Option 8 Software development and programming
advertisement
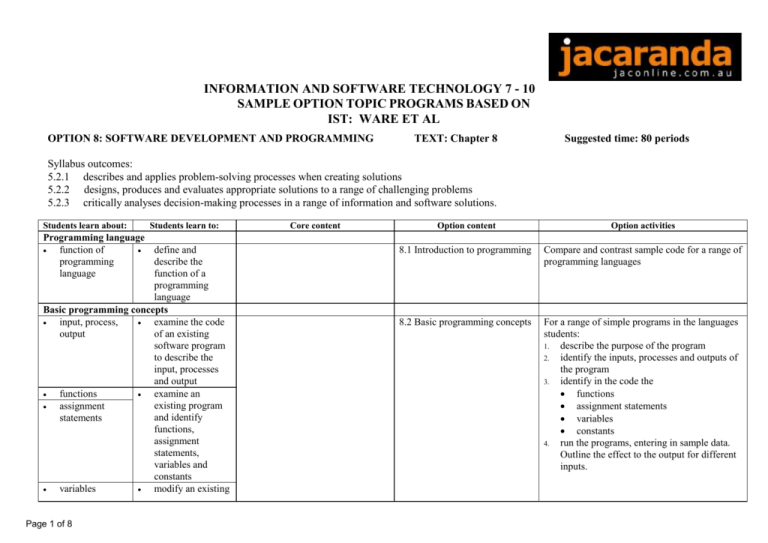
INFORMATION AND SOFTWARE TECHNOLOGY 7 - 10 SAMPLE OPTION TOPIC PROGRAMS BASED ON IST: WARE ET AL OPTION 8: SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT AND PROGRAMMING TEXT: Chapter 8 Suggested time: 80 periods Syllabus outcomes: 5.2.1 describes and applies problem-solving processes when creating solutions 5.2.2 designs, produces and evaluates appropriate solutions to a range of challenging problems 5.2.3 critically analyses decision-making processes in a range of information and software solutions. Students learn about: Students learn to: Programming language function of define and programming describe the language function of a programming language Basic programming concepts input, process, examine the code output of an existing software program to describe the input, processes and output functions examine an existing program assignment and identify statements functions, assignment statements, variables and constants variables modify an existing Page 1 of 8 Core content Option content Option activities Syllabus Outcomes 8.1 Introduction to programming Compare and contrast sample code for a range of programming languages 8.2 Basic programming concepts For a range of simple programs in the languages students: 1. describe the purpose of the program 2. identify the inputs, processes and outputs of the program 3. identify in the code the functions assignment statements variables constants 4. run the programs, entering in sample data. Outline the effect to the output for different inputs. constants Page 2 of 8 program to assess the effects of changing variables on the output of the program Students learn about: Data types such as character, integer, string, real, Boolean Students learn to: Data operators relational logical arithmetic operators GUI layout including graphics tools objects such as textboxes, list boxes and command buttons identify data types in existing code and explain their purpose compare the use of data types distinguish between various operators within existing code experiment with an existing GUI layout in a selected software program design a simple GUI layout for a specific problem and apply simple programming code conduct a peer evaluation on the designed GUI Core content 13.4 Interface design 13.5 Graphical user interface Option content Option activities 8.3 Data types and data operators For a range of simple programs in the languages students: 1. produce a data dictionary of the variables used in the code 2. identify the data operators used relational logical arithmetic operators 8.4 Graphical user interface layout Page 3 of 8 Syllabus Outcomes Evaluate the GUI of commercial software using the checklist on the CD-ROM On paper design an interface for a given scenario For a range of simple programs with GUI interfaces: Use the interface Evaluate the interface and suggest changes Have activities where students: modify the objects, such as move objects, rename buttons etc add objects to the interface Build an interface (don’t need to do coding) Students learn about: Algorithms definitions and descriptions representing algorithms examples such as recipes, directions, appliance instructions Algorithms Students learn to: repetition and/or iteration such as pre and post test Programming language Page 4 of 8 Option content 8.5 Algorithms represent algorithms by using either flowchart or pseudocode devise algorithms to solve everyday problems incorporating the use of control structures examine and analyse the existing code of a selected example and identify control structures develop prototypes using basic control structures Option activities 8.6 Control Structures Control structures sequencing selection such as binary and case define algorithms and describe examples in daily life explain the purpose of an algorithm when solving problems Core content Syllabus Outcomes Write instructions to go to another location in the school Swap with another student and follow the instructions. Do they end up where intended? Why? Why not? Convert the examples 8.6.1 to 8.6.7 in the language code they are using in class Rock paper scissors revision sheet on CDROM examples of a programming language Students learn about: Sub-programs purpose Students learn to: examples Data structures record file array Page 5 of 8 convert algorithms into basic code using a given language syntax examine existing code and algorithms to identify the purpose of subprograms for a range of examples incorporate subprograms into algorithms and working code examine data structures in existing code demonstrate the use of an array modify existing code to allow for changes to the array Core content Option content 8.7 Sub-programs and data structures Option activities Syllabus Outcomes Convert the examples 8.7.1 to 8.7.5 in the language code they are using in class Modify existing programs/algorithms to contain sub-programs Students learn about: Testing test data Students learn to: test programming code using test data to check for the desired outcome conduct a desk check on a selected algorithm modify an algorithm to produce the required output boundaries Desk checking Error detection including syntax identify and describe errors in logical a sample of given code run-time eliminate sources of error to create working code Error correction software tools debug all errors in code using peer checking, desk checking or software debugging tools Page 6 of 8 Core content Option content 8.8 Testing, error detection and correction Option activities Syllabus Outcomes Provide students with a range of algorithms, programs, get students to: Generate test data Desk check the algorithms Test the code/programs to Identify errors Fix/debug errors Students learn about: Documentation of programming code Students learn about: ` Students learn to: create appropriate user support documentation for code apply meaningful variable names and comments to code Students learn to: Project development processes and design, produce techniques and evaluate a simple project for a real-world application either separately for this option, or integrated with other options modifying an write code to solve existing program a real-world problem creating a new software solution Page 7 of 8 Core content 12.6 Social issues – equity, access and control Option content 8.9 Documentation of programming code Option activities Core content Chapter 9: Design, produce, evaluate Option content 8.10 Project – Developing a software solution Review and evaluate samples of user documentation for commercial software Create a user document for a commercial software package Add appropriate internal documentation to sample code programs Option activities Syllabus Outcomes Syllabus Outcomes Give students a working program with outline of changes to the original program problem. Get students to modify the existing program to meet the new needs. Design, produce and evaluate software solutions for: A range of simple tasks Real life problems Additional content Random and sequential files Object-oriented software development Page 8 of 8 compare and contrast existing code for processing random access and sequential files investigate developments of object-oriented software development 8.11 Random and sequential files [CD ROM] 8.12 Object-orientated software development [CD ROM]