K/year Optimizing current production – 250 K/year AFOSR (Air Force) Private Funds Planetary Science: Survival of extremophiles -- ~ 100K/year NASA I currently am director of a MURI (Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative) for MFC work, that includes 5 other PIs, and totals ~ 1.25 million per year. INVITED LECTURES AND SYMPOSIA: I don’t keep records of seminars and symposia at which I speak, as I tend to do this a couple of times a month, and consider it part of my regular job. I give 10 – 15 departmental seminars each year, and 2-5 Plenary Talks at national and international meetings. In addition I have presented more than 20 talks at Gordon Research Conferences, and have been Chair or Co-Chair at several Gordon Conferences, including: Environmental Science (water); Origin of Life; and Applied and Environmental Microbiology. Last year I gave a Plenary Lecture at a Max Planck workshop on life in the deep subsurface in Bremen, Germany, and a Plenary Lecture at the International Society for Environmental Microbiology (ISME), in Cairns, Australia. This year I will give the opening lecture at the AEM Gordon Conference; a Plenary Lecture at the American Society for Microbiology meeting in Philadelphia, and a Plenary Lecture at the Goldschmidt Conference in Davos, Switzerland. TEACHING: Over the years I have presented courses at USC to both upper level UG and Graduate students: 1) Microbial diversity; 2) Microbes and Minerals; 3) Habitable Planets; 4) Geobiology of Modern and Ancient Sediments; 5) The Living Planet (Geobiology). Currently I teach: Evolution and Adaptation of Bacteria; and, 2) Geobiology and Astrobiology. 5 STUDENTS TRAINED IN MY LABORATORY: Below is a list of students whose committees I was chairman or co-chairman, or with whom I interacted in a significant way during their training. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Dr. David Karl, Prof., Oceanography, Univ. Hawaii Dr. Robert Hodson, Prof., Microbiology, Univ. Georgia Dr. E.G. Ruby, Assoc. Prof., Biology, Univ. S. California Dr. Francisco Vidal, Res. Prof., UNAM, Mexico City Dr. Margo Haygood, Asst. Prof., Scripps Inst. Oceanogr., UCSD Dr. Bradley Tebo, Asst. Prof., Scripps Inst. Oceanogr., UCSD Dr. Sarah French, Assoc. Res. Prof., Molec. Biol., Univ. Va Dr. Dan Cohn, Assoc. Prof., Dept. of Medicine, UCLA Dr. David Burdige, Assoc. Prof. Oceanography, Old Dominion Univ. Dr. Gary Leisman, Senior Researcher, Post-Doc., NC State Univ. Dr. Paul Dunlap, Assoc. Professor, University of Michigan Dr. Carmen Aguilar, Postdoctoral Fellow, Research Scientist, Univ. Wisconsin Dr. Birgit Krause, Postdoctoral Fellow, Swiss Water Institute Dr. Duane Moser, Asst. Prof., UNLV, Desert Research Institute Dr. James Scott, 2002. Asst. Prof. Dartmouth Univ. Mr. Jerry Liu, 2002. Biotech Industry Consultant Mr. Derek Shannon, MS degree in 2007. Ms. Rachel Schelble, Ph.D. degree in 2007; Scientist, Exxon Mobile Ms. Brenda Fouch, MS degree in 2008 Dr. Orianna Bretschger, Ph.D. degree in 2008, Postdoc J.Craig Venter Inst. Dr. John McCrow, Ph.D. degree in 2008, Postdoc at J. Craig Venter Inst. Dr. Everett Salas, Ph.D. degree in 2009, Postdoc, Rice Univ. Dr. Laurie Barge, Ph.D. degree in 2009, Postdoc, Caltech Dr. Michael Waters, Ph.D degree in 2009, Postdoc, NIST Ms. Yanbing Wang, current, Ph.D. degree expected fall 2010 Ms. Beverly Flood, current, Ph.D. degree expected fall 2010 Mr. Lewis Hsu, current, Ph.D. degree expected fall 2010 Mr. Prithviraj Chulamurthy, current 3rd year: quals passed Ms. Carie Frantz, current, current 2nd year: quals passed Mr. Howard Harris, current, current 2nd year 6 POST DOCTORAL WORKERS IN MY LABORATORY: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Dr. Yehuda Cohen, 1970, Prof. Hebrew Univ. Dr. Reinhardt Rosson, 1975-77, Senior Researcher, Biotechnical Resources, Inc. Dr. Paul Kepkay, 1983-4, Prof., Dalhousie Univ.. Dr. Claire Reimers, 1982-84, Prof., Oregon State Univ. . Dr. Sally Look, 1984-85, Researcher, NIH Dr. Thomas Schmidt, 1985-87, Prof., Michigan State Univ. Dr. Bruce Bleakley, 1985-87, . Prof., So. Dak. State Univ. Dr. Charles Myers, 1987-89, Assoc. Prof., Medical College of Wisconsin. Dr. Susan Frackman, 1989-1992, Research Specialist, Pharmacia, Inc. Dr. David Bermudes, 1989-1992, Industry – own company Dr. Daad Saffarini, 1991-1995, Assoc. Prof., Univ. of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Dr. Joel Kostka, 1993 - 1995, Asst. Prof., Univ. Georgia Dr. Lea Cox, 1997-2000, Asst. Prof. Res., UCSB Dr. Henry Sun, 1998-2000, Asst. Prof. Res., DRI Dr. Brian Lanoil, 1998-2001, Asst. prof. Environmental Sciences, UC-Irvine Dr. Lisa Stein, 1999-2001, Asst. Prof. Environmental Chemistry, UC-Irvine Dr. Robert Rye, 2000-2001, Asst. Prof. Research, USC Dr. Eric Gaidos, 1998-2001, Assoc. Professor at Univ. Hawaii Dr. Corien Bakermans, 2000-, Post Doc, Mich. State Univ. Dr. Giovanna Tinetti, 2001 – present, Univ. of Torino, Italy Dr. Virginia Souza, 2001 – Asst. Prof, Univ. of Madrid, Spain Dr. Radu Popa, 2000 – Asst. Prof., Portland State Univ. Dr. Patrick Meister, present, from ETH in Switzerland Dr. Moh El-Naggar, 2007-2009, Asst. Prof. Physics, USC Dr. Zhen (Jason) He, 2008-2009, Asst. Prof. Engineering, U.W. Milwaukee Dr. Jae-Kyung Kang, scientist, Korean Inst. Sci. & Technology (KIST) Dr. Jinjun Kan, present, from Ctr. Marine Biotechnology, Maryland, USA 7 PUBLICATIONS: I have published ~300 reviewed papers, three edited books, and several reports from summer courses and other workshops as shown below Published Monographs and Reports: Margulis, L., K. Nealson, and I. Taylor. 1983. Biogeochemistry of Carbon and Early Life. NASA Tech. Memo. 86043. Report of the PBME Summer Research Program. NASA Press 134 pp. Nealson, K., L. Margulis, and D. Sagan. 1985. The Global Sulfur Cycle. NASA Tech. Memo. 87570. Report of the PBME Summer Research Program. NASA Press, 262 pp. Nealson, K., M. Nealson, and F.R. Dutcher. 1990. The Biogeochemistry of Metal Cycling. NASA Tech. Memo. 4295. Report of the PBME Summer Research Program. NASA Press , 206 pp. Nealson, K.H. (Chair, Task Group on Planetary Protection). 1992. Biological Contamination of MARS, Issues and Recommendations. Report of the Task Group on Planetary Protection of the Space Studies Board. Natl. Academy Press, Washington, D.C. 115 pp. Nealson, M.S., and K. Nealson. 1993. Molecular Ecology and the Global Nitrogen Cycle. NASA Tech. Memo 4497. Report of the PBME Summer Research Program. NASA Press, 170 pp. Nealson, K.H. (Chair, Task Group on Sample Return). 1997. Issues in Sample Return. Report of the Task Group on Issues in Sample Return of the Space Studies Board. Natl. Academy Press, Washington D.C. Books: Nealson, K.H. (editor). 1981. Bioluminescence: current perspectives. Burgess Publishing Company, Minneapolis, MN. Banfield, J. F. and K.H. Nealson (editors). 1997. Geomicrobiology: interactions between microbes and minerals. Reviews in Mineralogy Volume 35. Mineral. Soc. America, Washington, D.C. Banfield, J.F., Cervini-Silva, J., and K.H. Nealson. 2005. Molecular Geomicrobiology. Rev. Mineralogy. Vol. 59. Mineral. Soc. America. Washington, DC Reviewed Papers and Chapters: 1. Nealson, K., and A. Markovitz. 1970. Mutant analysis and enzyme subunit complementation in bacterial bioluminescence in Photobacterium fischeri. J. Bacteriol. 104:300-312. 2. Nealson, K., T. Platt, and J.W. Hastings. 1970. Cellular control of the synthesis and activity of the bacterial luminescent system. J. Bacteriol. 104:313-322. 3. Gunsalus-Miguel, A., E. Meighen, M. Nicoli, K. Nealson, and J.W. Hastings. 1972. Purification and properties of bacterial luciferase. J. Biol. Chem. 247:398-404. 4. Nealson, K., and J.W. Hastings. 1972. The inhibition of bacterial luciferase by mixed function oxidase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 247:888-894. 5. Nealson, K., A. Eberhard, and J.W. Hastings. 1972. Catabolite repression of bacterial bioluminescence: functional implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 59:1073-1076. 6. Hastings, J.W., A. Eberhard, T. Baldwin, M. Nicoli, T. Cline, and K. Nealson. 1973. Bacterial bioluminescence: Mechanistic implications of active site chemistry of luciferase. pp. 369-380. In: Chemiluminescence and 8 Bioluminescence. Ed. M. Cormier, D. Hercules, and J. Lee. Plenum Pub. Co., NY. 7. Keynan, A., K. Nealson, H. Sideropoulos, and J.W. Hastings. 1974. Marine transducing bacteriophage attacking a luminous bacterium. J. Virology. 14:74-86. 8. Morin, J., A. Harrington, K. Nealson, N. Krieger, T. Baldwin, and J.W. Hastings. 1975. A light for all reasons. Science 190:74-76. 9. Ruby, E.G., and K.H. Nealson. 1976. Symbiotic association of Photobacterium fischeri with the luminous fish Monocentris japonica: a model of symbiosis based on bacterial studies. Biol. Bull. 10. Nealson, K. H., and J.W. Hastings. 1977. Low oxygen is optimal for luciferase synthesis in some bacteria: Ecological implications. Arch. Microbiol. 112:9-16. 11. Nealson, K.H. 1977. Autoinduction of bacterial luciferase: Occurrence, mechanism and significance. Arch. Microbiol. 112:73-79. 12. Reichelt, J., K. Nealson, and J. Hastings. 1977. The specificity of symbiosis: Pony fish and luminescent bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 112:157-161. 13. Ruby, E.G., and K.H. Nealson. 1977. A luminous bacterium that emits yellow light. Science 14. Ruby, E.G., and K.H. Nealson. 1977. Pyruvate production and excretion by luminous marine bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 34:164-169. 15. Hastings, J.W., and K.H. Nealson. 1977. Bacterial bioluminescence. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 16. Nealson, K.H. 1978. The isolation and characterization of marine bacteria that catalyze manganese oxidation. Environ. Biogeochem. Geomicrobiol. 3:847-858. 17. Ruby, E.G., and K.H. Nealson. 1978. Seasonal changes in the species composition of luminous bacteria in nearshore seawater. Limnol. Oceanogr.. 23:530-533. 18. Nealson, K. H., 1978. Isolation, identif ication and manipulation of luminous bacteria. pp. 153-156. In: Methods in Enzymology, vol. 57. Ed. M. DeLuca. Academic Press, NY. 19. Gagosian, R., S. Ahmed, J. Farrington, R. Lee, R. Mantoura, K. Nealson, T. Packard, and K. Reinhart. 1978. Future research problems in marine organic chemistry. Mar. Chem. 6:375-383. 20. Bang, S., P. Baumann, and K. Nealson. 1978. Phenotypic characterization of Photobacterium logei (sp. nov.), a species related to Photobacterium fischeri. Current Microbiol. 1:285-288. 21. Holland, N., and K. Nealson. 1978. The fine structure of the echinoderm cuticle and the subcuticular bacteria of echinoderms. Acta. Zool. (Stockholm) 59:169-185. 22. Nealson, K.H. 1979. Alternative strategies of symbiosis of marine luminous fishes harboring light emitting bacteria. T. I. B. S. 4:105-110. 23. Tebo, B.M., D. Linthicum, and K. Nealson. 1979. Luminous bacteria and light emitting fish: Ultrastructure of the symbiosis. BioSystems 11:269-280. 24. Nealson, K., and J.W. Hastings. 1979. Bacterial bioluminescence: Its control and ecological significance. Microbiol. Rev. 43:469-518. 25. Poinar, G., G. Thomas, M. Haygood, and K. Nealson. 1980. Growth and luminescence of the symbiotic bacteria associated with the terrestrial nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 12:5-10. 9 26. Nealson, K.H., and J. Ford. 1980. Surface enhancement of bacterial manganese oxidation: Implications for aquatic environments. Geomicrobiol. J. 2:21-37. 27. Karl, D.M., and K. Nealson. 1980. Regulation of cellular metabolism during synthesis and expression of the luminous system in Beneckea and Photobacterium. J. Gen. Microbiol. 11 7:357-368. 28. Leisman, G., D. Cohn, and K. Nealson. 1980. Bacterial origin of luminescence in marine animals. Science 208:1271-1273. 29. Nealson, K.H., and B. Tebo. 1980. Structural features of manganese precipitating bacteria. Origins of Life 10:117-126. 30. Harwood, C., S. Bang, P. Baumann, and K. Nealson. 1980. Photobacterium logei sp. nov., nom. rev.; Beneckea nereida sp. nov. nom. rev.; and Beneckea gazogenes sp. nov., nom. rev. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 30:655-661. 31. Hastings, J.W., and K. Nealson. 1980. Exosymbiotic luminous bacteria occurring in luminous organs of higher animals. pp. 467-471. In: Endocytobiology. Ed. W. Schwemmler and H. Schenk. Walter de Gruyter and Co. NY. 32. Nealson, K., and J. Hastings. 1980. Luminescent bacterial endosymbionts in bioluminescent tunicates. pp. 461-465. In: Endocytobiology. Ed. W. Schwemmler and H. Schenk. Walter de Gruyter and Co. NY. 33. Jensen, M., B. Tebo, P. Baumann, M. Mandel, and K. Nealson. 1980. Characterization of Alteromonas hanadai (sp. nov.), a nonfermentative luminous species of marine origin. Current Microbiol. 3:311-315. 34. Hastings, J.W. and K. Nealson. 1981. The symbiotic luminous bacteria. pp. 1332-1346. In: The Prokarvotes Vol. 11. Ed. M. Starr, H. Stolp, H. Trueper, A. Balows, and H. Schlegel. Springer Verlag, NY. 35. Paul, V., S. Frautschy, W. Fenical, and K. Nealson. 1981. Antibiotics in microbial ecology: Isolation and structure assignment of several new antibacterial compounds from the insect symbiotic bacteria Xenorhabdus spp. J. Chem. Ecol. 3:589-597. 36. Burnette, B., and K. Nealson. 1981. Organic films and microorganisms associated with manganese nodules. Deep Sea Res. 282:299-304. 37. Dean, W., W. Moore, and K. Nealson. 1981. Manganese cycles and the origin of manganese nodules, Oneida Lake, NY, USA. Chem. Geol. 34:53-64. 38. Rosson, R., and K. Nealson. 1981. Autoinduction of bacterial bioluminescence in a carbon limited chemostat. Arch. Microbiol. 129:299-304. 39. Eberhard, A., C. Eberhard, and K. Nealson. 1981. Purification, identification and synthesis of Photobacterium fischeri autoinducer. pp. 113-120. In: Bioluminescence and Chemiluminescence. Ed. M. DeLuca and W. McElroy. Academic Press, NY. 40. Eberhard, A., A. Burlingame, C. Eberhard, G. Kenyon, K. Nealson, and N. Oppenheimer. 1981. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry 20:2444-2449. 41. Nealson, K., D. Cohn, G. Leisman, and B. Tebo. 1981. Coevolution of luminous bacteria and their eukaryotic hosts. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 361:76-91. 42. Nealson, K.H. 1982. Microbiological oxidation and reduction of iron. pp. 51-66. In: Mineral Deposits and the Evolution of the Biosphere. Ed. H. Holland and M. Schidlowski. Dahlem Konferenzen, Berlin. Springer-Verlag, NY. 10 43. Rosson, R., and K. Nealson. 1982. Manganese binding and oxidation by spores of a marine Bacillus. J. Bacteriol. 151:1027-1034. 44. Kepkay, P., and K. Nealson. 1982. Surface enhancement of sporulation and manganese oxidation by a marine Bacillus. J. Bacteriol. 151:1022-1036. 45. Emerson, S., L. Jacobs, S. Kalhorn, R. Rosson, B. Tebo and K. Nealson. 1982. Environmental oxidation rate of manganese: Bacterial catalysis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 46:1073-1079. 46. Rosson, R. and K. Nealson. 1982. Manganese bacteria and the marine manganese cycle. pp. 201-216. In: The Environment of the Deep Sea. Rubey symposium 11. Ed. J. Morin and W. Ernst. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ. 47. Nealson, K.H. 1982. Bacterial ecology of the deep sea. pp. 179-200. In: The Environment of the Deep Sea. Rubey Symposium 11. Ed. J. Morin and W. Ernst. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ. 48. Leisman, G., and K. Nealson. 1982. Characterization of a yellow fluorescent protein from Vibrio fischeri. pp383-386. In: Flavins and Flavoproteins. Ed: V. Massey and C. Williams. Elsevier North Holland. 49. Chapnick, S., W. Moore and K. Nealson. 1982. Manganese oxidation in a fresh water lake: Geochemical and microbiological studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17:1004-1014. 50. Leisman, G., and K. Nealson. 1982. Yellow luminescence in vivo from the luminous bacteria Vibrio fischeri Y1. pp. 302-313. In: Bioluminescence in the Pacific. Ed. J. Gitelson and J. Hastings. lnst. Physics and Biophysics, Krasnoyarsk, USSR. 51. Cohn, D., R. Ogden, J. Abelson, T. Baldwin, K. Nealson, M. Simon, and A. Mileham. 1983. Cloning of the Vibrio harveyi luciferase genes: Use of a synthetic oligonucleotide probe. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci USA 80:120123. 52. Nealson, K.H. 1983. Microbial oxidation and reduction of manganese and iron. pp. 459-479. In: Biomineralization and Biological Metal Accumulation. Ed: P. Westbroek and E. deJong. D. Reidel Pub. Co., Amsterdam. 53. Burdige, D., P. Kepkay and K. Nealson. 1983. An in situ method for determining microbial manganese oxidation rates in sediments. pp. 481-487. In: Biomineralization and Biological Metal Accumulation. Ed: P. Westbroek and E. deJong. D. Reidel Pub. Co., Amsterdam. 54. Engebrecht, J., K. Nealson and M. Silverman. 1983. Bacterial bioluminescence: Isolation and genetic analysis of functions from Vibrio fischeri. Cell 32:773-781. 55. Nealson, K.H. 1983. The microbial iron cycle. pp. 159-189. In: Microbial Geochemistry. Ed. W. Krumbein. Blackwell Sci. Pub. Ltd., Oxford, U.K. 56. Nealson, K.H. 1983. The microbial manganese cycle. pp. 191-222. ln: Microbial Geochemistry. Ed. W. Krumbein. Blackwell Sci. Pub. Ltd. Oxford, U.K. 57. Lidstrom, M., J. Engebrecht and K. Nealson. 1983. Evidence for plasmid-encoded manganese oxidation in a marine pseudomonad. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 19:1-6. 58. Burnett, B., and K. Nealson. 1983. Energy dispersive X-ray analysis of the surface of a deep sea ferromanganese nodule. Mar. Geol. 53:313-329. 59. Haygood, M., B. Tebo, and K. Nealson. 1984. Luminous bacteria of a monocentrid fish (Monocentris japonicus) and two anomalopid fishes (Photoblepharon palpebratus and Kryptophanaron alfredi): population 11 sizes and growth within the light organs, and rates of release into the seawater. Mar. Biol. 75:249-255. 60. Nealson, K., M. Haygood, B. Tebo, M. Roman, E. Miller, and J. McCosker. 1984. Contribution by symbiotically luminous fishes to the occurrence and bioluminescence of luminous bacteria in seawater. Microbial Ecol. 10:69-77. 61. Warner, J., A. Arneson, R. Austin, D. Bailey, G. Huszar, P. James, R. McConnaughey, K. Nealson, and E. Stephan. 1984. Scripps Canyon sea structure: A design and deployment for the study of oceanic bioluminescence. Mar. Tech. Soc. J. 17:40-47. 62. Kepkay, P., D. Burdige and K. Nealson. 1984. Kinetics of bacterial manganese binding and oxidation in the chemostat. Geomicrobiol. J. 3:245-262. 63. Rosson, R., B. Tebo and K. Nealson. 1984. Use of poisons in determination of microbial manganese binding rates in seawater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 47:740-745. 64. Nealson, K., and R. Cassin. 1984. Molecular genetic studies in bioluminescence. pp. 87-99. In: Bioluminescence and Chemiluminescence. Ed. S. Whitehead and L. Kricka. Academic Press, NY. 65. Haygood, M., and K. Nealson. 1984. Effects of iron on bacterial growth and bioluminescence: Ecological implications. pp. 56-61. In: Current Perspectives in Microbial Ecology. Ed. M. Klug and C. Reddy. Amer. Soc. Microbiol., Wash. D.C. 66. Reimers, C., S. Kalhorn, S. Emerson and K. Nealson. 1984. Oxygen consumption rates in pelagic sediments from the Central Pacific: First estimates from microelectrode profiles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 48:903-91 0. 67. Nealson, K., A. Arneson and A. Bratkovich. 1984. Preliminary results from studies of nocturnal bioluminescence with subsurface moored photometers. Mar. Biol. 75:185-191. 68. Orzech, J., and K. Nealson. 1984. Bioluminescence of marine snow: its effect on the optical properties of the sea. Proc. Internat. Soc. Optical Eng. 489:100-106. 69. Woese, C., E. Stackebrandt, W. Weisburg, B. Paster, M. Madigan, V. Fowler, C. Hahn, P. Blanz, R. Gupta, K. Nealson, and G. Fox. 1984. The phylogeny of purple bacteria: The alpha subdivision. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 5:315-326. 70. Tebo, B., K. Nealson, S. Emerson and L. Jacobs. 1984. Microbial mediation of Mn(II) and Co(II) precipitation at the 02/H2S interface in two anoxic fjords. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29:1247-1258. 71. Haygood, M., and K. Nealson. 1985. Mechanisms of iron regulation of luminescence in Vibrio fischeri. J. Bacteriol. 162:209-216. 72. Cohn, D., A. Mileham, M. Simon, K. Nealson, S. Rausch, D. Bonam and T. Baldwin. 1985. Nucleotide sequence of the luxA gene of Vibrio harveyi and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit of bacterial luciferase. J. Biol. Chem. 260:6139-6146. 73. Haygood, M., and K. Nealson. 1985. The effect of iron on the growth and luminescence of the symbiotic bacterium Vibrio fischeri. Symbiosis 1:39-51. 74. Burdige, D., and K. Nealson. 1985. Microbial manganese reduction by enrichment cultures from coastal marine sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 50:491-497. 75. Nealson, K., and Arneson, A. 1985. Marine bioluminescence: About to see the light. Oceanus 28:13-18. 76. Tebo, B., C. Taylor, K. Nealson and S. Emerson. 1985. In situ Mn(II) binding rates at the oxic/anoxic interface 12 in Saanich Inlet, B.C., Canada. pp. 210-221. In: Planetary Ecology. Ed. D. Caldwell, J. Brierly and C. Brierly 77. Nealson, K., A. Arneson and M. Huber. 1986. Identification of marine organisms using kinetic and spectral properties of their bioluminescence. Mar. Biol. 91:77-83. 78. Burdige, D., and K. Nealson. 1986. Chemical and microbiological studies of sulfide-mediated manganese reduction. Geomicrobiol J. 4:361-387. 79. Maki, J., B. Tebo, F. Palmer, K. Nealson and J. Staley. 1987. The abundance and biological activity of manganese-oxidizing bacteria and Metallogenium-like morphotypes in Lake Washington, USA. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 45:21-29. 80. Levisohn, R., Moreland, J. and K. Nealson. 1987. Isolation and characterization of a generalized transducing phage for the marine luminous bacterium Vibrio fischeri MJ-1. J. Gen. Microbiol. 133:1577-1582. 81. Delong, E., D. Steinhauer, A. Israel and K. Nealson. 1987. Isolation of the lux genes from Photobacterium leiognathi and expression in Escherichia coli. Gene 54:203-21 0. 82. Kepkay, P., and K. Nealson. 1987. Growth of a manganese oxidizing Pseudomonas sp. in continuous culture. Arch. Microbiol. 148:63-67. 83. Steinberg, D., G. Peterson, K. Nealson, and W. Maiese. 1987. Evaluation of bioluminescence as a prescreen for antitumor agents. pp. 511-514. In: Bioluminescence and Chemiluminescence: New Perspectives. Ed. J. Schoelmerich, R. Andreesen, A. Kapp, M. Ernst, and W. Woods. Wiley and Sons, NY. 84. Nealson, K., D. Steinberg, A. Israel, G. Peterson and W. Maiese. 1987. Chemical stimulation of bioluminescence in E. coli. pp. 393-396. In: Bioluminescence and Chemiluminescence: New Perspectives. Ed. J. Schoelmerich, R. Andreesen, A. Kapp, M. Ernst, and W. Woods. Wiley and Sons, NY. 85. Nealson, K. H. B. Tebo and R. Rosson. 1988. Occurrence and mechanisms of microbial oxidation of manganese.. Adv. Applied Microbiol. 33:279-318. 86. Nealson, K., T. Schmidt and B. Bleakley. 1988. Luminescent bacteria: symbionts of nematodes and pathogens of insects. pp. 101-113. In: Cell to Cell Signals in Plant, Animal and Microbial Symbiosis. Ed. S. Scannerini. Springer Verlag, Berlin. 87. Lapota, D., C. Galt, J. Losee, H. Huddell, J. Orzech and K. Nealson. 1988. Observations and measurements of planktonic bioluminescence in and around a milky sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 119:55-81. 88. Richardson, W., T. Schmidt and K. Nealson. 1988. Identification of an anthraquinone pigment and a hydroxystilbene antibiotic from Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54:1602-1605. 89. Myers, C. and K. Nealson. 1988. Bacterial manganese. reduction and growth with manganese oxide as the sole electron acceptor. Science 240:1319-1321. 90. Richardson, L., C. Aguilar and K. Nealson. 1988. Manganese oxidation in pH and 0 2 microenvironments produced by phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33:352-366. 91. Bleakley, B., and K. Nealson. 1988. Characterization of primary and secondary forms of Xenorhabdus luminescens strain Hm. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 53:241-250. 92. Schmidt, T., B. Bleakley and K. Nealson. 1988. Characterization of an extracellular protease from the insect pathogen Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54:2793-2797. 93. Myers, C., and K. Nealson. 1988. Microbial reduction of manganese oxides: Interactions with iron and sulfur. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52:2727-2732. 13 94. Nealson, K., R. Rosson and C. Myers. 1989. Mechanisms of oxidation and reduction of manganese. pp. 383411. In: Metal Ions and Bacteria. Ed. T. Beveridge and R. Doyle. John Wiley and Sons, NY. 95. Richardson, L., and K. Nealson. 1989. Distributions of manganese, iron and manganese oxidizing bacteria in Lake Superior sediments of different organic carbon content. J. Great Lakes Res. 1 5:123-132. 96. Schmidt, T., K. Kopecky and K. Nealson. 1989. Bioluminescence of the insect pathogen Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55:26-7-2612. 97. Seale, D., M. Boraas, D. Holen and K. Nealson. 1990. Use of bioluminescent bacteria, Xenorhabdus luminescens, to measure predation on bacteria by freshwater microflagellates. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 73:3140. 98. Bermudes, D., V. Gerlach and K. Nealson. 1990. Effects of culture conditions on mycelial growth and luminescence in Panellus stypticus. Mycologia 82:295-305. 99. Nealson, K. and C. Myers. 1990. Iron reduction by bacteria: A potential role in the genesis of banded iron formations. Amer. J. Sci. 290-A:35-45. 100. Nealson, K., T. Schmidt and B. Bleakley. 1990. Physiology and biochemistry of Xenorhabdus- pp. 271284. In: Entomopthogenic Nematodes in Biological Control. Ed. R. Gaugler and H. Kaya. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. 101. Frackman, S., and K. Nealson. 1990. The molecular genetics of Xenorhabdus. pp. 285-300. In: Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Biological Control. Ed. R. Gaugler and H. Kaya. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL 102. Frackman, S., M. Anhalt, and K. Nealson. 1990. Cloning, organization, and expression of the bioluminescence genes of Xenorhabdus luminescens. J. Bacteriol. 172:5767-5773. 103. Myers, C., and K. Nealson. 1990. Respiration-linked proton translocation coupled to anaerobic reduction of manganese(IV) and iron(III) in Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. J. Bacteriol. 172:6232-6238. 104. Myers, C., and K.H. Nealson. 1990. Iron Mineralization by bacteria: metabolic coupling of iron reduction to cell metabolism in Alteromonas putrefaciens strain MR-1. pp. 131-149 In: R.B. Frankel and R.P. Blakemore (eds) Iron Biominerals. Plenum Press, NY. 1990. 105. Wimpee, C.F., T. Nadeau, and K.H. Nealson. 1991. Development of species-specific hybridization probes for marine luminous bacteria by using in vitro DNA amplification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57:1319-1324. 106. Bermudes, D., M. E. Boraas and K.H. Nealson. 1991. In vitro antagonism of bioluminescent fungi by Trichoderma harzianum. Mycopathologia 115:19-29. 107. Nealson, K.H. 1991. Luminous bacteria symbiotic with entomopathogenic nematodes. pp. 205-218 In: L. Margulis and R. Fester (eds). Symbiosis as a source of Evolutionary Innovation. MIT Press, Boston, Mass. 108. Nealson, K.H., C.R. Myers, and B.B. Wimpee. 1991. Isolation and identification of manganese reducing bacteria and estimates of microbial Mn(IV)-reducing potential in the Black Sea. Deep Sea Res. 38:S907S920. 109. Nealson, K.H. and J.W. Hastings. 1991. The Luminous bacteria. pp. 625-639. In: The Prokaryotes. Second Edition. Vol-1. (eds.) A. Balows, H.G. Trueper, M. Dworkin, W. Harder, and K-H. Schleifer. Springer Verlag, New York, NY. 110. Nealson, K.H. 1991. The manganese-oxidizing bacteria. pp. 2310-2320. In: The Prokaryotes Second 14 Edition. Vol. 1. (eds.) A. Balows, H.G. Trueper, M. Dworkin, W. Harder, and K-H. Schleifer. Springer Verlag, New York, NY. 111. Tebo, B.M., Rosson, R.A. and Nealson, K.H. 1991. Potential for Mn(II) oxidation and Mn(IV) reduction to co-occur in the suboxic zone of the Black Sea. pp. 173-185: In: Black Sea Oceanography. Eds. E. lzdar and J.W. Murray. Kluwer Acad. Publishers, Netherlands. 112. Nealson, K.H. and C.R. Myers. 1992. Microbial reduction of manganese and iron: new approaches to carbon cycling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 439-443. 113. Burdige, D.J., S. P. Dhakar, and K.H. Nealson. 1992. Effects of manganese oxide mineralogy on microbial and chemical manganese reduction. Geomicrobiol. J. 10:27-48. 114. Bermudes, D., R.H. Petersen, and K.H. Nealson. 1992. Low-level bioluminescence detected in Mycena haematopus basidiocarps. Mycologia 84(5):799-802. 115. Perry, K.A., J.E. Kostka, G.W. Luther III and K.H. Nealson. 1993. Mediation of suIfur speciation by a Black Sea facultative aerobe. Science 259:801-803. 116. Nealson, K.H., B. Wimpee, and C. Wimpee. 1993. Identification of Vibrio splendidus as a member of the planktonic luminous bacteria from the Persian Gulf/Kuwait region using luxa probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59:2684-2689. 117. Nealson, K.H. 1993. Bacterial bioluminescence: Three decades of enlightenment. Nav. Res. Rev 45:1320. 118. Bermudes, D., K. Nealson and R. Akhurst. 1993. The genus Xenorhabdus. J. Coll. Sci. Teaching Nov:105-107. 119. Saffarini, D., and K.H. Nealson. 1993. Sequence and genetic characterization of etrA, an fnr analogue that regulates anaerobic respiration in Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1 . J. Bacteriol. 175:7938-7944. 120. Aguilar, C. and K.H. Nealson. 1993. Manganese reduction in Oneida Lake, New York: estimates of spatial and temporal manganese flux. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 51:185-196. 121. Scott, J.H. and K.H. Nealson. 1994. A biochemical study of the intermediary carbon metabolism of Shewanella putrefaciens. J. Bacteriol. 176:3408-3411. 122. Saffariini, D.A., T.J. DiChristina, D. Bermudes, and K.H. Nealson. 1994. Anaerobic respiration of Shewanella putrefaciens requires both chromosomal and plasmid-borne genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 119:271-278. 123. Nealson, K.H., D.A. Saffarini and S.J. Lukiewicz. 1994. Bacterial mutant strains unable to reduce nitroxides. Curr. Topics Biophys.18:39-45. 124. Nealson, K.H., D.A. Saffarini, D. Moser and M. J. Smith. 1994. A spectrophotometric method for monitoring tactic responses of bacteria under anaerobic conditions. J. Microbiol. Meth. 20:211-218. 125. Nealson, K.H. and D.A. Saffarini. 1994. Iron and manganese in anaerobic respiration: Environmental significance, physiology, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 48:311-343. 126. Myers, C.R. and K.H. Nealson. 1994. Biological and chemical mechanisms of manganese reduction in aquatic and sediment systems. pp. 205-223. In: Transport and Transformation of Contaminants Near the Sediment-Water Interface. (eds. J. V. DePinto, W. Lick and J. Paul). Lewis Publishers, Ann Arbor. 127. Tsapin, A.I., D.S. Burbaev, K.H. Nealson, and O.I. Keppen. 1994. Studies of the Iron-sulphur centers of 15 the bacteria Shewanella putrefaciens (MR-1). Appl. Magn. Reson. 7:559-566. 128. Namsareev, B., V. Samarkin, K. Nealson, J.V. Klump, L. Buchholz, C.C. Remsen, and C. Myers. 1995. Microbial processes of carbon and sulfur in Lake Michigan sediments. Microbiologia. 63: 730-735. 129. Kostka, J.E., G. W. Luther III, and K.H. Nealson. 1995. Chemical and biological reduction of Mn(III)pyrophosphate complexes: potential importance of dissolved Mn(III) as an environmental oxidant. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 59: 885-894. 130. Nealson, K.H., D. Moser, and D.A. Saffarini. 1995. Anaerobic electron acceptor chemotaxis in Shewanella putrefaciens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61:1551-1554. 131. Kostka, J.E., and K.H. Nealson. 1995. Dissolution and reduction of magnetite by bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 29:2535-2540. 132. Tsapin, A.I., D.S. Burbaev, K.H. Nealson, and O.I. Keppen. 1995. Investigations of succinate dehydrogenase and fumarate reductase in whole cells of Shewanella putrefaciens using electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Appl. Magn. Reson. 9:509-516. 133. Hosseini, P.K., and K.H. Nealson. 1995. Symbiotic luminous soil bacteria: unusual regulation for an unusual niche. Photochem. Photobiol. 62:633-640. 134. Forst, S., and K.H. Nealson. 1996. Molecular biology of the symbiotic-pathogenic bacteria Xenorhabdus spp. and Photorhabdus spp. Microbiol. Rev. 60:21-43. 135. Morse, D.E., and K.H. Nealson. 1996. Interdisciplinary research at the nation’s coastal laboratories. Biol. Bull. 190:260-268. 136. Moser, D.P. and K.H. Nealson. 1996. Growth of the facultative anaerobe Shewanella putrefaciens by elemental sulfur reduction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62:2100-2105. 137. Krause, B., T.J. Beveridge, C.C. Remsen, and K.H. Nealson. 1996. Structure and properties of novel inclusions in Shewanella putrefaciens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 139:63-69. 138. Kostka, J.E., J.W. Stucki, K.H. Nealson, and J. Wu. 1996. Reduction of structural Fe(III) in smectite by a pure culture of Shewanella putrefaciens strain MR-1. Clays Clay Min. 44:522-529. 139. Tsapin, A.I., K.H. Nealson, T. Meyers, M.A. Cusanovich, J. VanBeeumen, L.D. Crosby, B.A Feingerg, and C. Zhang. 1996. Purification and properties of a low-redox-potential tetraheme cytochrome c3 from Shewanella putrefaciens. J. Bacteriol. 178: 178:6386-6388. 140. Moser, D.P., J.R. Brozowski, and K.H. Nealson. 1996. Elemental analysis for biomass determination in the presence of insoluble substrates. J. Microbiol. Methods 26:271-278. 141. Nealson, K.H. 1997. Sediment bacteria: who’s there, what are they doing, and what’s new? Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 25:403-434. 142. Little, B., P. Wagner, K. Hart, R. Ray, K. Nealson, and C. Aguilar. 1997. The role of biomineralization in microbiologically influenced corrosion. Corrosion 97, Paper # 215:1-11. Nat. Assoc. Corr. Eng., Houston, TX. 143. MacGregor, B.J., D.P. Moser, K.H. Nealson, and D.A. Stahl. 1997. Crenarchaeota in Lake Michigan sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63:1178-1181. 144. Szallas, E., C. Koch, A. Fodor, J. Burghardt, O. Buss, A. Szentirmai, K. H. Nealson, and E. Stackebrandt. 1997. Phylogenetic evidence for the taxonomic heterogeneity of Photorhabdus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47:402407. 16 145. Hosseini, P. and K. H. Nealson. 1997. Control of bioluminescence in phase variants of Photorhabdus luminescens Hm and in Hyp, a hyperpigmented mutant obtained from a phase II variant. Symbiosis 22:191203. 146. Krause, B., and K. H. Nealson. 1997. Physiology and enzymology involved in denitrification by Shewanella putrefaciens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63:1-11. 147. Nealson, K. H., and B. Little. 1997. Breathing manganese and iron: solid-state respiration. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 45:213-239. 148. Kostka, J. and K.H. Nealson. 1997. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of iron- and manganesereducing bacteria. In: Techniques in Microbial Ecology (ed.) R. Burlage. pp. 58-78. 149. Nealson, K.H. and D.A. Stahl. 1997. Microorganisms and biogeochemical cycles: what can we learn from layered microbial communities? Pp. 1-34. In: Geomicrobiology, Banfield, J. and Nealson, K.H. (eds). Mineral. Soc. America, Washington, D.C. 150. Ferrenkopf, A.M., M.E. Dollhopf, S.N. Chadhain, G.W. Luther III, and K.H. Nealson. 1997. Iodate reduction by bacteria in the Arabian Sea. Mar. Chem. 57:347-354. 151. Nealson, K.H. 1997. The limits of life on Earth and searching for life on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 102:23,675-23,675-23686. 152. Nealson, K.H. 1997. Nannobacteria – Size limits and evidence. Science 276:1776. 153. Venkateswaren, K., M. E. Dollhopf, R. Aller, E. Stackebrandt, and K. H. Nealson. 1998. Shewanella amazonensis sp. nov., a novel metal-reducing facultative anaerobe from Amazonian shelf muds. Int. J. Systematic Bacteriol. 48: 965-972. 154. Larsen, I., B. Little, K. H. Nealson, R. Ray, A. Stone, and J. Tian. 1998. Manganite reduction by Shewanella putrefaciens MR-4. Amer. Mineralogist 83:1564-1572. 155. Little, B., P. Wagner, K. Hart, R. Ray, D. Lavoie, K. Nealson, and C. Aguilar. 1998. The role of biomineralization in microbiologically influenced corrosion. Biodegradation 9:1-10. 156. Aguilar, C. and K. H. Nealson. 1998. Biogeochemical cycling of manganese in Oneida Lake, New York: whole lake studies of manganese. J. Great Lakes Res. 24:93-104. 157. Brown, G.E., V.E. Henrich, W.H. Casey, D.L. Clark, C. Eggleston, A. Felmy, D. W. Goodman, M. Gratzel, G. Maciel, M. I. McCarthy, K. H. Nealson, D. A. Sverjensky, M. F. Toney, J. M. Zachara. 1999. Metal Oxide Surfaces and Their Interactions with Aqueous Solutions. Chem. Rev. 99:77-174. 158. Nealson, K. H. 1999. Early observations defining quorum-dependent gene expression. Pp. 277-289. In: Cell to Cell Signalling in Bacteria (eds. G. M. Dunny and S. Winans) Amer. Soc. Microbiol., Washington, D.C. 159. Nealson, K. H. 1999. Post-Viking microbiology: new approaches, new data, new insights. Origins of Life and Evol. Biosph. 29:73-93. 160. Nealson, K.H. 1999. The search for extraterrestrial life. Engineering and Science. No. 1-2:30-39. 161. Leonardo, M.R., D. P. Moser, E. Barbieri, C. Brantner, B. Paster, E. Stackebrandt, and K. H. Nealson. 1999. Shewanella pealeana sp. Nov., a member of a microbial community associated with the accessory nidamental gland of the squid Loligo pealei. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49:1341-1351. 162. Venkateswaren, K., D. P. Moser, M. E. Dollhopf, D. Pl. Lies, D. A. Saffarini, B. J. MacGregor, D. B. 17 Ringelberg, D. C. White, M. Nishijima, H. Sano, J. Burghardt, E. Stackebrandt, and K. H. Nealson. 1999. Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus Shewanella and description of Shewanella oneidensis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49:705-724. 163. Kostka, J.E., J. Wu, K. H. Nealson, and J. W. Stucki. 1999. The impact of structural Fe(III) reduction by bacteria on the surface chemistry of smectite clay minerals. Geochim. Geochos. Acta 63:3705-3713. 164. Gaidos, E.J., K.H. Nealson, and J.L. Kirschvink. 1999. Life in ice-covered oceans. Science 284:16311633. 165. Nealson, K. H. and P. G. Conrad. 1999. Life: past, present and future. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. B 354: 1-17. 166. Beard, B.L., C.M. Johnson, L. Cox, H. Sun, K. H. Nealson and C. Aguilar. 1999. Iron isotope biosignatures. Science. 285:1889-1892. 167. Teece, M., M. Fogel, M. Dollhopf, and K. Nealson. 1999. Isotopic fractionation associated with biosynthesis of fatty acids by a marine bacterium under oxic and anoxic conditions. Org. Geochem. 30:15711579. 168. Leys, D.L., A. S. Tsapin, K. H. Nealson, T. E. Meyer, M. A. Cusanovich, and J. J. Van Beeumen. 1999. Structure and mechanism of the flavocytochrome c fumarate reductase of Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. Nature Struct. Biol. 6:1113-1117. 169. Rothe, J., E. Kneedler, K. Pecher, B. P. Tonner, K. H. Nealson, T. Grundl, W. Meyer-Ilse, and T. Warwick. 1999. Spectromicroscopy of Mn-distributions in micronodules produced by biomineralization. J. Synchrotron Rad. 6:359-361. 170. Tonner, B., T. Droubay, J. Denlinger, W. Meyer-Ilse, T. Warwick, J. To the, E. Kneedler, K. Pecher, K. Nealson, and T. Grundl. 1999. Soft X-ray spectroscopy and imaging of interfacial chemistry in environmental specimens. Surf. Interface Anal. 27:247-258. 171. Anbar, A.D., J. Roe, J. Barling, and K. H. Nealson. 2000. Nonbiological fractionation of iron isotopes. Science 288:126-128. 172. Weiss, B.P., Y. Yung, and K. H. Nealson. 2000. Atmospheric energy for subsurface life on mars? Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 97:1395-1399. 173. Grimes, D.J., A. L. Mills, and K. H. Nealson. 2000. The importance of viable but nonculturable bacteria in biogeochemistry. Pp. 209-227 In: Nonculturable Microorganisms in the Environment. (R. R. Colwell and D. J. Grimes, eds.). ASM Press, Wash. D.C. 174. Ozawa, K., A. Tsapin, K. H. Nealson, M. A. Cusanovich, and H. Akutsu. 2000. Expression of a tetraheme protein, Desulfovibrio vulgaris Miyazaki F. Cytochrome c3, in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66:4168-4171. 175. Tsapin, A.I., M. G. Goldfeld, G. D. McDonald, and K. H. Nealson. 2000. Iron(VI): hypothetical candidate for the martian oxidant. Icarus 147:68-78. 176. Kemner, K.M., B. Lai, J. Maser, M.A. Schneegurt, Z. Cai, P.P. Ilinski, C.F. Kulpa, D.G. Legnini, K. H. Nealson, S. T. Pratt, W. Rodrigues, M. L. Tischler, and W. yun. 2000. Use of the high-energy X-ray microprobe at the advanced photon source to investigate the interactions between metals and bacteria. Pp. 319-322 In: X-Ray Microscopy: Proc. 6th Int. Conf. W. Meyer-Ilse, T. Warwick, and D. Attwood (eds.) Amer. Inst. Physics. 177. Dollhopf, M.E., K.H. Nealson, D.M. Simon and G.W. Luther III. 2000. Kinetics of Fe(III) and Mn(IV) 18 reduction by the Black Sea strain of Shewanella putrefaciens using in situ solid state voltammetric Au/Hg electrodes. Mar. Chem. 70:171-180. 178. Tsapin, A.I., M. Storrie-Lombardi, G.D. McDonald, and K.H. Nealson. 2000. Application of computer tomography (CT) for search for life in extreme environments. New Era in Bioastronomy 213:387-389. 179. Conrad, P.G., and K. H. Nealson. 2001. A non-earthcentric approach to life detection. Astrobiology 1:1524. 180. Duxbury, N.S., I.A. Zotikov, K.H. Nealson, V.E. Romanovsky, and F.D. Carsey. 2001. A numerical model for an alternative origin of Lake Vostok and its exobiological implications for Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 106: 1453-1462. 181. Stein, L., M. LaDuc, T. Grundl, and K. Nealson. 2001. Bacterial and archael populations associated with freshwater ferromanganous micronodules and sediments. Environmental Microbiol. 3: 10-18. 182. Tsapin, A., I. Vandenberghe, K. Nealson, J. Scott, T. Meyer, M. Cusanovich, E. Harada, T. Kaizu, H. Akutsu, D. Leys, and J. Van Beeumen. 2001. Identification of a small tetraheme cytochrome c and a flavocytochrome c as two of the principal soluble cytochromes c in Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67:3236-3244. 183. Van Mooy, B., B. MacGregor, D. Hollander, K. Nealson, and D. Stahl. 2001. Evidence for tight coupling between active bacteria and particulate organic carbon during seasonal stratification of Lake Michigan. Limnol. Oceanogr. 46:1202-1208. 184. MacGregor, B., D. Moser, B. Baker, E. Alm, M. Maurer, K. Nealson, and D. Stahl. 2001. Seasonal and spatial variability in Lake Michigan sediment small-subunit rRNA concentrations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67:3908-3922. 185. Duxbury, N.S., K.H. Nealson, V.E. Romanovsky 2001. On the possibility of clathrate hydrates on the Moon, J. Geophys. Res. -PLANETS, No E11, 27811-27813 186. Ching, W.K., A.J. Colussi, H.J. Sun, K.H. Nealson, and M.R. Hoffman. 2001. Escherischi coli disinfection by electrolytic discharges. Env. Sci. Tech. 35:4139-4144. 187. Bergmann, U., P. Glatzel, J. Robblee, J. Messinger, C. Fernandez, R. Cinco, H. Visser, K. McFarlane, E. Bellacchio, S. Pizarro, K. Sauer, V. Yachandra, M. Klein, B. L. Cox, K. Nealson, and S. Cramer. 2001. Highresolution X-ray spectroscopy of rare events: a different look at local structure and chemistry. J. Synchrotron Rad. 8: 199-203. 188. Murray, A.E., D. Lies, G. Li, K. Nealson, J. Zhou, and J. Tiedje. 2001. DNA/DNA hybridization to microarrays reveals gene-specific differences between closely related microbial genomes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 98: 9853-9858. 189. Kemner, K., S. Kelly, K. Orlandini, A.I. Tsapin, M.G. Goldfeld, Y.D. Perfiliev, and K. H. Nealson. 2001. XAS investigations of Fe(VI). J. Synchrotron Rad. 8: 949-951. 190. Lanoil, B.D., R. Sassen, M. LaDuc, S.T. Sweet, and K.H. Nealson. 2001. Bacteria and Archaea physically associated with Gulf of Mexico gas hydrates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67:5143-5153. 191. Storrie-Lombardi, M.C., W. Hug, G. McDonald, A. Tsapin, and K. Nealson. 2001. Hollow cathode ion lasers for deep ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy and fluorescence imaging. Rev. Sci. Instruments 72:44524459. 192. De Stasio, G., B. Gilbert, B.H. Frazer, K. H. Nealson, P.G. Conrad, V. Livi, M. Labrenz, and J. F. Banfield. 2001. The multidisciplinarity of spectromicrosccopy: from geomicrobiology to archaeology. J. Elec. 19 Spectroscopy Rel. Phenom. 114-116:997-1003. 193. Nealson, K.H., and W. A. Ghiorse. 2001. Geobiology: exploring the interface between the biosphere and the geosphere. Amer. Acad. Microbiology. Wash. D.C. 194. Nealson, K.H. 2001. Searching for life in the universe: Lessons from the Earth. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 950:241-258. 195. Thompson, D.K., A.S. Beliaev, C.S. Giometti, S.L. Tollaksen, T. Khare, D.P. Lies, K.H. Nealson, H. Lim, J. Yates III, C.C. Brandt, J.M. Tiedje, and J. Zhou. 2002. Transcriptional and proteomic analysis of a ferric uptake regulator (Fur) mutant of Shewanella oneidensis: Possible involvement of Fur in energy metabolism, transcriptional regulation, and oxidative stress. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68(2):881-892. 196. Beliaev, A.S., D.K. Thompson, T. Khare, H. Lim, C.C. Brandt, G. Li, A.E. Murray, J.F. Heidelberg, C.S. Giometti, J. Yates III, K.H. Nealson, J.M. Tiedje, and J. Zhou. 2002. Gene and protein expression profiles of Shewanella oneidensis during anaerobic growth with different electron acceptors. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 6(1): 197. Sorokin, D.Y., V.M. Gorlenko, T. P. Tourova, T. V. Kalganova, A. I. Tsapin, K. H. Nealson, and G.J. Kuenen. 2002. Thioalkalimicrobium cyclicum sp.nov., and Thioalkalivibrio jannaschii sp. Nov., new species of haloalkaliphilic, obligately chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria from hypersaline alkaline Mono Lake (California). Int. J. Syst. Env. Microbiol. 52:913-920. 198. Salmassi, T.M., K. Venkateswaren, M. Satomi, K.H. Nealson, D.K. Newman, and J.G. Hering. 2002. Oxidation of arsenite by Agrobacterium albertimagni, AOL15, sp.nov., Isolated from Hot Creek, CA. Geomicrobiol. J. 19:53-66. 199. Johnson, C.M., J.L. Skulan, B.L. Beard, H. Sun, K.H. Nealson, and P.S. Braterman. 2002. Isotopic fractionation between Fe(III) and Fe(II) in aqueous solutions. Earth Plan. Sci. Let. 195:141-153. 200. Nealson, K.H. and B. Lea Cox. 2002. Microbial metal-ion reduction and Mars: extraterrestrial expectations? Curr. Opp. Microbiol. 5:296-300. 201. Beliaev, A.S., D.K. Thompson, M.W. Fields, L.Wu, D. P. Lies, K.H. Nealson, and J. Zhou. 2002. Microarray transcription profiling of a Shewanella oneidensis etrA mutant. J. Bacteriol. 184:4612-4616. 202. Cox, L., R. Popa, D.A. Bazylinski, B. Lanoil, S. Douglas, A. Belz, D. L. Engler, and K.H. Nealson. 2002. Organization and elemental analysis of P-, S-, and Fe-rich inclusions in a population of freshwater magnetococci. Geomicrobiol. J. 19:387-406. 203. Stein, L.S., G. Jones, B. Alexander, K. Edmund, C. Wright-Jones, and K.H. Nealson. 2002. Intriguing microbial diversity associated with metal-rich particles from a freshwater reservoir. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 1421:1-10. 204. Tsapin, A., M. Goldfeld, and K. Nealson. 2002. Viking’s experiments and hypothesis that Fe(VI) is a possible candidate as a Martian oxidant. Icarus 159:268. 205. Nealson, K.H., A. Belz, and B. McKee. 2002. Breathing metals as a way of life: geobiology in action. Ant. V. Leeuwenh. 81:215-222. 206. Heidelberg, J. and others. 2002. Genome sequence of the dissimilatory metal ion-reducing bacterium Shewanella oneidensis Nature Biotech. 20, 1118 – 1123 207. Nealson, K.H., A. Tsapin, and M. Storrie-Lombardi. 2002. Searching for life in the Universe: unconventional methods for an unconventional problem. Int. Microbiol. 5:223-230. 20 208. Beard, B.L., C.M. Johnson, J.L. Skulan, K.H. Nealson, L. Cox, and H. Sun. 2003. Applications of Fe isotopes to tracing the geochemical and biological cycling of Fe. Chem. Geol. 14137:1-31. 209. Takai, K., F. Inagaki, S. Nakagawa, H. Hirayama, T. Nunoura, Y. Sako, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2003. Isolation and phylogenetic diversity of members of previously uncultivated ε-proteobacteria in deep-sea hydrothermal fields. FEMS Microbio. Lett. 218:167-174. 210. Nealson, K.H. 2003. Harnessing microbial appetites for remediation. Nature Biotech. 21:5-6. 211. Bakermans, C., A.I. Tsapin, V. Souza-Egipsy, D.A. Gilichinsky, and K.H. Nealson. 2003. Reproduction and metabolism at -10oC of bacteria isolated from Siberian permafrost. Environ. Microbiol. 5: 321-326 212. Pecher, K., D. McCubbery, E. Kneidler, J. Rothe, J. Bargar, G. Meigs, L. Cox, K. Nealson and B. Tonner. 2003. Quantitative charge state analysis of manganese biominerals in aqueous suspension using Scanning Transmission X-ray Microscopy (STXM). Geochim Cosmochim. Acta 67:1089-1098 213. Giometti, C.S., T. Khare, S.L. Tollaksen, A. Tsapin, W. Zhu, J.R. Yates III, and K.H. Nealson. 2003. Analysis of the Shewanella oneidensis proteome by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis under nondenaturing conditions. Proteomics 3: 1-15. 214. Christensen, P.R., J.L. Bandfield, J.F. Bell, III, N. Gorelick, V. E. Hamilton, A. Ivanov, B. M. Jakosky, H.H. Kieffer, M.D. Lane, M.C. Malin, T. McConnochie, A.S. McEwen, H.Y. McSween, Jr., G.L. Mehall, J.E. Moesch, K.H. Nealson, J.W. Rice, Jr., M.I Richardson, S.W. Ruff, M.D. Smith, T.N. Titus, and M.B. Wyatt. 2003. Morphology and composition of the surface of Mars: Mars Odyssey THEMIS results. Science 300:2056-20. 215. Kloepfer, J.A., R.E. Mielke, M.S. Wong, K.H. Nealson, G. Stucky, and J.L. Nadeau. 2003. Quantum dots as strain- and metabolism-specific microbiological labels. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69:4205-4213. 216. Inagaki, F., K. Takai, H. Hirayama, Y. Yamato, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2003. Distribution and phylogenetic diversity of the subsurface microbial community in a Japanese epithermal gold mine. Extremophiles. 7:307-317. 217. Nealson, K.H. and W. Berelson. 2003. Layered microbial communities and the search for life in the universe. Geomicrobiol. J. 20:451-462. 218. Dorn ED, G.D.McDonald GD, M.C. Storrie-Lombardi, and K.H. Nealson KH. 2003 Principal component analysis and neural networks for detection of amino acid biosignatures. Icarus 166:403-409. 219. Nealson, K.H., and J. Scott. 2003. Ecophysiology of the Genus Shewanella. In: Dworkin et al. eds. The Prokaryotes: An evolving electronic resource for the microbiological community. 3rd Ed. Release 3.7., Nov. 2003. Springer-Verlag, N.Y. http://link.springer-ny.com/link/service/books/10125/. 220. Jakosky, B.M., K.H. Nealson,l C. Bakermans, R.E. Ley, and M.T. Mellon. 2003. Sub-freezing activity of microorganisms and the potential habitability of Mars’ polar regions. Astrobiol. J. 3: 343-350. 221. DesMarais, D.J. and others. 2003. The NASA Astrobiology Roadmap. Astrobiol. J. 3:219-235. 222. Inagaki, F., K. Takai, H. Kobayashi, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2003. Sulfurimonas autotrophica gen. nov., sp. Nov., a novel sulfur-oxidizing ε-proteobacterium isolated from hydrothermal sediments in the mid-Okinawa trough. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53:1801-1805. 223. Takai, K., H. Kobayashi, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2003. Deferribacter desulfuricans sp. Nov., a novel sulfur-, nitrate- and arsenate-reducing thermophile isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53: 839-846. 21 224. Nealson, K.H. and R. Rye. 2003. Evolution of Metabolism. Pp.41-61 in: Treatise on Geochemistry, Volume 8. Ed. W.H. Schlesinger, H.D. Holland, and K.K. Turekian. Elsevier Pergammon, Amsterdam. 225. Gilbert, B., B.H. Frazer, A. Belz, P. Conrad, K. Nealson, D. Haskel, J.C. Lang, G.Srajer, and G. DeStasio. 2003. Multiple scattering calculations of bonding and X-ray absorption spectroscopy of manganese oxides. J. Phys. Chem. A 107:2839-2847 226. Takai, K., K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2004. Hydrogenomonas thermophila gen. nov., sp. Nov., a novel thermophilic, hydrogen-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph within the ε-Proteobacteria, isolated from a black smoker in a Central Indian Ridge hydrothermal field. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54: 25-32. 227. Bakermans, C. and K.H. Nealson. 2004. Relationship of Critical Temperature to Macromolecular Synthesis and Growth Yield in Psychrobacter cryopegella. J. Bact. 186:2340-2345. 228. Venter, J.C., K. Remington, J. Heidelberg, A. Halpern, D. Rusch, J. Eisen, D. Wu, I. Paulsen, K. Nealson, W. Nelson, D. Fouts, S. Levy, A. Knap, M. Lomas, K. Nealson, et al. 2004. Environmental genomic shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 304:66-74. 229. Takai, K., H. Oida, Y. Suzuki, H. Kirayama, S. Nakagawa, T. Nunora, F. Inagaki, K. H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2004. Spatial distribution of marine Chrenarchaeota Group I in the vicinity of deep-sea hydrothermal systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70:2403-2413. 230. Suzuki, Y., F. Inagaki, K. Takai, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2004. Microbial diversity in inactive chimney structures from deep-sea hydrothermal systems. Microbio. Ecol. 47: 186-196. 231. Kemner, K.M., S.D. Kelly, B. Lal, J. Maser, E. J. O’Loughlin, D. Sholto-Douglas, Z. Cai, M. Schneegurt, C.F. Kulpa Jr., K.H. Nealson. 2004. Elemental and redox analysis of single bacterial cells by X-ray microbeam analysis. Science 306:686-687. 232. Johnson, C.M., B.L. Beard, E.E. Roden, D.K. Newman, and K.H. Nealson. 2004. Isotopic constraints on Biogeochemical cycling of Fe. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 55:359-408. 233. Inagaki, F., U. Tsunogai, M. Suzuki, A. Kosaka, H. Machiyama, K. Takai, T. Nunoura, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2004. Characterization of C1-metabolizing prokaryotic communities in methane seep habitats at the Kuroshima Knoll, southern Ryukyu Arc, by analyzing pmoA, mmoX, mxaF, mcrA, and 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70:7445-7455. 234. Meyer, T.E., A.I Tsapin, I. Vandenberghe, L. DeSmet, D. Frishman, K.H. Nealson, M.A. Cusanovich, and J.J. VanBeeumen. 2004. Identification of 42 possible cytochrome C genes in the Shewanella oneidensis genome and characterization of six soluble cytochromes. OMICS: J. Integr. Biol. 8:57-77 235. Abboud, R., R. Popa, V. Souza-Egipsy, C.S. Giometti, S. Tollaksen, J.J. Mosher, R.H. Findlay, and K.H. Nealson. 2005. Low-temperature growth of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71:811816. 236. Kolker, E., A.F. Picone, M.Y. Galperin, M.F. Romine, R. Higdon, K.S. Makarova, N. Kolker, G.A. Anderson, X. Qiu, K.J. Auberry, G. Babnigg, A.S. Beliaev, P. Edlefsen, D.A. Elias, Y. Gorby, T. Holzman, J. Klappenback, K. T. Konstantinidis, M.L. Land, M.S. Lipton, L. McCue, M. Monroe, L. Pasa-Tolic, G. Pinchuk, S. Purvine, M. Serres, S. Tsapin, B.A. Zakrajsek, W. Zhu, J. Zhou, F.W. Larimer, C. Lawrence, M. Riley, F.R. Collart, J.R. Yates, III, R.D. Smith, C. Giometti, K. Nealson, J.K. Fredrickson, and J.M. Tiedje. 2005. Global profiling of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1: Expression of hypothetical genes and improved functional annotations. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 102:2099-2014. 237. Nealson, K.H. 2005. Hydrogen and energy flow as “sensed” by molecular genetics. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 102: 3889-3890. 22 238. Takai, K., C.L. Moyer, M. Miyazaki, Y. Nogi, H. Hirayama, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2005. Marinobacter alkaliphilus sp. nov., a novel alkaliphilic bacterium isolated from subseafloor alkaline serpentine mud from Ocean Drilling Program Site 1200 at South Chamorro Seamount, Mariana Forearc. Extremophiles 9:17-27. 239. Inagaki, F., H. Okada, A.I. Tsapin, and K.H. Nealson. 2005. The Paleome: A sedimentary genetic record of past microbial communities. Astrobiology. 5: 141-153. 240. Hirayama, H., K. Takai, F. Inagaki, Y. Yamato, M. Suzuki, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2005. Bacterial community shift along a subsurface geothermal water stream in a Japanese gold mine. Extremophiles 9:169184. 241. Kus, E., R. Abboud, R. Popa, K.H. Nealson, and F. Mansfeld. 2005. The concept of the bacterial battery. Corrosion Sci. 47:1063-1069. 242. Hirayama, H., K. Takai, F. Inagaki, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2005. Thiobacter subterraneus gen. nov., sp. nov., an obligately chemolithoautotrophic, thermophilic, sulfur-oxidizing bacterium from a subsurface hot aquifer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55:467-472. 243. Lanoil, B., M.T. LaDuc, M. Wright, M. Kastner, K.H. Nealson, and D. Bartlett. 2005. Archael diversity in ODP legacy borehole 892b and associated seawater and sediments of the Cascadia Margin. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 54: 167-177. 244. Schelble, R.T., G.D. McDonald, J.A. Hall, and K.H. Nealson. 2005. Community structure comparison using FAME analysis of desert varnish and soil, Mojave Desert, California. Geomicrobiol. J. 22:353-360. 245. Nealson, K.H. and R. Popa. 2005. Metabolic diversity in the microbial world: relevance to exobiology. In: SGM symposium. Vol. 65. pp. 1151-171. Micro-organisms and Earth systems – advances in geomicrobiology. Ed. G.M. Gadd, K.T. Semple, and H.M. Lappin-Scott. Cambridge Univ. Press., Oxford, UK. 246. Nealson, K.H., F. Inagaki, and K. Takai. 2005. Hydrogen-driven subsurface lithoautotrophic microbial ecosystems (SLiMEs): do they exist and why should we care? Trends in Microbiol. 13:405-410. 247. Beliaev, A.S., D.M.Stanek, J.A. Klappenbach, L. Wu, M.F. Romine, J.M. Tiedje, K.H. Nealson, J.K. Fredrickson, and J. Zhou. 2005. Global transcriptome analysis of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 exposed to different terminal electron acceptors. J. Bacteriol. 187:7138-7145. 248. Nunoura, T., H. Hirayama, H. Takami, H. Oida, S. Nishi, S. Shimamura, Y. Suzuki, F. Inagaki, K. Takai, K. H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshil 2005. Genetic and functional properties of uncultivated thermophilic crenarchaeotes from a subsurface gold mine as revealed by analysis of genome fragments. Environ. Microbiol. 7:1967-1984 249. Nealson, K.H. and R. Popa. 2005. Introduction and overview: what do we know for sure? Amer. J. Sci. 305:449-466. 250. Lüttge, A., L. Zhang, and K.H. Nealson. 2005. Mineral surfaces and their implications for microbial attachment: results from Monte Carlo Simulations and direct surface observations. Amer. J. Sci. 305:766790. 2006: 251. Inagaki, F. and K.H. Nealson. 2006. The Paleome: Letters from ancient Earth. pp. 21-39. In: Past and Present Water Column Anoxia. Ed: L.N. Neretin. Springer. Amsterdam. 252. Inagaki, F., T. Nunoura, S. Nakagawa, A. Teske, M. Lever, A. Lauer, M. Suzuki, K. Takai, M. delwiche, F.S. Colwell, K.H. Nealson, K. Horikoshi, S. D’Hondt, and B.B. Jorgensen. 2006. Biogeographical distribution 23 and diversity of microbes in methane hydrate-bearing deep marine sediments on the Pacific Ocean margin. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 103:2815-2820. 253. Chang, I.S., H. Moon, O. Bretschger, J.K. Jang, H.I. Park, K.H. Nealson, and B.H. Kim. 2006. Electrochemically active bacteria (EAB) and mediator-less microbial fuel cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 16:163-177. 254. Inagaki, F., and K.H. Nealson. 2006. Molecular signals from ancient materials: challenges to deepbiosphere and paleoenvironmental research – a response to the comments of Sinninghe Damste’ and Coolen. Astrobiology 6:303-307. 255. Suzuki, Y., S. Kojima, T. Sasaki, M. Suzuki, T. Utsumi, H. Watanabe, H. Urakawa, S. Tsuchida, T. Nunoura, H. Hirayama, K. Takai, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2006. Host-symbiont relationships in hydrothermal vent gastropods of the genus Alviniconcha from the southwest Pacific. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72:1388-1393. 256. Nealson, K.H. and J.W. Hastings. 2006. Quorum sensing on a global scale: massive numbers of bioluminescent bacteria make milky seas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72: 2295-2297 257. Capone, D.B., R. Popa, B. Flood, and K.H. Nealson. 2006. Follow the nitrogen. Science 312:708-709. 258. Gorby, Y., S. Yanina, J.S. McLean, K.M. Rosso, D. Moyles, A. Dohnalkova, T.J. Beveridge, I-S. Chang, B-H. Kim, K-S. Kim, D.E. Culley, S.B. Reed, M.F. Romine, D.A. Saffarini, E.A. Hill, L. Shi, D.A. Elias, D.W. Kennedy, G. Pinchuk, D. Watanabe, S. Ishii, B. Logan, K.H. Nealson, and J.K. Fredrickson. 2006. Electrically conductive bacterial nanowires produced by Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1 and other microorganisms. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103:11358-11363. 259. Nealson, K.H. 2006. Lakes of liquid CO2 in the deep sea. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 103:13903-13904. 260. Gao, H., A. Obraztsova, N. Stewart, R. Popa, J.K. Fredrickson, J.M. Tiedje, K.H. Nealson, and J. Zhou. 2006. Shewanella loihica sp. Nov., isolated from iron-rich microbial mats in the Pacific Ocean. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56: 1911-1916. 261. Hagadorn, J.W., X. Xiaqo, P.C.J. Donoghue, S. Bengtson, N.J. Gostling, M. Pawlowskaq, E.C. Raff, R.A. Raff, R. Turner, Y. Chongyu, C. Zhou, X. Yuan, M.B. McFeely, M. Stampanoni, and K. H. Nealson. 2006. Cellular and Subcellular Structure of Neoproterozoic Animal Embryos. Science 314: 291-294. 262. Nonura, T., H. Oida, N. Masui, F. Inagaki, K. Takai, S. Hirano, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2006. Culture-dependent and –independent analyses of subsurface microbial communities in oil-bearing strata of the Sagara oil reservoir. Island Arc. 15: 328-337. 263. Yang, X., Rodionov, D., C. Li, O.N. Laikova, M.S. Gelfand, O.P. Zagnitko, M.F. Romine, A.Y. Obraztsova, K.H. Nealson, and A.L. Osterman. 2006. Comparative genomics and experimental characterization of Nacetylglucosamine utilization pathway of Shewanella oneidensis. J. Biol. Chem. 281(40):29872-29875. 2007: 264. Rusch, D.B., Halpern, A.L., Heidelberg, K.B., Sutton, G., Williamson, S., Yooseph, S., Wu, D., Eisen, J.A., Hoffman, J.M., Howard, C.H., Foote, C., Dill, B.A., Remington, K., Beeson, K. Tran, B., Smith, H., BadenTillson, H., Stewart, C., Thorpe, J., Freemen, J., Andrews-Pfannkoch, C., SVenter, J.E., Li, K. Kravitz, S., Heidelberg, J.F., Utterback, T. Rogers, Y-H. Falcon, L.I., Souza, V., Bonilla-Rosso, G. Eguiarte, L.E., Karl, D.M., Sathyendranath, S., Platt, T., Bermingham, E., Gallardo, V., Tamayo-Castillo, G., Ferrari, M.R., Strausberg, R.L., Nealson, K., Friedman, R., Frazier, M., and Venter, J.C. The Sorcerer II Global Ocean 24 Samplig Expedition: Northwest Atlantic through Eastern Tropical Pacific. PLoS Biology5(3):e77.doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050077. 265. Boldareva, E.N., I.A. Bryantseva, A. Tsapin, K. Nealson, D.Yu. Sorokin, T.P. Tourova, V.A. Boichenko, I.N. Stadnichuk, and V.M. Gorlenko. 2007. The new alkaliphilic Bacteriochlorophyll a-containing bacterium Roseinanatronobacter monicus sp. No. from the hypersaline soda Mono Lake (California, U.S.). Microbiology. 76:82-92. 266. Davis K.J., A. Lüttge, and K. H. Nealson. 2007. Calcite and dolomite dissolution rates in the context of microbe-mineral surface interactions. Geobiology 5:191-205 267. Rabaey, K., J. Rodriquez, L. Blackall, J. Keller, P. Gross, D. Batstone, W. Verstraete, and K. H. Nealson. 2007. Microbial eology meets electrochemistry: electricity-driven and driving communities. The ISME Journal 1:9-18. 268. Nealson, K.H. and J.C. Venter. 2007. Metagenomics and the global ocean survey: what’s in it for us, and why should we care. The ISME Journal 1:185-187. 269. Popa, R., P.K. Weber, J. Pett-Ridge, J.A. Finzi, S.J. Fallon, I. D. Hutcheon, K.H. Nealson, and D.G. Capone. 2007. Carbon and nitrogen fixation and metabolite exchange in and between individual cells of Anabaena oscillarioides. The ISME Journal 1:354-360 270. Bretschger, O., A. Obraztsova, C.A. Sturm, I.S. Chang, Y.A. Gorby, S.B. Reed, B.E. Culley, C.L. Reardon, S. Barua, M.f. Romine, J. Zhou, A. A. Beliaev, R. Bouhenni, D. Saffarini, F. Mansfeld, B-H. Kim, J.K. Fredrickson, and K.H. Nealson. 2007. Current production and metal oxide reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 wild type and mutants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73:7003-7012. 2008: 271. Pinchuk, G.E., C. Ammons, D.E. Culley, S-M. W. Li, J.S. McLean, M.F. Romine, K.H. Nealson, J.K. Fredrickson, and A. Beliaev. 2008. Utilization of DNA as a sole source of phosphorus, carbon, and energy by Shewanella spp.: ecological and physiological implications for dissimilatory metal reduction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74:1198-1208. 272. Manohar, A.K., O. Bretschger, K.H. Nealson, and F. Mansfeld. 2008. The polarization behavior of the anode in a microbial fuel cell. Electrochem. Acta. 3508-3513. 273. Nealson, K.H. 2008. A Korarchaeote yields to genome sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105: 8805-8806. 274. Manohar, A.K., O. Bretschger, K.H. Nealson, and F. Mansfeld. 2008. The Use of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) in the Evaluation of the Electrochemical Properties of a Microbial Fuel Cell. Bioelectrochemistry 72:149 - 159. 275. Kus, E., K. Nealson, and F. Mansfield. 2008. The effect of different exposure conditions on biofilm/copper properties. Corrosion Science 49: 3421-3427 276. Kus, E., K. Nealson, and F. Mansfeld. 2008. The bacterial battery and the effect of different exposure conditions on biofilm properties. Electrochem. Acta. 54:47-52. 277. Waters, M.S., C.A. Sturm, M.Y. El-Naggar, A. Luttge, F.E. Udwadia, D.G. Cvitkovitch, S.D. Goodman, and K.H. Nealson. 2008. In search of the microbe/mineral interface: quantitative analysis of bacteria on metal surface using vertical scanning Interferometry. Geobiology 6:254-262. 278. Fredrickson, J.K., M.F. Romine, A.S. Beliaev, J.M. Auchtung, M.E. Driscoll, T.s. Gardner, K.H. Nealson, A.L. Osterman, G. Pinchuk, J.L. Reed, D.A. Rodionov, J.L.M. Rodrigues, D.A. Saffarini, M. H. Serres, A.M. 25 Spormann, I.G. Zhulin, and J. M. Tiedje. 2008. Towards Environmental Systems Biology of Shewanella. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 6:592-603 279. El-Naggar, M., Y. A. Gorby, W. Xia, and K.H. Nealson. 2008. The Molecular Density of States in Bacterial Nanowires., Biophys. J. 95:10-12. 280. Borg, L.E., DesMarais, D.J., Beaty, D.W., Aharonson, O., Benner, S.A., Bogard, D.D., Bridges, J.C., Rudney, C.J., Calvin, W.M., Clark, B.C., Eigenbrode, J.L., Grady, M.M., Head, J.W., Hemming, S.R., Hinners, N.W., Hipkin, V., MacPherson, G.J., Marinangeli, L., McLennan, S.M., McSween, H.Y., Moersch, J.E., Nealson, K.H., Pratt, L.M., Righter, K., Ruff, S.W., Shearer, C.K., Steele, A., Sumner, D.Y., Symes, S.J., Vago, J.L., and Westall, F. 2008. Science priorities for Mars sample return. Astrobiology 8:489-536. 281. Bhartia, R., W.F. Hug, E.C. Salas, R.D. Reid, K. K. Sijapati, A. Tsapin, W. Abbey, P.G. Conrad, K.H. Nealson, and A.L. Lane. 2008. Classification of Organic and Biological Materials with Deep UV Excitation. Appl. Spectroscopy 62:1070-1077. 282. Schelble, R.T., J.A. Hall, K.H. Nealson, and A. Steele. 2008. DNA perseverance of microorganisms exposed to silica: an experimental study. Geobiology. 6:503-511. 283. Biffinger, J.C., J. Pietron, O. Bretschger, L. J. Nadeau, G.R. Johnson, C.C. Williams, K.H. Nealson, and B.R. Ringeisen. 2008. The influence of acidity on microbial fuel cells containing Shewanella oneidensis. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 24:906-911. 2009: 284. Waters, M.S., M.Y. El-Naggar, L. Hsu, C.A. Sturm, A. Luttge, F.E. Udwadia, D.G. Cvitkovitch, S.D. Goodman, and K.H. Nealson. 2009. Simultaneous interferometric measurement of corrosive or demineralizing bacteria and their mineral interfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75:1445-1449. 285. Nealson, K.H. and W. Berelson. 2009. Sediment habitats, including watery. Encyclopedia of Microbiology. Pp 350-360. Oxford:Elsevier 286. Finzi-Hart, J.A., J. Pett-Ridge, P.Weber, R. Popa, S.J. Fallon, T. Gunderson, I. Hutcheon, K. Nealson, and D.G. Capone 2009. Fixation and fate of C and N in the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium using nanometer Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106:6345-6350 287. Gao, H., Z.K. Yang, S. Barua, S. B. Reed, M.F. Romine, K.H. Nealson, J.K. Fredrickson, J.M. Tiedje, and J. Zhou. 2009. Reduction of nitrate in Shewanella oneidensis depends on atypical NAP and NRF systems with NapB as a preferred electron transport protein from CymA to NapA. The ISME J. 3:966-976. 288. He, Z., J. Kan, Y. Wang, Y. Huang, F. Mansfeld, and K.H. Nealson. 2009. Electricity production coupled to ammonium in a microbial fuel cell. Env. Sci. Technol. 43: 3391-3397. 289. He, J., J. Kan, F. Mansfeld, L. Angenent, and K. Nealson. 2009. Self-sustained phototrophic microbial fuel cells based on the synergistic cooperation between photosynthetic microorganisms and heterotrophic bacteria. Envir. Sci. Technol. 43: 1648-1654. 290. Biffinger, J.C, B. R. Ringeisen; M. Ribbens; S, Finkel; K. Nealson, and J. J. Pietron. 2009. Characterization of electrochemically active bacteria (EAB) utilizing a high-throughput voltage-based screening assay Biotechnology and Bioengineering 102: 436-444. 291. Nealson, K.H. 2009. Taking the concept to the limit: uncultivable bacteria and astrobiology. Microbiol. Monographs 10: 195-204. 26 292. Popa, R., W. Fang, K.H. Nealson, V. S-Egipsy, T.S. Berquo, S.K. Banerjee, L.R. Penn. 2009. Effect of oxidative stress on the growth of magnetic particles in Magnetospirillum magneticum. Internat. Microbiol. 12: 49-57. 293. Namsaraev, Z., V. Akimov, E. Barinova, A. Tasapin, K. Nealson, and V. Gorlenko. 2009. Marinospirillum celere sp. Nov., a novel alkaliphilic helical bacterium isolated from Mono Lake. Int. J. Syst. Environ. Microbiol. 59:2329 – 2332 (on line publication: doi: ijs.0.006825-0[pii]) 294. Prakash, G., F. Viva, O. Bretschger, B. Yang, M. Ell-Naggar, and K. Nealson. 2009. Inoculation procedures and characterizationof membrane electrode assemblies for microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources (in press published on line: doi:10.1016/j.powsour.2009.06.081). 295. Waters, M.S., E.C. Salas, S.d. Goodman, F.E. Udwadia, and K.H. Nealson. 2009. Early detection of oxidized surfaces using Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 as a tool. Biofouling. 25:163-172. 296. Schubbe, S., T. J. Williams, G. Xie, H. E. Kiss, T.S. Brettin, D. Martinez, C.A. Ross, D. Schuler, B. L. Cox, K.H. Nealson, and D.A. Bazylinski. 2009. Complete genome sequence of the chemolithoautotrophic marine magnetotactic coccus strain MC-1. Appl. Envion. Microbiol. 75: 4835-4852. 297. Konstantinidis, K., et al. 2009. Comparative systems biology across an evolutionary gradient within the Shewanella genus. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 106: 15909-15914. 298. Jang, J.K., I.S. Chang, H.Y. Hwang, Y.F. Choo, J. Lee, K.S. Cho, B.H. Kim, and K.H. Nealson. 2009. Electricity generation coupled to oxidation of propionate in a microbial fuel cell. Biotechnol. Lett. (in press) 299. Harris, H.W., M.Y. El-Naggar, O. Bretschger, M.J. Ward, D.A. Saffarini, M. F. Romine, A.Y. Obraztsova, and K.H. Nealson. 2008. Electrokinesis is a microbiall behavior that requires extracellular electron transport. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (in press) 300. Karpinets, T.V. et al. 2009. Conserved synteny at the protein family level reveals genes underlying Shewanella species’ cold tolerance and predicts their novel phenotypes. Funct. Integr. Genomics (in press) 27